Have you ever wondered how to choose the right aluminum alloy for your project? With a vast array of options, each with unique properties, it can be a daunting task. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of aluminum alloys, focusing on their hardness. We’ll explore how hardness is measured, the factors that influence it, and provide a comprehensive hardness chart to guide your decision-making process. Get ready to gain valuable insights that will help you select the perfect aluminum alloy for your needs.

Hardness in aluminium refers to the material’s ability to resist localized plastic deformation, which can occur due to indentation, abrasion, or penetration. This property is crucial for understanding how aluminium alloys will perform under various mechanical stresses and conditions. Hardness is a significant parameter that influences the durability, wear resistance, and overall mechanical performance of aluminium alloys.
The hardness of aluminium alloys is a key factor in determining their suitability for different applications. It directly affects the material’s resistance to wear and tear, its ability to hold shape under mechanical stress, and its overall longevity in service. For instance, higher hardness values in aluminium alloys are desirable in applications where abrasion resistance and structural integrity are critical, such as in aerospace and automotive components.
Hardness also correlates with other mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and yield strength, making it a vital consideration in the material selection process. Understanding the hardness of aluminium alloys helps engineers and manufacturers ensure that the chosen material will meet the performance requirements of specific applications, enhancing safety, reliability, and efficiency.
Hardness in aluminium alloys can be measured using several different methods, each with its own relevance and application. The most common methods include Brinell, Rockwell, and Vickers hardness tests.
For example, the 6061 aluminium alloy typically has a Brinell hardness of around 95 BHN, while the 7075 aluminium alloy, known for its high strength, has a Brinell hardness of approximately 150 BHN. These values illustrate how different aluminium alloys can vary significantly in hardness, influencing their application.
Several factors influence the hardness of aluminium alloys, including alloying elements, heat treatment, and work hardening.
Work Hardening: The process of deforming the aluminium alloy at room temperature can increase its hardness. Cold working, such as rolling or hammering, introduces dislocations in the material’s crystal structure, making it harder and stronger.
Alloying Elements: Elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, and zinc are added to aluminium to enhance its mechanical properties, including hardness. For instance, the addition of zinc in the 7075 aluminium alloy significantly increases its hardness and strength.
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes, such as solution heat treatment and aging, can alter the microstructure of aluminium alloys, thereby affecting their hardness. For example, the T6 tempering process for 6061 aluminium involves solution heat treatment followed by artificial aging, resulting in improved hardness and mechanical properties.
The table below provides typical Vickers hardness values measured with a Tianxing W-20 Vickers hardness tester for nearly 400 different grades of aluminum alloy materials with different heat treatment processes.
The Vickers hardness values in the table are actual measured typical hardness values of various aluminum alloy materials and are not used as the basis for whether the material is qualified. The hardness qualification values for various materials should refer to the corresponding product technical specifications. For example, it is stipulated in the national standard GB 5237.1 “Aluminum Alloy Building Profiles Part 1: Base Material” that the Vickers hardness value of 6063-T5 should not be less than 8HW, and the Vickers hardness value of 6063A-T5 should not be less than 10HW.
The Brinell hardness, Vickers hardness, Rockwell hardness, and Barcol hardness are for reference only and cannot be used for conversion. If conversion is required, it is recommended to use the hardness conversion table of the American standard ASTM E140.
