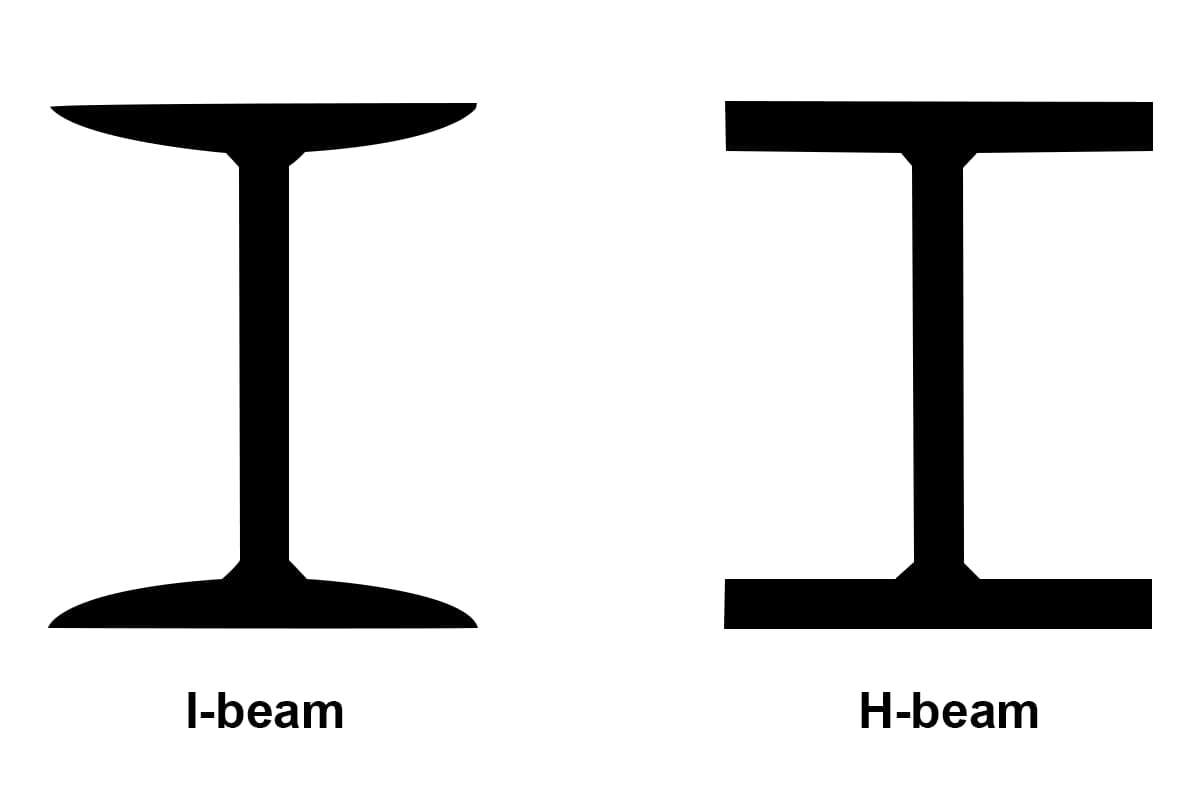
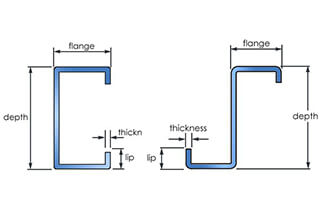
Have you ever wondered what makes modern construction so efficient and durable? This article explores the fascinating world of C-section and Z-section steel purlins, essential building materials that revolutionize construction. Learn how their unique properties and applications can enhance your next project!
As far as the construction site of relevant construction projects is concerned, at present, what everyone should know is about the use of building materials in the current construction market.
There is no doubt that the two most widely used building materials are actually Z-section steel purlin and C-section steel purlin.
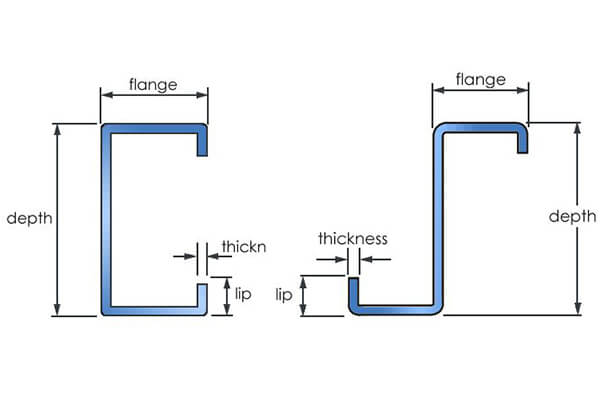
Two types of building materials, Z-section steel and C-section steel, have been developed and put into use in recent years, and Z-section steel and C-section steel have been widely used in the construction industry shortly after they were introduced because of their low carbon and durability.
