Have you ever considered how vital clean air is in industrial settings? This article explores the mechanics and benefits of dust collectors, featuring insights from seasoned mechanical engineers. Discover how these devices protect workers’ health and improve efficiency, and learn practical tips for selecting the right system for your needs.
With the increasing global focus on sustainability, environmental protection has become a paramount concern, particularly for industries associated with significant pollution. In recent years, stringent environmental regulations have led to the closure of numerous factories that failed to meet these standards, underscoring the critical importance of effective pollution control measures.
In light of this trend, we will delve into the fundamental working principles of dust collectors, a crucial technology in industrial air pollution control. These systems play a vital role in maintaining air quality within manufacturing facilities and reducing environmental impact. By understanding these principles, engineers and facility managers can make informed decisions about implementing and optimizing dust collection systems.
Furthermore, in upcoming articles, we will explore practical case studies demonstrating the application of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in managing various dust collector systems within industrial settings. These real-world examples will illustrate how advanced control systems can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of dust collection processes, potentially leading to improved environmental performance and regulatory compliance.
We encourage industry professionals, environmental engineers, and those involved in factory operations to stay tuned for this valuable information. The insights provided will be instrumental in navigating the complex landscape of environmental regulations while maintaining productive and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Dust collectors can be categorized based on various criteria, including their operational principles, installation configurations, and the presence or absence of liquid in the dust removal process.
Each type of dust collector offers specific advantages and is selected based on factors such as particle size distribution, gas stream properties, collection efficiency requirements, and operational conditions. The choice of dust collector significantly impacts the overall performance and efficiency of air pollution control systems in industrial processes.
A dust collector system comprises several key components, each playing a crucial role in the efficient removal of particulate matter from industrial air streams. The main components include:
(1) Capture Separation Process
① Capture and Transition Stage: Dust Concentration
In this initial phase, dust particles, initially dispersed or suspended in the carrier medium, enter the dust removal chamber of the collector. External forces act upon these particles, directing them towards the separation interface. As the dust migrates, its concentration increases progressively, preparing it for efficient solid-gas separation.
② Separation Phase:
As the high-concentration dust flow reaches the separation interface, two primary mechanisms come into play:
Firstly, the carrier medium’s dust-carrying capacity approaches its limit. The balance between dust suspension and sedimentation shifts predominantly towards sedimentation, facilitating the separation of dust from the carrier medium through gravitational settling.
Secondly, within the high-concentration dust flow, particle behavior transitions from diffusion to agglomeration. Particles tend to coalesce with each other or adhere to and be adsorbed by the medium interface, further enhancing separation efficiency.
(2) Dust Extraction Process
Post-separation, the concentrated dust particles are channeled through the designated dust outlet for collection or further processing.
(3) Exhaust Process
The purified air stream, now substantially free of particulate matter, is discharged via the exhaust port, completing the dust removal cycle.
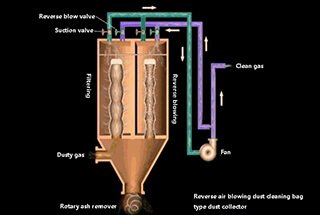
A bag filter is a type of dust removal equipment based on the filtration principle. It uses organic or inorganic fiber filter cloth to filter out dust in the gas.
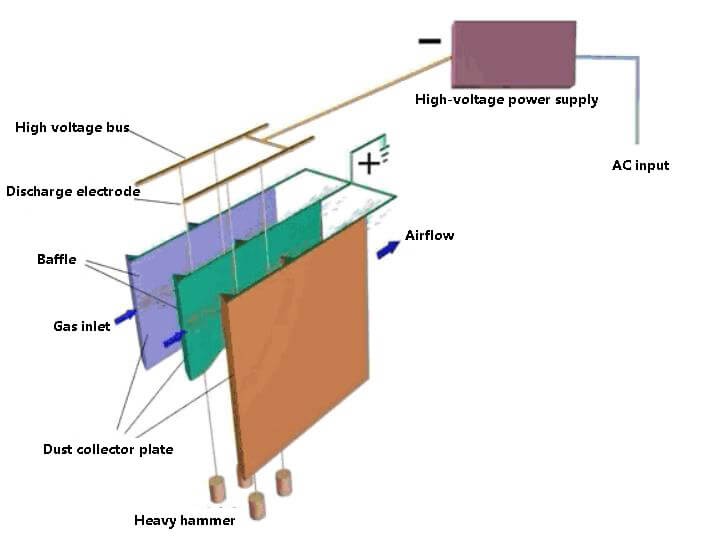
The structure of a pulse jet dust cleaning bag filter is composed of an upper box, a middle box, a lower box, and a control valve. The dust-containing gas enters the middle box of the bag type dust collector through the air inlet and into the cloth bag from outside the bag.