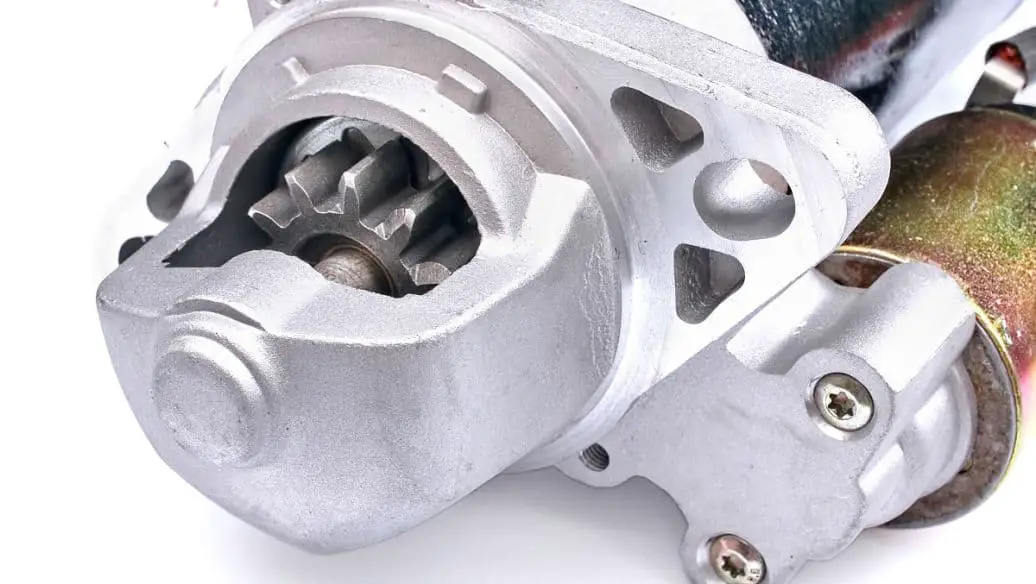

| No | Aluminum Alloy Grade | HW | HB | HV | HRB | HBA |
| 1 | Alpase K100-S™ Plate | 11.4 | 62 | 69 | ||
| 2 | Alpase K100™ Plate | 11 | 60 | 68 | ||
| 3 | Alpase M-1™ Plate | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 4 | Weldural alloy, 100 mm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 79 | 88 |
| 5 | Weldural alloy, 200 mm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 79 | 88 |
| 6 | Weldural alloy, 300 mm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 79 | 88 |
| 7 | Weldalite 049-T81 | 17.2 | 123 | 140 | 76 | 87 |
| 8 | Weldalite 049-Solution treatment | 17.4 | 129 | 147 | 78 | 88 |
| 9 | Weldalite 049-T3 | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 10 | 1050-H14 | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 11 | 1050-H16 | 2.5 | 35 | 51 | ||
| 12 | 1050-H18 | 6.3 | 43 | 58 | ||
| 13 | 1060-H12 | 0 | 23 | 35 | ||
| 14 | 1060-H14 | 0 | 26 | 40 | ||
| 15 | 1060-H16 | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 16 | 1060-H18 | 2.5 | 35 | 51 | ||
| 17 | 1100-H12 | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 18 | 1100-H14 | 0 | 32 | 47 | ||
| 19 | 1100-H16 | 4.2 | 38 | 54 | ||
| 20 | 1100-H18 | 6.8 | 44 | 59 | ||
| 21 | 1100-H19 Foil | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 22 | 1100-O | 0 | 23 | 35 | ||
| 23 | 1145-H18 | 4.2 | 39 | 54 | ||
| 24 | 1145-H19 Foil | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 25 | 1180-H18 | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 26 | 1199-H18 | 0 | 31 | 46 | ||
| 27 | 1235-H19 Foil | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 28 | 1235-O Foil | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 29 | 1350-H12 | 0 | 26 | 40 | ||
| 30 | 1350-H14 | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 31 | 1350-H16 | 1.3 | 34 | 49 | ||
| 32 | 1350-H19 | 8.8 | 50 | 63 | ||
| 33 | 1350-O | 0 | 23 | 35 | ||
| 34 | 2011-T3 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 35 | 2011-T3 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 36 | 2011-T4 | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 37 | 2011-T6 | 15.3 | 97 | 109 | 61 | 80 |
| 38 | 2011-T8 | 15.3 | 100 | 112 | 63 | 80 |
| 39 | 2011-T8 | 15.3 | 100 | 112 | 63 | 80 |
| 40 | 2014-O | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 41 | 2014-T4; 2014-T451 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 67 | 82 |
| 42 | 2014-T6; 2014-T651 | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 43 | 2017-O | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 44 | 2017-T4; 2017-T451 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 45 | 2018-T61 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 46 | 2024-O | 7.8 | 47 | 61 | ||
| 47 | 2024-T3 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 48 | 2024-T361 | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 49 | 2024-T4; 2024-T351 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 50 | 2024-T6 | 17.2 | 125 | 142 | 78 | 87 |
| 51 | 2024-T81 | 17.4 | 128 | 146 | 79 | 88 |
| 52 | 2024-T851 | 17.4 | 128 | 146 | 79 | 88 |
| 53 | 2024-T86 | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 54 | 2025-T6 | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 55 | 2036-T4 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 56 | 2048 | 16.9 | 122 | 139 | 76 | 86 |
| 57 | 2090-O | 10.6 | 57 | 67 | ||
| 58 | 2090-T3 | 14.3 | 86 | 97 | 53 | 77 |
| 59 | 2090-T84 | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 60 | 2091-T8x | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 71 | 84 |
| 61 | 2091-T8x, 0.1 Cold deformation | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 62 | 2117-T4 | 12.6 | 70 | 81 | 72 | |
| 63 | 2124-T351 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 64 | 2124-T851 | 17.4 | 128 | 146 | 79 | 88 |
| 65 | 2218-T61 | 16.4 | 115 | 126 | 71 | 84 |
| 66 | 2218-T71 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 67 | 2218-T72 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 68 | 2219-O | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 69 | 2219-T31 | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 70 | 2219-T351 | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 71 | 2219-T37 | 16.7 | 117 | 133 | 73 | 85 |
