Why do some welds succeed while others fail? The secret lies in understanding the welding thermal process. This article dives into the critical aspects of how heat affects metal during welding, including the impacts on the molten pool, metallurgical reactions, and potential for defects. By mastering these principles, you’ll enhance both the quality and efficiency of your welding projects. Read on to uncover the key characteristics that make or break your welds.

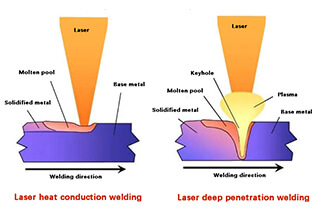
In the welding process, metal undergoes a complex thermal cycle involving heating, melting or reaching a thermoplastic state, followed by solidification and continuous cooling. This phenomenon, known as the welding thermal process, is driven by heat input and transmission dynamics.
The welding thermal process is a critical factor influencing both weld quality and productivity. Its impact manifests through several key mechanisms:

The welding thermal process exhibits significantly higher complexity compared to conventional heat treatment methods, characterized by four primary attributes:
a. Localized Concentration of Heat Input
Unlike uniform heating in traditional processes, welding applies intense thermal energy to a highly localized area. This concentrated heat input creates extreme temperature gradients across the weldment, resulting in non-uniform heating and cooling patterns that can significantly affect the material’s microstructure and properties.
b. Dynamic Nature of Heat Source
The welding heat source continuously traverses the workpiece, creating a moving thermal field. As the heat source approaches a given point, the temperature rises rapidly, often exceeding the material’s melting point. Upon passing, the area experiences rapid cooling, establishing complex thermal cycles that vary spatially and temporally across the weldment.
c. Rapid Thermal Transients
Welding processes, particularly arc-based methods, induce exceptionally high heating rates, often exceeding 1500°C/s. This rapid energy transfer results in near-instantaneous melting and subsequent rapid solidification. The cooling rates are similarly extreme due to the localized nature of heating and the movement of the heat source, leading to potential formation of non-equilibrium microstructures.
d. Multi-modal Heat Transfer Mechanisms
The welding thermal process involves intricate heat transfer phenomena:
These concurrent heat transfer modes, coupled with phase transformations and potential chemical reactions, render the welding thermal process a complex, multi-physics problem that requires sophisticated modeling and analysis for accurate prediction and control.
The interplay of these characteristics profoundly influences the weld quality, residual stress distribution, and final properties of the welded joint, necessitating a thorough understanding for optimal process design and control in advanced manufacturing applications.
The characteristics mentioned above underscore the intricate nature of heat transfer in welding processes. This complexity, however, does not diminish the importance of welders comprehending its fundamental principles. A thorough understanding of how various process parameters influence heat transfer is crucial for several reasons:
By mastering these concepts, welding professionals can significantly enhance their ability to produce high-quality welds consistently, improve overall productivity, and adapt to the evolving demands of modern manufacturing and fabrication industries. This knowledge forms the cornerstone of advanced welding practices and is indispensable for staying competitive in the field.