The dust is blocked on the surface outside the filter bag, and the purified air enters the bag, then enters the upper box from the upper part of the cloth bag, and finally is discharged by the exhaust pipe.
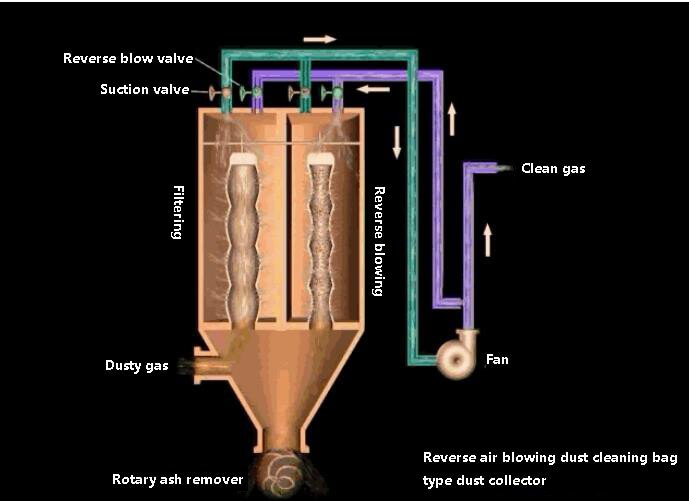
To prevent the filter bag from being sucked and deflated during filtration, a support frame is set in the filter bag. The pulse valve controls the pulse to eject high-speed and high-pressure air flow into the filter bag, causing the filter bag to expand and contract sharply, creating shock and vibration.
Part of the dust attached outside the bag falls into the lower ash bag by gravity, and part of it is blown down by the instantaneous air flow from inside to outside and enters the ash hopper. Finally, it is discharged through the dust discharge valve.
This type of dust collector can clean ash without stopping the air.
It is mainly used to separate particulate and fine dust from industrial waste gas and is widely used in industries such as metallurgy, mining, cement, thermal power plants, building materials, casting, chemical industry, tobacco, asphalt mixers, grain, machining, and boiler dust removal.
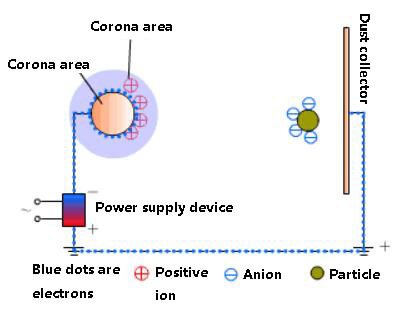
The working principle of an electrostatic precipitator air purifier involves using a high-voltage DC electric field to ionize gas molecules in the air, producing a large number of electrons and ions that move to the two poles under the action of electric field force.
As these charged particles move, they encounter dust particles and bacteria in the air flow and charge them. The charged particles move to the polar plate with opposite charges under the action of electric field force. Under the action of the electric field, free ions in the air also move to the two poles.
The higher the voltage and electric field intensity, the faster the movement speed of the ions.
Advantages of electrostatic precipitator:
① High separation efficiency, which can effectively remove particles;
② Large amount of treated gas and low resistance;
③ Suitable for high temperature and corrosive gases;
④ Low operation cost.
Disadvantages:
① High investment cost, huge equipment and large floor area;
② High requirements for equipment manufacturing, installation and maintenance;
③ It is sensitive to the characteristics of dust.
1) Basic types of electrostatic precipitators
An electrostatic precipitator is composed of a precipitator body and a power supply device.
The dust collector body includes a discharge electrode, a dust collection electrode, an air flow distribution device, an ash cleaning mechanism, an insulation device, a shell, and other parts.
① Single zone (stage) electrostatic precipitator
In a single-zone dust collector, the charging and dust collection processes of particles are carried out in the same area, meaning the corona electrode and dust collector are in the same area.