| 72 | 2219-T62 | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 72 | 84 |
| 73 | 2219-T81 | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 74 | 2219-T851 | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 75 | 2219-T87 | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 76 | 2618-T61 | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 72 | 84 |
| 77 | 3003-H12 | 2.5 | 35 | 51 | ||
| 78 | 3003-H14 | 4.7 | 40 | 55 | ||
| 79 | 3003-H16 | 7.8 | 47 | 61 | ||
| 80 | 3003-H18 | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 81 | 3003-H19 Foil | 12.2 | 68 | 76 | 71 | |
| 82 | 3003-O | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 83 | 3004-H19 | 13.7 | 79 | 89 | 75 | |
| 84 | 3004-H32 | 9.2 | 52 | 64 | ||
| 85 | 3004-H34 | 11.4 | 63 | 73 | 69 | |
| 86 | 3004-H36 | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 87 | 3004-H38 | 13.3 | 77 | 87 | 74 | |
| 88 | 3004-O | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 89 | 3005-H14 | 8.3 | 49 | 62 | ||
| 90 | 3005-H18 | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 91 | 3005-O | 2.5 | 35 | 51 | ||
| 92 | 3104-H19 | 13.3 | 78 | 88 | 74 | |
| 93 | 3105-H12 | 5.3 | 41 | 56 | ||
| 94 | 3105-H14 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 95 | 3105-H16 | 9.7 | 53 | 65 | ||
| 96 | 3105-H18 | 10.6 | 58 | 67 | ||
| 97 | 3105-H25 | 8.3 | 49 | 62 | ||
| 98 | 3105-O | 0 | 31 | 46 | ||
| 99 | 4032-T6 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 100 | 4032-T651 | 16.9 | 120 | 136 | 75 | 86 |
| 101 | 4032-T86 | 16.9 | 120 | 136 | 75 | 86 |
| 102 | 4043-H14 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 103 | 4043-H16 | 9.7 | 54 | 65 | ||
| 104 | 4043-H18 | 13.3 | 77 | 87 | 74 | |
| 105 | 4043-O | 4.2 | 39 | 54 | ||
| 106 | 5005-H12 | 4.2 | 38 | 54 | ||
| 107 | 5005-H14 | 6.3 | 43 | 58 | ||
| 108 | 5005-H16 | 8.3 | 49 | 62 | ||
| 109 | 5005-H18 | 9.7 | 54 | 65 | ||
| 110 | 5005-H32 | 3.1 | 36 | 52 | ||
| 111 | 5005-H34 | 5.3 | 41 | 56 | ||
| 112 | 5005-H36 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 113 | 5005-H38 | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 114 | 5005-O | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 115 | 5042-H19 | 15 | 96 | 108 | 60 | 79 |
| 116 | 5050-H32 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 117 | 5050-H34 | 9.7 | 53 | 65 | ||
| 118 | 5050-H36 | 10.6 | 58 | 67 | ||
| 119 | 5050-H38 | 11.4 | 63 | 73 | 69 | |
| 120 | 5050-O | 3.1 | 36 | 52 | ||
| 121 | 5052-H19 Foil | 14.3 | 88 | 99 | 54 | 77 |
| 122 | 5052-H32 | 11 | 60 | 68 | 68 | |
| 123 | 5052-H34 | 12.2 | 68 | 78 | 71 | |
| 124 | 5052-H36 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 125 | 5052-H38 | 13.3 | 77 | 87 | 74 | |
| 126 | 5052-O | 7.8 | 47 | 61 | ||
| 127 | 5056-H18 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 128 | 5056-H191 Foil | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 129 | 5056-H38 | 15.3 | 100 | 112 | 63 | 80 |
| 130 | 5056-O | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 131 | 5082-H19 | 15.9 | 106 | 120 | 67 | 82 |
| 132 | 5083-H112 | 13.7 | 81 | 91 | 50 | 75 |
| 133 | 5083-H116; 5083-H321 | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 134 | 5083-H32; 5083-H323 | 14.3 | 87 | 98 | 54 | 77 |
| 135 | 5083-H34; 5083-H343 | 14.7 | 93 | 104 | 58 | 78 |
| 136 | 5083-O | 13.3 | 77 | 87 | 74 | |
| 137 | 5086-H112 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 138 | 5086-H116; 5086-H32 | 13.3 | 78 | 88 | 74 | |
| 139 | 5086-H34 | 14.3 | 87 | 98 | 54 | 77 |
| 140 | 5086-O | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 141 | 5154-H112 | 11.4 | 63 | 73 | 69 | |
| 142 | 5154-H32 | 12.2 | 67 | 77 | 71 | |
| 143 | 5154-H34 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 144 | 5154-H36 | 12.2 | 67 | 77 | 71 | |
| 145 | 5154-H38 | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 146 | 5154-O | 10.6 | 58 | 67 | ||
| 147 | 5182-H19 | 16.2 | 112 | 127 | 70 | 83 |
