How can factories reduce labor costs while increasing production efficiency? Enter the CNC automated stud welding machine. This advanced equipment automates the welding of studs onto metal, enhancing speed, precision, and flexibility in manufacturing. By integrating this technology, manufacturers can tackle the challenges of rising labor costs and diverse production demands. Discover how CNC automated stud welding machines are transforming the industry, providing high-quality welds, and boosting productivity. Dive into this article to learn about the basics, benefits, and applications of this game-changing technology.

Currently, the process of welding studs onto a metal base material through various welding methods is widely used in electrical cabinets, home appliances, furniture, automotive parts, and various hardware sheet metal parts.
These welding methods can generally be divided into two types: energy storage welding and arc welding.

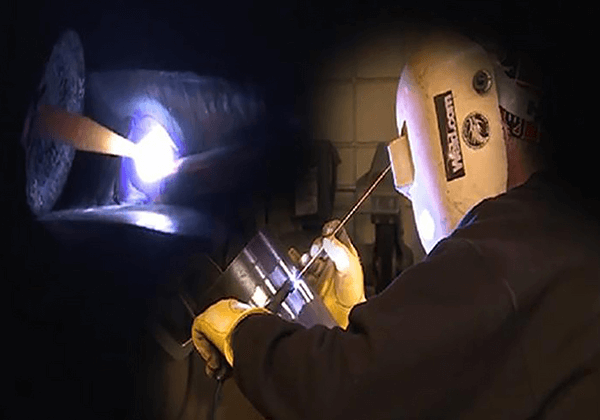
Energy storage welding is most commonly used for welding studs with smaller diameters. The principle involves the release of stored energy from a capacitor at the moment the stud contacts the base material, causing the area where the stud and the base material meet to melt and weld together.
This type of welding is completed instantaneously and has the advantages of simple operation, small welding surface marks, high efficiency, compact equipment, and easy portability. It is now widely used in various fields of thin plate stud welding production.
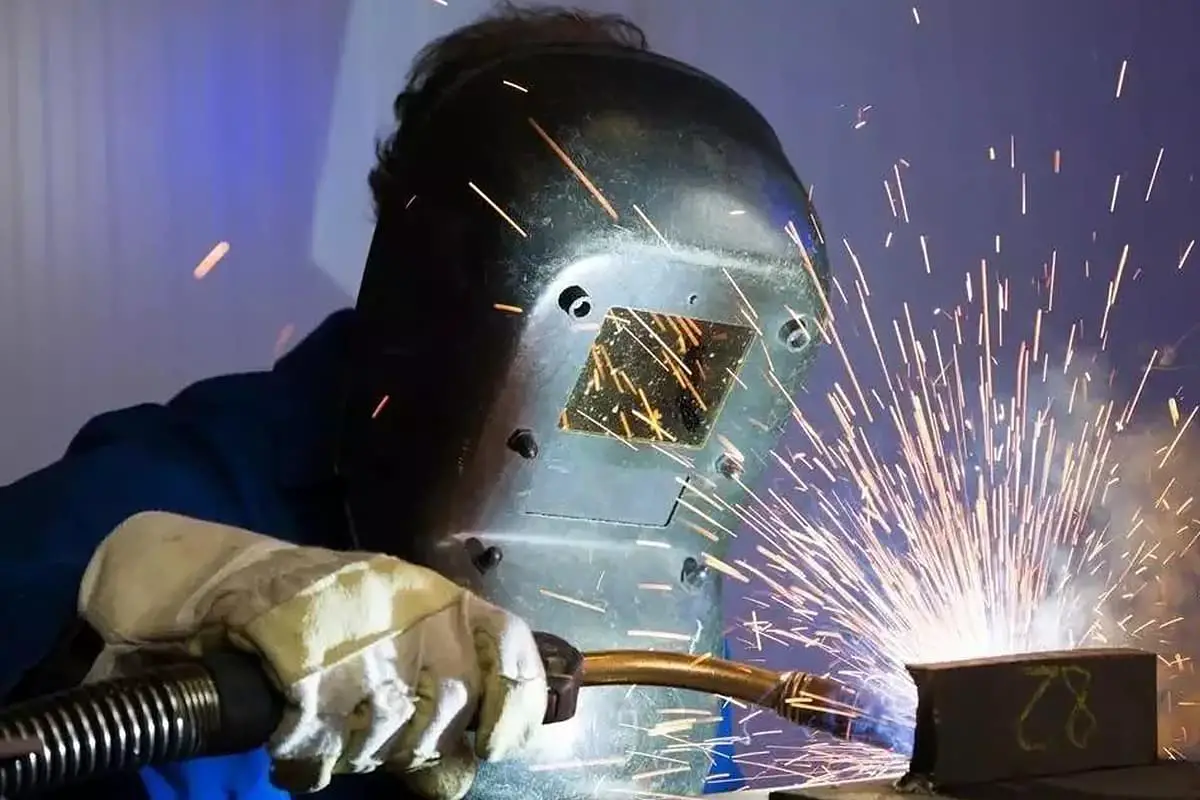
Arc welding applies voltage through a coil between the stud and the base material. As the stud contacts and then withdraws from the base material, a short circuit occurs, and an electric arc is pulled out.