In the field of the construction industry now involved, there is a very large amount of data on the use of steel in the specific construction process.
In addition, because the current Z-section steel purlin and C-section steel purlin have greatly replaced the status of some more traditional building materials in a certain sense, in fact, this has created a large number of Z-section steel and C-section steel to a certain extent.
| Aspect | C-Section Steel Purlin | Z-Section Steel Purlin |
|---|---|---|
| Included Angle | 90 degrees | 60-75 degrees |
| Mechanical Properties | Different strong and weak axis properties | More balanced mechanical properties |
| Connection to Steel Frame | Usually screw connection; considered as simple support | Often preferred due to better stress distribution |
| Preferred Usage Based on Roof Slope | Preferred for wall purlins and low-slope roofs | Preferred for roofs with large slope |
| Section Modulus on Roof Slope | Slightly lower compared to Z-purlin | Increases symmetrically for larger slopes |
| Choice for Walls | Comparable to Z-purlin | Comparable to C-purlin |
| Continuous Structural Members | Less suitable for overlapping | More suitable due to ease of overlapping |
| Overall Usage | Widely used in various applications | Preferred in specific situations for its advantages |
In order to understand the essential difference between C-section steel purlin and Z-section steel purlin, we need to have a corresponding understanding of C/Z section steel purlin
Next, I will tell you about C-section steel purlin and Z-section steel purlin respectively, and then analyze their essential differences according to the understanding of their use.
The angle between C-shaped steel purlin and Z-shaped steel purlin is different.
The included angle of C-shaped steel purlin is 90 degrees, and the included angle of Z-shaped steel purlin is less than 90 degrees, about 60-75 degrees.
Therefore, the included angle of purlin must be considered in the selection and combined with the corresponding stress knowledge.
Compared with Z purlin, the mechanical properties of the strong and weak axes of C purlin are very different
The connection between C-section steel and steel frame usually adopts screw connection, which must be considered as simple support in the calculation, so the latter is more reasonable in stress, calculation results and structure.
Therefore, in addition to other special processing needs such as door and window openings, Z-shaped steel section shall be preferred, and C-shaped steel shall be preferred for wall purlins and house purlins with small slope;
The roof purlin with large slope shall be Z-shaped.
What kind of purlin should be used in what environment? This is crucial for selecting appropriate building materials.
1. Roof slope considerations:
2. Wall applications:
The choice between Z-shaped and C-shaped purlins for wall girts is relatively interchangeable, with minimal performance differences.
3. Continuous structural members:
Z-shaped steel purlins are recommended for continuous spans due to their ease of overlapping, which simplifies installation and improves structural continuity.
Environmental factors influencing purlin selection:
While Z-shaped purlins offer specific advantages in certain scenarios, C-shaped purlins remain widely used due to their versatility, ease of manufacture, and familiarity among builders. The choice often depends on specific project requirements, local building codes, and design preferences.
In conclusion, understanding these key differences between C and Z steel purlins enables informed decision-making in structural design. Always consult with a structural engineer and adhere to local building codes when selecting and implementing purlin systems.
C-section steel is automatically processed and formed by C-section steel forming machine.
The machine can automatically complete the forming process according to the given size.
C-section steel is processed by hot coil cold bending, with thin wall, lightweight, excellent section performance and high strength.
Compared with traditional channel steel, the same strength can save 30% of materials.
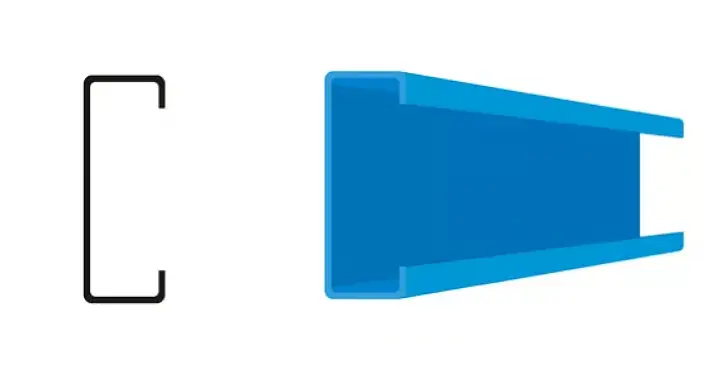
C-section steel, also known as C-channel or C-profile, is a versatile structural element widely utilized in the construction of steel-framed buildings. Its primary applications include purlins and wall girts, where it provides excellent load-bearing capacity and ease of installation. The C-shaped cross-section offers high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for lightweight roof trusses, brackets, and various other building components.