| 148 | 5182-H32 | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 149 | 5182-H34 | 14.7 | 91 | 102 | 57 | 78 |
| 150 | 5182-O | 12.9 | 74 | 84 | 73 | |
| 151 | 5252-H25; 5252-H38 | 12.2 | 68 | 78 | 71 | |
| 152 | 5252-H28 | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 153 | 5252-O | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 154 | 5254-H112 | 11.4 | 63 | 73 | 69 | |
| 155 | 5254-H32 | 12.2 | 67 | 77 | 71 | |
| 156 | 5254-H34 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 157 | 5254-H36 | 13.3 | 78 | 88 | 74 | |
| 158 | 5254-H38 | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 159 | 5254-O | 10.6 | 58 | 67 | ||
| 160 | 5454-H111; 5454-H311 | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 161 | 5454-H112 | 11.4 | 62 | 69 | ||
| 162 | 5454-H32 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 163 | 5454-H34 | 13.7 | 81 | 75 | ||
| 164 | 5454-O | 11.4 | 62 | 72 | 69 | |
| 165 | 5456-H111 | 14.3 | 87 | 98 | 54 | 77 |
| 166 | 5456-H112 | 14 | 83 | 94 | 51 | 76 |
| 167 | 5456-H116; 5456-H321 | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 168 | 5456-H24 | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 169 | 5456-O | 14 | 83 | 94 | 51 | 76 |
| 170 | 5457-H25 | 8.3 | 48 | 62 | ||
| 171 | 5457-H28; 5457-H38 | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 172 | 5457-O | 0 | 32 | 47 | ||
| 173 | 5652-H32 | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 174 | 5652-H34 | 12.2 | 68 | 78 | 71 | |
| 175 | 5652-H36 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 176 | 5652-H38 | 13.3 | 77 | 87 | 74 | |
| 177 | 5652-O | 7.8 | 47 | 61 | ||
| 178 | 5657-H25 | 4.7 | 40 | 55 | ||
| 179 | 5657-H28; 5657-H38 | 8.8 | 50 | 63 | ||
| 180 | 5657-O | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 181 | 6005-T1 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 182 | 6005-T5 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 183 | 6009-T4 | 11.4 | 62 | 70 | 69 | |
| 184 | 6009-T6 | 14.7 | 91 | 102 | 57 | 78 |
| 185 | 6010-T4 | 13.3 | 78 | 88 | 74 | |
| 186 | 6013-T651 | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 187 | 6013-T8 0.3-1.9 cm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 188 | 6013-T8 1.9-3.8 cm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 189 | 6013-T8 3.8-8.2 cm | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 190 | 6020-T651 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 191 | 6020-T8 | 15.3 | 100 | 112 | 63 | 80 |
| 192 | 6020-T9 | 16.9 | 120 | 136 | 75 | 86 |
| 193 | 6053-O | 0 | 26 | 40 | ||
| 194 | 6053-T6 | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 195 | 6061-O | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 196 | 6061-T4; 6061-T451 | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 197 | 6061-T6; 6061-T651 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 198 | 6061-T8 | 16.9 | 120 | 136 | 75 | 86 |
| 199 | 6061-T91 | 15.9 | 108 | 123 | 69 | 82 |
| 200 | 6061-T913 | 17.2 | 123 | 139 | 76 | 87 |
| 201 | 6063-O | 0 | 25 | 38 | ||
| 202 | 6063-T1 | 5.8 | 42 | 57 | ||
| 203 | 6063-T4 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 204 | 6063-T5 | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 205 | 6063-T6 | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 206 | 6063-T83 | 14 | 82 | 92 | 50 | 76 |
| 207 | 6063-T831 | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 208 | 6063-T832 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 209 | 6063-T835 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 210 | 6066-O | 6.3 | 43 | 58 | ||
| 211 | 6066-T4; 6066-T451 | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 212 | 6066-T6; 6066-T651 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 213 | 6070-O | 2.5 | 35 | 51 | ||
| 214 | 6070-T4 | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 215 | 6070-T6 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 216 | 6101-H111 | 0 | 26 | 40 | ||
| 217 | 6101-T6 | 12.6 | 71 | 81 | 72 | |
| 218 | 6151-T6 | 15.3 | 100 | 112 | 63 | 80 |
| 219 | 6201-T6 | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 220 | 6201-T81 | 14.3 | 88 | 99 | 55 | 77 |
