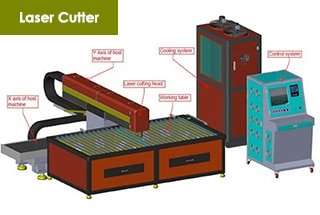
The quality of a laser cutting machine is mainly determined by its cutting quality, which is the most direct way to assess the machine. When purchasing a laser cutting machine, new customers typically request to see a sample cutting process performed by the machine.
See also:
The cutting speed of the laser cutting equipment is important for customers to consider. Additionally, they should also focus on the cutting quality of the sample.
So, how do you assess the quality of laser cutting, and what should you pay attention to? Let me provide you with some more details.
The following nine standards are important to keep in mind.

Roughness
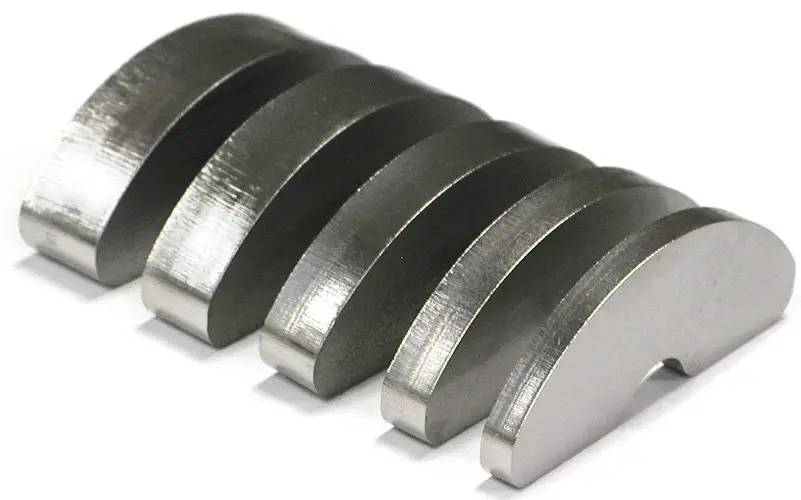
The laser cutting produces vertical lines, and the depth of these lines determines the roughness of the cutting surface.
The lighter the line, the smoother the cutting section is.
Roughness affects not only the appearance of the edge but also the friction characteristics.
In most cases, the roughness should be minimized as much as possible, and therefore, the lighter the lines are, the higher the cutting quality will be.
Perpendicularity
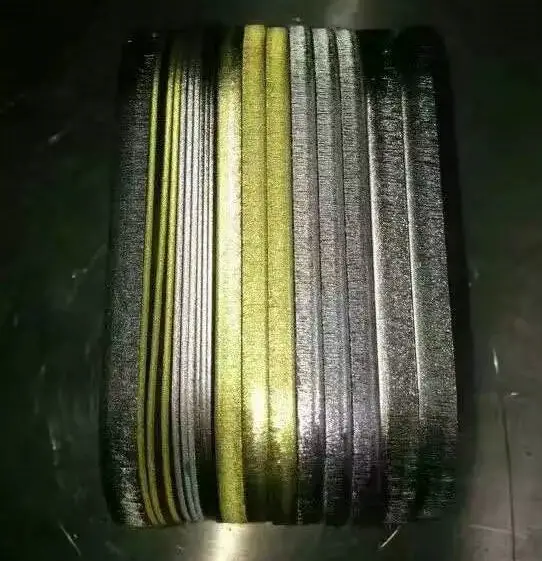

If the sheet metal thickness exceeds 10mm, the vertical degree of the cutting edge becomes very important.
The laser beam diverges when it is far away from the focus, causing the cutting width to enlarge toward the top or bottom, depending on the focus position.
The cutting edge may deviate a few millimeters from the vertical line. The more vertical the edge, the higher the cutting quality will be.
Cutting width
Notch width, in general, does not affect the cutting quality, except when forming the outline of parts with special precision. In such cases, the cutting width will be affected because it determines the minimum inner diameter of the outlined shape.
When the plate thickness increases, the cutting width will also increase.
Therefore, to ensure the same high precision, regardless of the width of the cut, the working area of the workpiece in the laser cutter should remain constant.
See also:

Lines
When cutting thick plates at high speed, molten metal will not accumulate in the incision below the vertical laser beam but instead will be sprayed out at the end of the laser beam.
This results in curved lines forming at the cutting edge that follow the moving laser beam.
To address this problem, reducing the feed rate at the end of the cutting process can significantly reduce the formation of these curved lines.
Burr
Burr formation is a crucial factor that determines the quality of laser cutting, as the removal of burrs requires additional work.
Therefore, the severity and amount of burrs are the most important factors in assessing the cutting quality.
Material deposited
Before melting the perforation, the laser cutter sprays a special layer of oily liquid on the surface of the workpiece.
During the cutting process, the vaporization of various materials necessitates that the customer use air flow to remove the incision. However, this can also cause deposition to form on the surface in the upward or downward direction.
Depression and corrosion
Sag and corrosion can have an adverse effect on the surface of the cutting edge, thereby affecting the appearance of the workpiece.
In general, they are cutting errors that should be avoided.
Thermal Zone
In laser cutting, the area near the incision is heated, and the structure of the metal changes as a result.
For instance, some metals will harden during this process.
The depth of the region where the internal structure changes is known as the thermal influence region.

Deformation
If the cutting process causes rapid heating of the part, it can result in deformation.
This is especially significant in fine processing since the outlines and connections are usually only a few millimeters wide.
Controlling laser power and using short laser pulses can help reduce the heat generated in the parts and prevent deformation.