In steel structure design, C-section profiles can be efficiently combined to create composite members with enhanced structural performance. For instance, back-to-back C-sections can form box beams with increased load-carrying capacity and torsional rigidity. This adaptability allows architects and engineers to optimize material usage while meeting specific design requirements.
Beyond construction, C-section steel finds extensive use in mechanical and light industrial manufacturing. Its applications include support columns for conveyor systems, machine frames, and cantilever arms for equipment mounting. The profile’s inherent stiffness and ease of fabrication make it a cost-effective solution for various industrial structures and fixtures.
Moreover, the standardized dimensions and wide availability of C-section steel facilitate modular design approaches, enabling rapid assembly and potential future modifications in both construction and industrial settings.
Discharging ① – leveling ② – forming ③ – setting ④ – straightening ⑤ – length measurement ⑥ – punching the round hole of tie bar ⑦ – punching the elliptical connecting hole ⑧ – forming and cutting ⑨
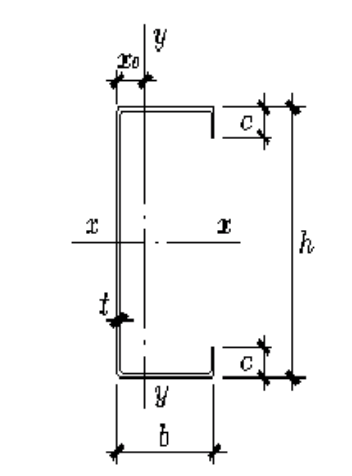
C-shaped steel purlins are divided into five specifications: 80, 100, 120, 140 and 160 according to different heights.
The length can be determined according to the engineering design, but considering the conditions such as transportation and installation, the total length is generally no more than 12m.
Meaning of numbers in each line (take C80×40×20×2.5 as an example):
| Model | Sizes (mm) | Cross-sectional area (cm²) | Weight (kg/m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h | b | c | t | |||
| C80 | 80 | 40 | 20 | 2.25 | 4.29 | 3.37 |
| C80 | 80 | 40 | 20 | 2.50 | 4.75 | 3.72 |
| C80 | 80 | 40 | 20 | 2.75 | 5.19 | 4.08 |
| C80 | 80 | 40 | 20 | 3.00 | 5.64 | 4.42 |
| C80 | 80 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 4.74 | 3.72 |
| C80 | 80 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 5.25 | 4.12 |
| C80 | 80 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 5.74 | 4.51 |
| C80 | 80 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 6.24 | 4.89 |
| C100 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 5.19 | 4.08 |
| C100 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 5.75 | 4.51 |
| C100 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 6.29 | 4.94 |
| C100 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 6.84 | 5.36 |
| C120 | 120 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 5.64 | 4.43 |
| C120 | 120 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 6.25 | 4.90 |
| C120 | 120 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 6.84 | 5.37 |
| C120 | 120 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 7.44 | 5.84 |
| C140 | 140 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 6.09 | 4.78 |
| C140 | 140 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 6.75 | 5.29 |
| C140 | 140 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 7.39 | 5.80 |
| C140 | 140 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 8.03 | 6.31 |
| C140 | 140 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 6.54 | 5.13 |
| C140 | 140 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 7.25 | 5.69 |
| C140 | 140 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 7.94 | 6.23 |
| C140 | 140 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 8.64 | 6.78 |
| C160 | 160 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 6.54 | 5.13 |
| C160 | 160 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 7.25 | 5.69 |
| C160 | 160 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 7.94 | 6.23 |
| C160 | 160 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 8.64 | 6.78 |
| C160 | 160 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 6.99 | 5.49 |
| C160 | 160 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 7.75 | 6.08 |
| C160 | 160 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 8.49 | 6.67 |
| C160 | 160 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 9.24 | 7.25 |
| C160 | 160 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.44 | 5.84 |
| C160 | 160 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.25 | 6.47 |
| C160 | 160 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.04 | 7.10 |
| C160 | 160 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 9.84 | 7.72 |
| C180 | 180 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 6.99 | 5.49 |
| C180 | 180 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 7.75 | 6.08 |
| C180 | 180 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 8.49 | 6.67 |
| C180 | 180 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 9.24 | 7.25 |
| C180 | 180 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.44 | 5.84 |
| C180 | 180 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.25 | 6.47 |
| C180 | 180 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.04 | 7.10 |
| C180 | 180 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 9.84 | 7.72 |
| C180 | 180 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.89 | 6.19 |
| C180 | 180 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.75 | 6.86 |
| C180 | 180 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.59 | 7.53 |
| C180 | 180 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 10.44 | 8.19 |
| C180 | 180 | 80 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.34 | 6.55 |