| 221 | 6205-T1 | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 222 | 6205-T5 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 223 | 6262-T6 | 12.6 | 71 | 81 | 72 | |
| 224 | 6262-T8 | 15.6 | 103 | 116 | 65 | 81 |
| 225 | 6262-T9 | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 226 | 6351-T4; 6351-T451 | 12.2 | 67 | 77 | 71 | |
| 227 | 6351-T54 | 10.6 | 58 | 67 | ||
| 228 | 6351-T6; 6351-T651 | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 229 | 6463-O | 0 | 25 | 38 | ||
| 230 | 6463-T1 | 5.8 | 42 | 57 | ||
| 231 | 6463-T4 | 7.3 | 46 | 60 | ||
| 232 | 6463-T5 | 11 | 60 | 68 | 68 | |
| 233 | 6463-T6 | 12.9 | 74 | 84 | 73 | |
| 234 | 6951-O | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 235 | 6951-T6 | 14 | 82 | 92 | 50 | 76 |
| 236 | 7001-O | 11 | 60 | 68 | ||
| 237 | 7005-O | 9.7 | 53 | 65 | ||
| 238 | 7005-T53 | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 239 | 7005-T6, 7005-T63 | 15 | 94 | 106 | 59 | 79 |
| 240 | 7005-T6351 | 15 | 94 | 106 | 59 | 79 |
| 241 | 7005-W | 14.7 | 93 | 105 | 50 | 78 |
| 242 | 7016-T5 | 15 | 96 | 108 | 60 | 79 |
| 243 | 7021-T62 | 16.2 | 112 | 127 | 70 | 83 |
| 244 | 7029-T5 | 16.4 | 115 | 128 | 71 | 84 |
| 245 | 7039-O | 11.4 | 61 | 69 | 69 | |
| 246 | 7039-T61 | 17.2 | 123 | 140 | 76 | 87 |
| 247 | 7039-T64 | 17.6 | 133 | 153 | 81 | 89 |
| 248 | 7049-T73; 7049-T7352 | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 249 | 7050-T73511; 7050-T73510 | 17.6 | 132 | 151 | 80 | 89 |
| 250 | 7050-T7451 (7050-T73651) | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 251 | 7072-H12 | 0 | 28 | 42 | ||
| 252 | 7072-H14 | 0 | 32 | 47 | ||
| 253 | 7075-O | 11 | 60 | 68 | 68 | |
| 254 | 7075-T73; 7075-T735x | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 255 | 7175-T7351 | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 256 | 7175-T736;7175-T7365x | 18.2 | 145 | 169 | 86 | 92 |
| 257 | 7178-O | 11 | 60 | 68 | 68 | |
| 258 | 7475-T7351 | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 259 | 7475-T761 | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 260 | 7475-T7651 | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 261 | 8001-H18 | 9.7 | 54 | 65 | ||
| 262 | 8001-O | 0 | 30 | 45 | ||
| 263 | 8081-H112 | 9.7 | 53 | 65 | ||
| 264 | 8081-H25 | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 265 | 8090-T3 | 14.7 | 91 | 102 | 57 | 78 |
| 266 | 8090-T511;+B35 8090-T6511 | 17.8 | 137 | 158 | 83 | 90 |
| 267 | 8090-T81 | 16.7 | 116 | 137 | 73 | 85 |
| 268 | 8090-T8151 | 16.9 | 121 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 269 | 8090-T852 | 17.4 | 128 | 146 | 79 | 88 |
| 270 | 8090-T8771; 8090-T651 | 18 | 138 | 158 | 83 | 91 |
| 271 | 8090-T8x | 17.4 | 130 | 149 | 80 | 88 |
| 272 | 8280-H18 | 11 | 59 | 67 | 68 | |
| 273 | 8280-O | 0 | 31 | 46 | ||
| 274 | 201.0-T6 Casting alloy | 17.8 | 135 | 155 | 82 | 90 |
| 275 | 201.0-T7 Sand casting | 17.2 | 125 | 153 | 77 | 87 |
| 276 | 201.0-T4 Sand casting | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 277 | 204.0-T4 Die casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 278 | 204.0-T4 Sand casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 279 | 204.0-T6 Sand casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 280 | 204.0-T6 Sand casting | 17.2 | 125 | 143 | 77 | 87 |
| 281 | 204.0-T6 Die casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 282 | 204.0-T6 Die casting, | 17.2 | 125 | 143 | 77 | 87 |
| 283 | 208.0-T4 Die casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 45 | 74 |
| 284 | 208.0-T6 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 285 | 208.0-T7 Die casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 286 | 208.0-F Sand casting | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 287 | 206.0-T7 Casting alloy | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 288 | A206.0-T7 Casting alloy | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 289 | 222.0-O Sand casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 290 | 222.0-T551 Die casting | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 72 | 84 |