This high-temperature electric arc melts the contact surface of the stud and the base material. After a while, it is pressed tightly, firmly welding the stud and the base material together.
This method is primarily used in areas that require higher welding strength, such as automotive parts and steel plate parts.
In accordance with these two welding methods, we have developed stud welding equipment, including handheld stud welding, arc welding equipment, CNC automated stud welding machines, robotic stud welding workstations, and desktop automatic stud welding machines. This article mainly introduces the CNC automated stud welding machine.
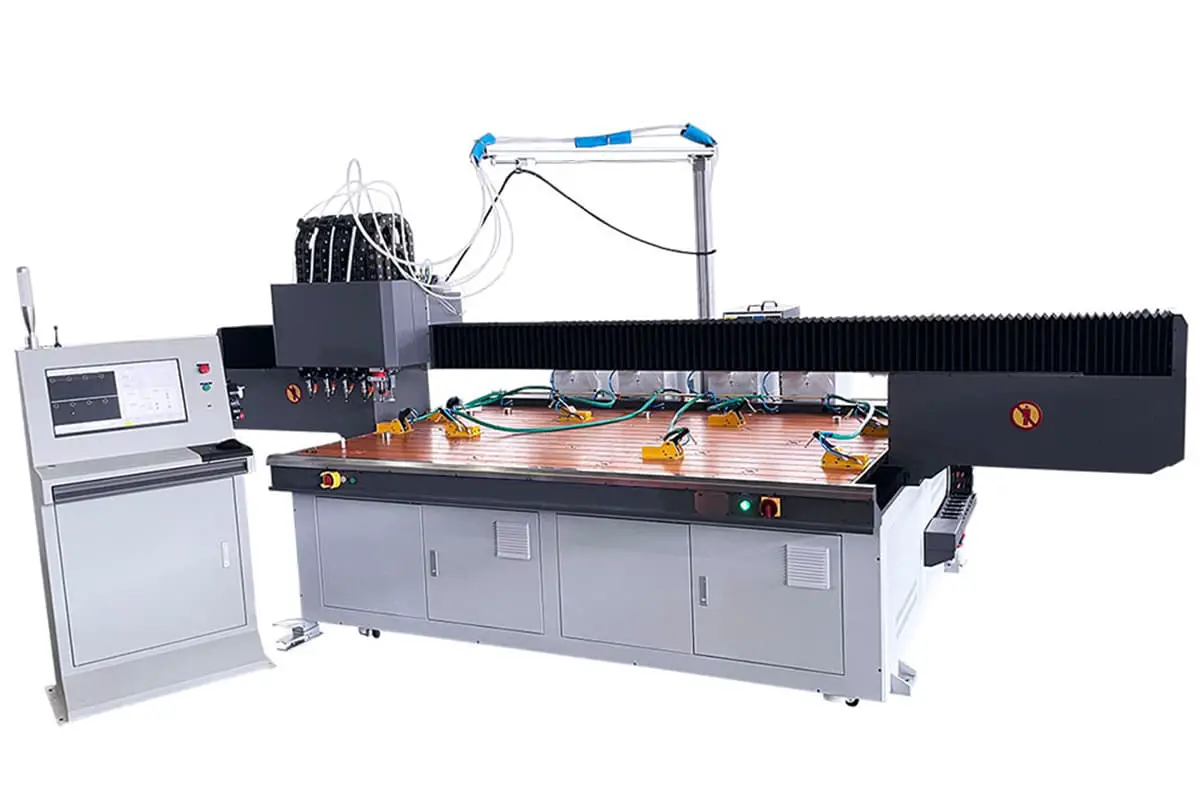
As shown in Figure 1, the CNC automated stud welding machine is an automated device developed to help customers handle the bulk welding of studs.
With the continuous increase of labor costs in factories, the variety and quantity of products that need to be welded with studs are increasing, and production tasks are trending towards small batches and multiple varieties.
This automated equipment can meet such production needs well and is gradually becoming standard equipment in sheet metal factories and metal processing factories.
The CNC automated stud welding machine mainly consists of eight parts: the rack structure, bed structure, transmission system, drive system, control system, welding platform, automatic nail selection and feeding mechanism, and automatic welding torch head.
The rack structure is divided into vertical and horizontal structures. Generally, if the workpiece length exceeds 3200mm or the width exceeds 1200mm, a vertical structure is used, as shown in Figure 2.

