Have you ever wondered what makes mechanical design so crucial in engineering? This comprehensive guide on the basics of mechanical design explores essential concepts such as standardization, types of connections, bearing classifications, and gear mechanisms. Readers will gain a foundational understanding of key principles, aiding in efficient and innovative design processes. Dive into this article to enhance your knowledge and improve your mechanical design skills!


① Reduces the design workload;
② Standard parts are produced in large quantities by professional factories with high efficiency, low cost, and reliable quality;
③ Makes maintenance and repair more convenient;
④ The principle of “Three Modernizations” should be followed in design and is also a national technical policy.
Sliding bearings are further divided into radial and thrust bearings based on the load they carry.
Features of oil bearing: low strength, no impact resistance, simple structure, and low cost.
Advantages:
① Low friction resistance, sensitive starting, high efficiency, low heating, and low temperature rise;
② Small axial dimension contributes to the compactness and simplicity of the entire machine mechanism;
③ Small radial clearance, which can be adjusted by the pre-tightening method, leading to high rotation accuracy;
④ Simple lubrication, low oil consumption, and easy maintenance;
⑤ Standard parts, mass production, cost-effective, and easy to use and replace.
Disadvantages: large radial size, limited ability to bear impact loads, high noise when running at high speeds, and short working life.
a. Reduce impact and absorb vibrations;
b. Control movement;
c. Store and release energy;
d. Provide measurement indication;
e. Maintain elastic contact.
b. Manufacturing process of cylindrical spiral springs: winding formation, end processing or hook production, and heat treatment.
① Low pairs: door and window hinges, ceiling fans, which have surface contact, can bear large loads, wear slowly, have long service lives, and low pressure, making them low pairs.
② High pairs: the meshing of gears, the ball heel ring of rolling bearings, the contact between train wheels and rails, and the contact between cams and push rods are all line or point contacts with high pressure. They allow for more accurate movement and high manufacturing requirements, making them high pairs.
① Crank-rocker mechanism (e.g. agricultural manual thresher, liquid mixer, rocking horse, sewing machine);
② Double crank mechanism (e.g. linkage mechanism of train wheels, umbrella);
③ Double rocker mechanism (e.g. electric fan oscillating mechanism, automobile wiper).
b. Classification based on the shape of the follower: pointed followers, roller followers, and flat bottom followers.
c. Classification based on the movement form of the follower: direct moving followers and oscillating followers.
Advantages:
① They can reduce impact, absorb vibrations, provide smooth operation, and have low noise;
② Simple structure, easy maintenance and replacement, and low cost;
③ Can easily achieve transmission between large center distances;
④ When overloaded, the conveyor belt will slip on the wheel to avoid damaging the machine.
Disadvantages:
① Cannot guarantee accurate and constant transmission ratio in belt transmission;
② Low mechanical transmission efficiency;
③ The shaft and shaft are subjected to large radial forces, which are unfavorable for machine operation.
② Neutral layer: located between the top and bottom rubber layers, its length and width do not change due to the tension of the V-belt on the pulley;
③ Pitch width: the width of the neutral layer of the V-belt;
④ There are three types of V-belt pulleys based on the size of their benchmark diameter: solid type, spoke plate type, and spoke type.
Advantages:
① Meshing transmission can ensure a constant average transmission ratio;
② No initial tension is required and there is minimal shaft bending force;
③ Greater strength compared to belt drives, allowing for the transmission of larger loads;
④ Strong adaptability, can be used in challenging work conditions.
Disadvantages:
① Cannot guarantee constant instantaneous transmission ratios like gears;
② High noise and vibration;
③ Higher manufacturing and installation requirements compared to belt drives;
④ The direction of the sprocket shaft is restricted.
Advantages:
① High transmission accuracy;
② Wide range of applications;
③ Can achieve transmission between any two shafts in space;
④ Reliable operation and long service life;
⑤ High transmission efficiency.
Disadvantages:
① High manufacturing and installation requirements, and high cost;
② Strict requirements for ring mirror conditions, generally need to be placed in a cover to prevent dust and scale, and attention must be given to lubrication;
③ Not suitable for long-distance transmissions;
④ Vibration damping and impact resistance are not as good as belt transmissions.
① Obtain large transmission ratios;
② Achieve variable speed and reverse transmission;
③ Achieve multi-channel transmission;
④ Achieve gear transmission over large distances;
⑤ Synthesize and decompose motion.
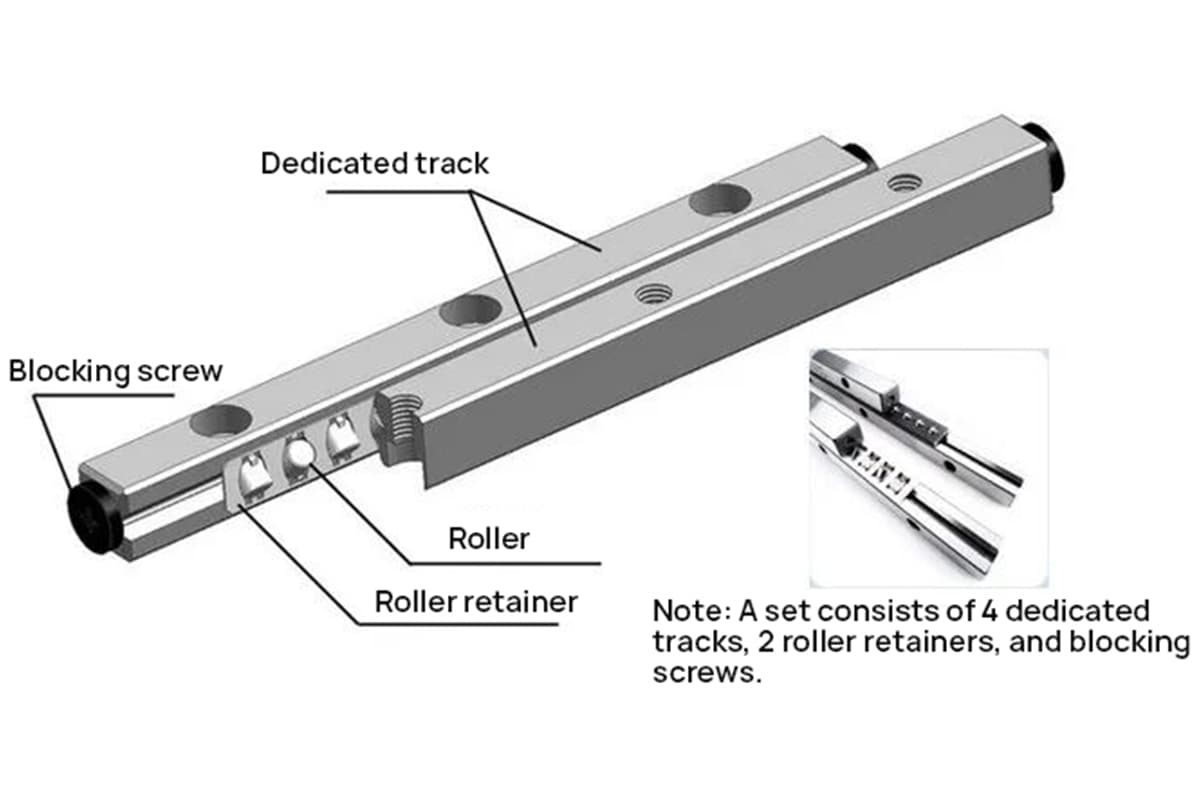
① Integral sliding bearings;
② Partial sliding bearings;
③ Self-aligning sliding bearings;
④ Thrust sliding bearings.