| 291 | 222.0-T61 Sand casting | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 72 | 84 |
| 292 | 222.0-T65 Die casting | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 293 | 242.0-O Sand casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 294 | 242.0-T571 Die casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 295 | 242.0-T571 Sand casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 296 | 242.0-T61 Die casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 297 | 242.0-T61 Sand casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 298 | 242.0-T77 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 299 | 242.0-T21 Sand casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 300 | 295.0-T4 Sand casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 301 | 295.0-T6 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 302 | 295.0-T62 Sand casting | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 303 | 295.0-T7 Sand casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 304 | 296.0-T6 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 305 | 296.0-T4 Casting alloy | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 306 | 296.0-T7 Casting alloy | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 307 | 308.0-F Die casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 308 | 319.0-F Die casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 309 | 319.0-F Sand casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 310 | 319.0-T5 Sand casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 311 | 319.0-T6 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 312 | 319.0-T6 Sand casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 313 | 328.0-F Sand casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 314 | 328.0-T6 Sand casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 315 | 332.0-T5 Die casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 316 | 333.0-F Die casting | 14 | 83 | 94 | 51 | 76 |
| 317 | 333.0-T5 Die casting | 14.3 | 88 | 99 | 55 | 77 |
| 318 | 333.0-T6 Die casting | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 319 | 333.0-T7 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 320 | 336.0-T551 Die casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 321 | 336.0-T65 Die casting | 17.2 | 125 | 143 | 77 | 87 |
| 322 | 355.0-T51 Die casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 323 | 355.0-T51 Sand casting | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 324 | 355.0-T6 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 325 | 355.0-T6 Sand casting | 14.3 | 88 | 99 | 55 | 77 |
| 326 | 355.0-T62 Die casting | 15.9 | 105 | 118 | 66 | 82 |
| 327 | 355.0-T7 Die casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 328 | 355.0-T7 Sand casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 329 | 355.0-T71 Die casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 330 | 355.0-T71 Sand casting | 13.3 | 78 | 88 | 74 | |
| 331 | C355.0-T6 Sand casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 332 | C355.0-T61 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 333 | 356.0-F Die casting | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 334 | 356.0-F Sand casting | 10.1 | 55 | 66 | ||
| 335 | 356.0-T51 Die casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 336 | 356.0-T51 Sand casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 337 | 356.0-T6 Die casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 338 | 356.0-T6 Sand casting | 12.9 | 73 | 83 | 73 | |
| 339 | 356.0-T7 Die casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 340 | 356.0-T7 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 341 | 356.0-T71 Die casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 342 | 356.0-T71 Sand casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 343 | A356.0-T6 Sand casting | 14.3 | 88 | 99 | 55 | 77 |