If the workpiece length is less than 3200mm or the width is within 1200mm, a horizontal structure is used, as shown in Figure 3, facilitating workpiece loading and equipment operation.

The Y-axis adopts a double-drive gantry way, the X-axis beam uses a special extruded aviation aluminum profile, and the moving beam is light, sturdy, and not easily deformed.
The aluminum profile beam is precision milled by a CNC gantry to ensure that the parallelism and straightness accuracy of the equipment is within 0.02mm.
The X-axis direction at both ends is a cantilever structure, allowing the machine head to move out of the worktable plane, facilitating machine head maintenance, reducing the volume of the machine tool, and maximizing the use of the platform’s effective area.
Bed Structure
Due to the small production volume and high price of this type of equipment, most manufacturers use a square assembly with a simple structure and low cost.
There are typically two forms: one is assembled from all-aluminum profiles, which is easy to produce and assemble, does not require welding, annealing, or precision machining, and has a low production cost.
The drawback is that its strength is not sufficient, the frame is prone to deformation, and transportation and handling can lead to inaccurate positioning, resulting in a low machine tool operating speed.
Another type involves retrofitting the bed of a common engraving machine available on the market. There are many manufacturers of such beds, and the prices are low. The advantage is that they are easy to produce and assemble without incurring much production cost.
The downside is that engraving machine styles are monotone, generally vertical structures, and due to fierce market competition, the bed material and processing control vary widely, making it difficult to guarantee product quality consistency.
The equipment we produce uses a bed made from heavy-duty steel welded together. After annealing, the X and Y axis drive guide groove installation surfaces are processed by a large CNC gantry milling machine. The machine operates at a stable speed, ensuring excellent product quality.
Transmission System
The standard transmission part is equipped with a high-precision belt (Figure 4) or gear rack (Figure 5) for transmission, guided by a linear guide rail (Figure 6), ensuring high-precision and high-speed operation.



The optional configuration is a linear motor (Figure 7) + metal grating (Figure 8) for transmission.


The linear motor has a long service life, lower power consumption, more stable transmission, and more precise positioning. It comes with a high-precision magnetic cabinet that is durable, not prone to aging, highly accurate, and strong in anti-pollution capability.
Drive System
All traveling mechanisms are driven by high-precision servo motors (Figure 9), achieving precise positioning. The Y-axis adopts dual-drive servo motor control (Figure 10), ensuring high precision and stability during high-speed operation of the equipment.


Control System
The control system adopts a touch-teaching integrated numerical control system. The controller is an imported new generation dedicated multi-axis linkage motion controller, developed based on industrial robot systems.
It is stable, reliable, and powerful. The human-machine interface is a movable full-color handheld box, which is convenient to operate, as shown in Figure 11.

The servo motor controller adopts a three-axis system, which is small in size, easy to install, simple to wire, and stable in control.
Depending on different customer needs, on-site operation conditions, product batch size, and operating habits, we provide three different programming methods: teaching, CAD, and coordinates. The system also has practical functions like riveting and dry running, making operation simple and convenient.
The teaching journey is equipped with an infrared indicator. The handwheel of the manipulator is used for point positioning, which facilitates the entry of the stud coordinates and makes the process convenient and quick.
CAD programming can generate work programs from CAD drawings on the computer using specialized software, which can then be copied into the system via USB for direct production.
The coordinate position can be input into the system table based on the machining drawings, allowing the system to generate the processing program. The system also supports program calling by scanning a QR code with a barcode scanner.
The system also has a data saving function, which can save all dimensional data of the process points, gun head data, etc., into a custom file for easy recall.
Welding Platform
The welding platform is composed of a floating ball insulating platform, a pneumatic clamp, and a moving positioning block, as shown in Figure 12.