② Double zone (stage) electrostatic precipitator
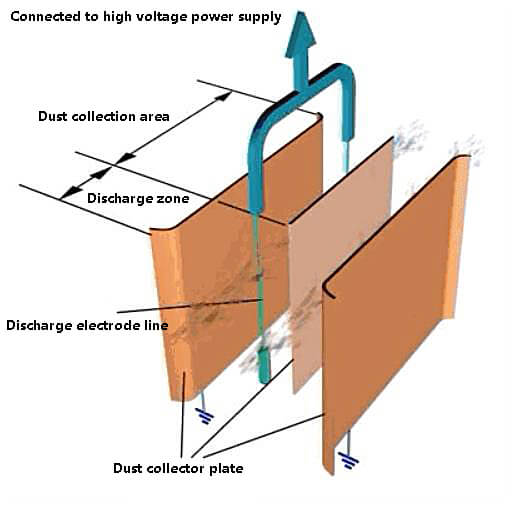
In a double-zone electrostatic precipitator, particle charging and settling dust collection are carried out in two separate areas.
A group of electrodes is installed in the first area to charge the dust particles, and another group of electrodes is installed in the second area to settle and collect the dust particles.
It is mostly used in air conditioning systems.
Mechanical precipitator is a device that uses mechanical force, including gravity, inertia force, and centrifugal force, to separate dust particles from gas.
This type of dust collector mainly includes gravity dust collector, inertial dust collector, and cyclone dust collector.
The mechanical dust removal device is characterized by its simple structure, low cost, convenient use and maintenance, and the ability to handle gas with high particle concentration and large gas volume. It can also adapt to the treatment of high-temperature flue gas.
However, it is generally used for multi-stage dust removal or applications where high dust removal efficiency is not required.
It is also known as a gravity sedimentation chamber.
It is a dust removal equipment that uses the difference in density between dust particles and gas to allow the dust particles to settle and separate naturally from the air flow by the action of gravity.
This is the simplest type of dust removal equipment.
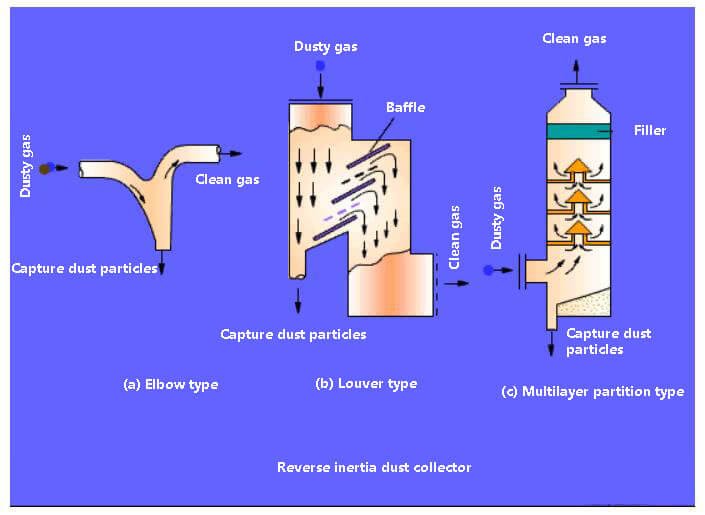
Main features:
The device has a simple structure and low resistance.
Compared to a gravity sedimentation chamber, its dust removal efficiency is higher, but it still falls under the category of a low efficiency dust collector. Generally, it is used for primary dust removal or as the front stage dust removal of a high-efficiency dust collector.
This equipment is suitable for capturing metal or mineral dust with a particle size of more than 10~20µm. However, it is not suitable for cohesive and fibrous dust, as it is prone to blockages.
Due to the explosive nature of dust, there has been an increasing focus on the potential hazards it poses.
As a result, the use of wet dust collectors has also become more prevalent.