| 344 | A356.0-T61 Die casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 345 | 357.0-T6 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 346 | A357.0-T61 Die casting | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 347 | 359.0-T61 Die casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 348 | 359.0-T62 Die casting | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 349 | 383.0-F Die-casting alloy | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 350 | 384.0-F Die-casting alloy | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 351 | A384.0-F Die-casting alloy | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 352 | A390.0-F Sand casting | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 353 | A390.0-T6 Sand casting | 18 | 140 | 162 | 84 | 91 |
| 354 | A390.0-T7 Sand casting | 16.4 | 115 | 130 | 72 | 84 |
| 355 | A390.0-F, -T5 Die casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 356 | A390.0-T6 Die casting | 18.2 | 145 | 169 | 86 | 92 |
| 357 | A390.0-T7 Die casting | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 358 | 390.0-F Traditional die casting | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 359 | 390.0-T5 Traditional die casting | 17.2 | 125 | 143 | 77 | 87 |
| 360 | 390.0-F Twin-plunger die casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 361 | 390.0-T5 Twin-plunger die casting | 16.2 | 110 | 124 | 69 | 83 |
| 362 | 390.0-T7 Twin-plunger die casting | 17.2 | 125 | 143 | 77 | 87 |
| 363 | 443.0-F Die casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 364 | 443.0-F Sand casting | 4.7 | 40 | 55 | ||
| 365 | B443.0-F Die casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 366 | B443.0-F Sand casting | 4.7 | 40 | 55 | ||
| 367 | 512.0-F Sand casting | 8.8 | 50 | 63 | ||
| 368 | 513.0-F Die casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 | |
| 369 | 514.0-F Sand casting | 8.8 | 50 | 63 | ||
| 370 | 518.0-F Die-casting alloy | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 371 | 520.0-T4 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 372 | 535.0-F or 535.0-T5, | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 373 | A535.0-F or 535.0-T5, | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 374 | B535.0-F or 535.0-T5, | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 375 | 705.0-F Sand casting | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 376 | 705.0-T5 Die casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 377 | 705.0-T5 Sand casting | 11.8 | 65 | 75 | 70 | |
| 378 | 707.0-T5 Sand casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 379 | 707.0-T7 Die casting | 15 | 95 | 107 | 60 | 79 |
| 380 | 707.0-T7 Sand casting | 13.7 | 80 | 90 | 49 | 75 |
| 381 | 710.0-T5 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 382 | 711.0-T1 Die casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 383 | 712.0-T5 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 384 | 712.0-F Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 385 | 713.0-F Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 386 | 713.0-T5 Die casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 387 | 713.0-T5 Sand casting | 13.3 | 75 | 85 | 74 | |
| 388 | 771.0-T5 Sand casting | 15.3 | 100 | 113 | 63 | 80 |
| 389 | 771.0-T51 Sand casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 390 | 771.0-T52 Sand casting | 14 | 85 | 96 | 53 | 76 |
| 391 | 771.0-T6 Sand casting | 14.7 | 90 | 101 | 56 | 78 |
| 392 | 771.0-T71 Sand casting | 16.9 | 120 | 137 | 75 | 86 |
| 393 | 850.0-T5 Die casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 394 | 850.0-T5 Sand casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 395 | 851.0-T5 Die casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 396 | 851.0-T5 Sand casting | 6.8 | 45 | 59 | ||
| 397 | 852.0-T5 Die casting | 12.6 | 70 | 80 | 72 | |
| 398 | 852.0-T5 Sand casting | 11 | 60 | 70 | 68 |
Conducting a comparative analysis of aluminium hardness involves evaluating various factors such as alloy type, temper, and the presence of reinforcing materials. The comparison is typically based on standardized hardness testing methods like Rockwell, Brinell, and Vickers. These tests provide quantifiable measurements that can be used to compare different alloys’ hardness levels under similar conditions.