When manually loading materials, the floating ball rises to prevent the workpiece, especially stainless steel workpieces, from scratching the surface due to friction on the insulating platform.
During operation, the floating ball falls, and the clamp clamps the workpiece securely to the ground. The round moving positioning block makes it easy to fix any shape of workpiece, and can position the outer edge and inner hole of the workpiece.
The workbench is evenly distributed with modular installation dovetail grooves, which can adjust the installation position of the pneumatic clamp workpiece positioning block at will. This way, manual loading and unloading saves time and effort.
According to customer product requirements, A and B positions can be set, realizing the alternate use of A and B positions, significantly improving production efficiency.
Automatic Nail Selection and Delivery Mechanism
The nail selection and delivery mechanism is divided into a vibration disk selection and delivery mechanism and a drum-type selection and delivery mechanism, as shown in Figure 13.

The standard configuration is the drum type. The vibration disk is suitable for special studs, and the drum-type is suitable for ordinary studs.
The automatic nail delivery device consists of a nail selector, a pneumatic nail delivery mechanism, an automatic welding gun, and a nail delivery tube.
It can achieve automatic nail delivery and welding, has high nail delivery reliability, can automatically detect the presence of nails, improves system efficiency and reliability, and has a simple and reasonable design structure that is stable and reliable.
The dedicated nail delivery mechanism has features such as large bearing capacity, low noise, and energy-saving and consumption reduction. The nail specifications range from M3 to M8 (non-standard can be customized).
Automatic Welding Gun Head
As shown in Figure 14, the automatic welding gun head uses a servo motor drive (stroke 150mm) and a precision slide cylinder (direct gun stroke 50mm, oblique gun stroke 150mm) to move the welding gun mechanism.

This ensures that the welding gun head welding height is adjustable within the 0-200mm or 0-300mm range.
The distance between the stud and the sheet metal can be adjusted through the servo motor, and the lifting height of the welding gun mechanism can be adjusted according to the shape of the sheet metal to avoid collisions between the workpiece and the welding gun.
Different welding guns can also be used to fine-tune the gap between the stud and the sheet metal when welding studs of different lengths, ensuring welding speed, and stable, adjustable pressure to accommodate uneven surfaces of the sheet metal.
(1) Precise positioning: Utilizes computer programming control for flexible, convenient, and stable positioning.
(2) High welding quality: Can rapidly and firmly weld studs of various specifications onto metal surfaces, leaving no trace on the back of the welded sheet, and no noticeable depression or protrusion.
(3) Wide material adaptability: Capable of welding cold plates, stainless steel, aluminum plates, galvanized plates, and other materials as shown in Figure 15.

(4) High efficiency: Provides automatic stud feeding and welding, eliminating the need for tedious traditional processes such as drilling, riveting, arc welding, and post-welding treatment. It can weld 25-30 studs per minute, saving time and effort.
(5) CNC programming: Can meet more complex welding scheme requirements.
The CNC Automatic Stud Welding Machine is equipped with a milling cutter gun head independently developed by our company, as shown in Figure 16, enabling “de-coating”, splash prevention, and blow-off functions.

The “de-coating” function is used when processing galvanized plates. Due to the material difference between the surface zinc layer and the inner plate, if not surface-treated, problems such as scorching and false welding will occur during the nailing process, affecting the processing quality and increasing post-processing workload.
Our independently developed “de-coating” technology can avoid these issues.
When users activate the “de-coating” function in the program, the device will automatically use the milling cutter gun head to clean the surface coating, and the “de-coating” depth can be adjusted as needed to ensure the device is applicable to any coating thickness.
This not only makes the processing area more aesthetically pleasing and ensures processing quality but also significantly improves processing efficiency and reduces waste of manpower and materials in post-processing.
The splash prevention function connects the gun head to high-efficiency welding splash prevention fluid to prevent welding splatter oxides from sticking to the parent material due to high temperature, reducing false welding and missed welding, and protecting workers from welding slag injuries.
Before welding, spray the anti-splatter fluid on both sides of the weld seam. The fallen slag significantly reduces, and any remaining slag on the surface can be wiped clean with a cloth, leaving no trace and preventing rust, without affecting subsequent surface painting.
The blow-off function can blow off the iron filings after the milling cutter gun head processing, preventing blowing with mouth or hand cleaning, which can cause iron filings to fly into eyes or cut fingers.
The CNC Automatic Stud Welding Machine has outstanding features and clear advantages, and is widely used in thin sheet stud welding production in fields such as electrical, electronics, boiler, power construction, decoration and home appliances, elevators, automotive industry, shipbuilding industry, and aerospace industry.