| C180 | 180 | 80 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.25 | 7.26 |
| C180 | 180 | 80 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.14 | 7.96 |
| C180 | 180 | 80 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.04 | 8.66 |
| C200 | 200 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.44 | 5.84 |
| C200 | 200 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.25 | 6.47 |
| C200 | 200 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.04 | 7.10 |
| C200 | 200 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 9.84 | 7.72 |
| C200 | 200 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.89 | 6.19 |
| C200 | 200 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.75 | 6.86 |
| C200 | 200 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.59 | 7.53 |
| C200 | 200 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 10.44 | 8.19 |
| C200 | 200 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.34 | 6.55 |
| C200 | 200 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.25 | 7.26 |
| C200 | 200 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.14 | 7.96 |
| C200 | 200 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.04 | 8.66 |
| C200 | 200 | 80 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.79 | 6.90 |
| C200 | 200 | 80 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.75 | 7.65 |
| C200 | 200 | 80 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.69 | 8.39 |
| C200 | 200 | 80 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.64 | 9.13 |
| C220 | 220 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 7.89 | 6.19 |
| C220 | 220 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 8.75 | 6.86 |
| C220 | 220 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 9.59 | 7.53 |
| C220 | 220 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 10.44 | 8.19 |
| C220 | 220 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.34 | 6.55 |
| C220 | 220 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.25 | 7.26 |
| C220 | 220 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.14 | 7.96 |
| C220 | 220 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.04 | 8.66 |
| C220 | 220 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.79 | 6.90 |
| C220 | 220 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.75 | 7.65 |
| C220 | 220 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.69 | 8.39 |
| C220 | 220 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.67 | 9.13 |
| C220 | 220 | 80 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.24 | 7.25 |
| C220 | 220 | 80 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.25 | 8.04 |
| C220 | 220 | 80 | 20 | 2.75 | 11.24 | 8.82 |
| C220 | 220 | 80 | 20 | 3.00 | 12.24 | 9.60 |
| C240 | 240 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.34 | 6.55 |
| C240 | 240 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.25 | 7.26 |
| C240 | 240 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.14 | 7.96 |
| C240 | 240 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.04 | 8.66 |
| C240 | 240 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.79 | 6.90 |
| C240 | 240 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.75 | 7.65 |
| C240 | 240 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.69 | 8.39 |
| C240 | 240 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.64 | 9.13 |
| C240 | 240 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.24 | 7.25 |
| C240 | 240 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.25 | 8.04 |
| C240 | 240 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 11.24 | 8.82 |
| C240 | 240 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 12.24 | 9.60 |
| C240 | 240 | 80 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.69 | 7.61 |
| C240 | 240 | 80 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.75 | 8.43 |
| C240 | 240 | 80 | 20 | 2.75 | 11.79 | 9.26 |
| C240 | 240 | 80 | 20 | 3.00 | 12.84 | 10.07 |
| C250 | 250 | 50 | 20 | 2.25 | 8.57 | 6.72 |
| C250 | 250 | 50 | 20 | 2.50 | 9.50 | 7.45 |
| C250 | 250 | 50 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.42 | 8.18 |
| C250 | 250 | 50 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.34 | 8.90 |
| C250 | 250 | 60 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.02 | 7.08 |
| C250 | 250 | 60 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.00 | 7.85 |
| C250 | 250 | 60 | 20 | 2.75 | 10.97 | 8.61 |
| C250 | 250 | 60 | 20 | 3.00 | 11.94 | 9.37 |
| C250 | 250 | 70 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.47 | 7.43 |
| C250 | 250 | 70 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.50 | 8.24 |
| C250 | 250 | 70 | 20 | 2.75 | 11.52 | 9.04 |
| C250 | 250 | 70 | 20 | 3.00 | 12.54 | 9.84 |
| C250 | 250 | 75 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.69 | 7.61 |
| C250 | 250 | 75 | 20 | 2.50 | 10.75 | 8.43 |
| C250 | 250 | 75 | 20 | 2.75 | 11.79 | 9.26 |
| C250 | 250 | 75 | 20 | 3.00 | 12.84 | 10.07 |
| C250 | 250 | 80 | 20 | 2.25 | 9.92 | 7.78 |
| C250 | 250 | 80 | 20 | 2.50 | 11.00 | 8.63 |
| C250 | 250 | 80 | 20 | 2.75 | 12.07 | 9.47 |
| C250 | 250 | 80 | 20 | 3.00 | 13.14 | 10.31 |
Z-section steel is a widely used cold-formed thin-walled structural element, characterized by its distinctive Z-shaped cross-section. Typically manufactured with thicknesses ranging from 1.6mm to 3.0mm and section heights varying between 120mm and 350mm, Z purlins offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio for various structural applications.