Several key factors influence the hardness of aluminium alloys:
The factors influencing hardness play a crucial role in determining the suitability of an aluminium alloy for specific applications.
Selecting the best aluminium alloy for a specific application requires considering the desired balance of hardness, strength, ductility, and other mechanical properties. This decision-making process involves:
By understanding and comparing the hardness and mechanical properties of different aluminium alloys, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions to select the most appropriate materials for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in their applications.
Compliance with industry standards is essential to ensure the reliability, safety, and performance of aluminium alloys across various applications. These standards provide a uniform framework for testing, classification, and quality assurance, ensuring that aluminium parts meet the stringent requirements of different industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Several key standards govern the hardness and other properties of aluminium alloys, facilitating consistency and quality control across manufacturing and application processes.
The specification AMS 2658D, “Hardness and Conductivity Inspection of Wrought Aluminum Alloy Parts,” is crucial in the aerospace industry. It establishes the acceptance criteria for the hardness and electrical conductivity of finished or semi-finished parts of wrought aluminium alloys. This standard specifies the required values for hardness and conductivity, ensuring that the materials meet the necessary performance criteria for aerospace applications.
The ASTM B647-10(2016) standard describes the use of the Webster hardness gage for measuring the hardness of aluminium alloys. Although less sensitive than Rockwell or Brinell hardness machines, the Webster gage is valuable for production control and field testing. This standard helps maintain quality during manufacturing and ensures that the aluminium parts adhere to specified hardness levels.
The EN standards provide a comprehensive framework for aluminium alloys, covering mechanical properties, heat treatment designations, and corrosion resistance. These standards, which have replaced older standards like BS1470, ensure consistency and quality across different applications and industries. They are essential for manufacturers to produce aluminium parts that meet the required specifications and performance criteria.
Different aluminium alloys have specific standards and properties that must be met to ensure their suitability for intended applications. For instance:
Manufacturers must adhere to industry standards to ensure the quality and performance of aluminium alloys. This involves rigorous testing and certification processes to verify that the materials meet the specified criteria.
Non-compliance with industry standards can have severe consequences, including:
Ensuring compliance with standards such as AMS 2658D, ASTM B647-10(2016), and the EN standards is essential for maintaining the quality, safety, and performance of aluminium alloys across various applications. These standards provide a framework for testing, classification, and application, helping manufacturers produce reliable and high-quality aluminium parts that meet the stringent requirements of different industries.
Elements such as magnesium, manganese, titanium, and rare earth elements (like lanthanum and yttrium) can be added to an aluminum alloy to enhance its hardness. Incorporating magnesium can notably increase the tensile strength of aluminum; for each 1% increase in magnesium, the tensile strength increases by approximately 34 MPa.
The introduction of manganese can supplement the strengthening effect and also decrease the susceptibility to thermal cracking.
Furthermore, the addition of rare earth elements (like lanthanum and yttrium) can enhance the resistance to the peeling of the oxidation layer. Hence, the incorporation of these elements can boost the hardness of aluminum alloys to varying degrees.
There are several methods that can be employed to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of aluminum alloys through surface treatment:
Anodic oxidation treatment: This common method involves forming a dense oxide film on the surface of the aluminum alloy, thereby enhancing its hardness and corrosion resistance.
Surface electroplating: By coating a layer of metal (such as tin or copper) on the surface of the aluminum alloy, its hardness and wear resistance can be effectively improved.
Spraying wear-resistant coatings: A special wear-resistant coating is evenly sprayed on the surface of the aluminum alloy material to form a uniform, dense, and hard coating. This method not only improves wear resistance and corrosion resistance but also enhances the appearance.
Cold work hardening: This method hardens the aluminum alloy at room temperature through cold working, suitable for aluminum alloy materials that need to maintain their original shape.
Heat treatment: For certain specific types of aluminum alloys (like 6061), their strength and hardness can be enhanced through aging treatment. This usually involves an aging treatment after solution treatment.
Direct current magnetron sputtering deposition of amorphous CrAlN coating: This method deposits an amorphous CrAlN coating on the surface of the aluminum alloy, improving its corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Thermal spraying and self-propagating high-temperature synthesis: These methods can prepare wear-resistant ceramic coatings on the surface of the aluminum alloy, significantly improving the wear resistance of the aluminum alloy.