The primary materials used in Z purlin production are hot-rolled steel (which may be painted for corrosion protection) and galvanized steel. The latter provides superior corrosion resistance, making it particularly suitable for exposed or high-humidity environments.
Manufacturing processes and quality standards for Z purlins in China adhere to the GB50018-2002 specification, which outlines requirements for cold-formed thin-walled steel structures. This standard ensures consistent quality, dimensional accuracy, and structural integrity across different manufacturers.
Z-section steel finds extensive application in large-scale steel structure facilities, such as industrial warehouses, commercial buildings, and agricultural structures. Its design allows for efficient load transfer and easy installation, contributing to reduced construction time and costs.
Custom fabrication of Z purlins is common practice, with lengths and hole patterns tailored to specific project requirements. Advanced CNC machinery enables precise cutting, punching, and forming operations, ensuring that each purlin meets exact specifications for optimal performance in its intended application.
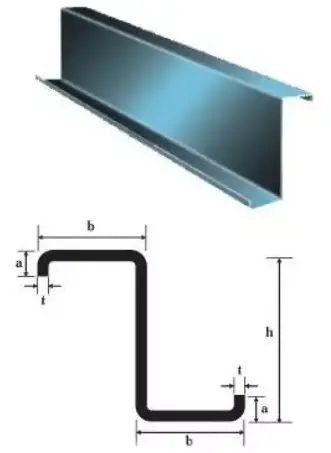
Cold-formed Z-shaped steel profiles offer significant advantages, including customizable specifications, versatile sizing options, and exceptional compressive strength-to-weight ratios. These characteristics make Z-section purlins highly adaptable for a wide range of industrial and construction applications.
Z-section purlins find extensive use across various sectors, including:
Construction and Infrastructure:
Transportation:
Energy and Utilities:
Agriculture:
Industrial and Commercial:
Specialized Applications:
The versatility of Z-section purlins, combined with their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance (when galvanized), makes them an ideal choice for engineers and designers seeking efficient, cost-effective structural solutions across a diverse range of industries and applications.
| No | Item | Model | Unit | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cold Bend Z Section Steel | Z80×40×2.5 | kg/m | 2.947 |
| 2 | Cold Bend Z Section Steel | Z80×40×3.0 | kg/m | 3.491 |
| 3 | Cold Bend Z Section Steel | Z100×50×2.5 | kg/m | 3.732 |
| 4 | Cold Bend Z Section Steel | Z100×50×3.0 | kg/m | 4.432 |
| 5 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z100×40×20×2.0 | kg/m | 3.208 |
| 6 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z100×40×20×2.5 | kg/m | 3.932 |
| 7 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z120×50×20×2.0 | kg/m | 3.835 |
| 8 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z120×50×20×2.5 | kg/m | 4.718 |
| 9 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z120×50×20×3.0 | kg/m | 5.569 |
| 10 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z140×50×20×2.5 | kg/m | 5.11 |
| 11 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z140×50×20×3.0 | kg/m | 6.04 |
| 12 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z160×60×20×2.5 | kg/m | 5.895 |
| 13 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z160×60×20×3.0 | kg/m | 6.982 |
| 14 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z160×70×20×2.5 | kg/m | 6.288 |
| 15 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z160×70×20×3.0 | kg/m | 7.453 |
| 16 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z180×70×20×2.5 | kg/m | 6.679 |
| 17 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z180×70×20×3.0 | kg/m | 7.924 |
| 18 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z200×70×20×2.5 | kg/m | 7.073 |
| 19 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z200×70×20×3.0 | kg/m | 8.394 |
| 20 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z230×75×25×3.0 | kg/m | 9.573 |
| 21 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z230×75×25×4.0 | kg/m | 12.51 |
| 22 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z250×75×25×3.0 | kg/m | 10.04 |
| 23 | Cold Bend Z Purlin Steel | Z250×75×25×4.0 | kg/m | 13.14 |