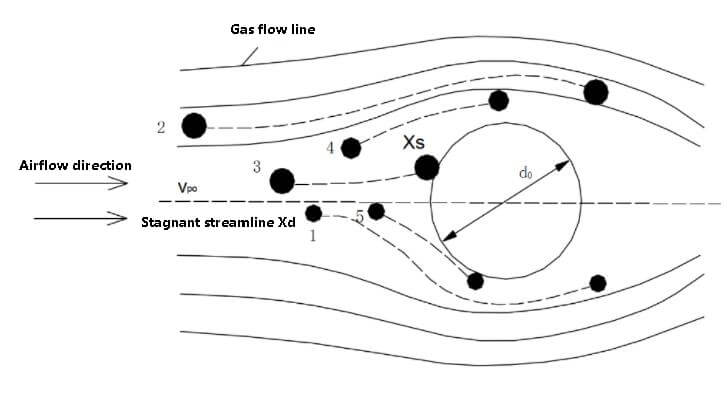
The fundamental principle behind all wet dust collectors is to facilitate the contact and combination of droplets with relatively small dust particles, thereby producing larger particles that are easier to capture.
During this process, dust particles grow in size using various methods, including the combination of larger droplets with dust particles, the absorption of water to increase mass or density, and the formation and growth of condensable particles at lower temperatures in the dust collector.
Wet dust collectors can be categorized based on their structure as follows:
Gravity spray scrubbers are known for their simple structure, low resistance, and ease of operation. However, they have high water consumption, require large equipment and area, and have low dust removal efficiency.
Gravity spray wet dust collectors, such as spray scrubbers, fall into this category.
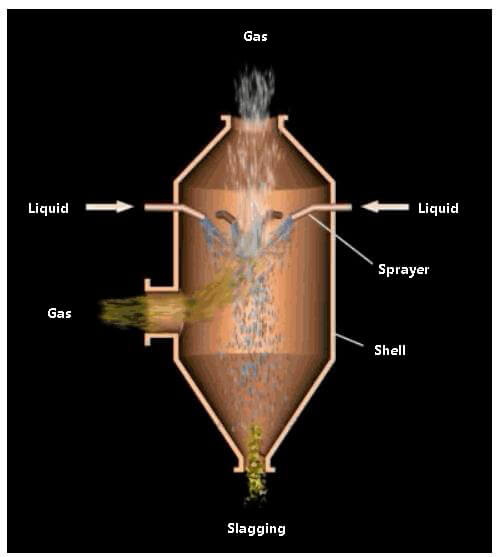
Spray type washing dust collector
The cyclone scrubber is suitable for removing dust particles larger than 5 μm. For the purification of submicron dust, it is often connected in series behind a venturi scrubber to function as a dehydrator for condensed water droplets. The cyclone can also be used to absorb certain gaseous pollutants.
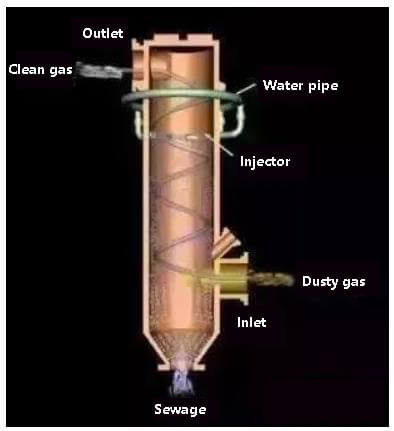
Vertical cyclone water film dust collector
Self-excited dust collectors have the advantages of a compact structure, small footprint, ease of construction and installation, good load adaptability, and low water consumption.
However, they are relatively expensive and can have high pressure loss.
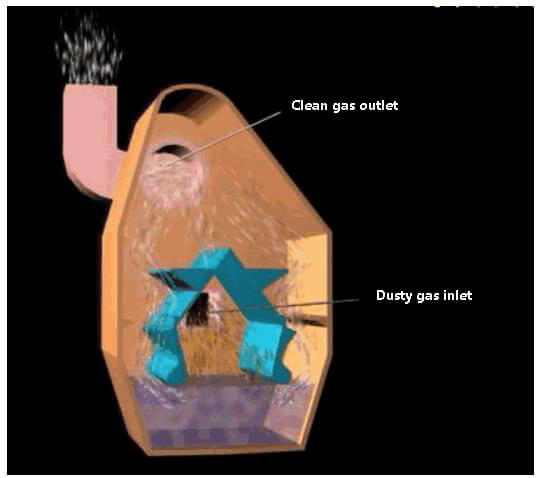
Self excited wet dust collector
Packed wet dust collector, such as packed tower and turbulent ball tower.
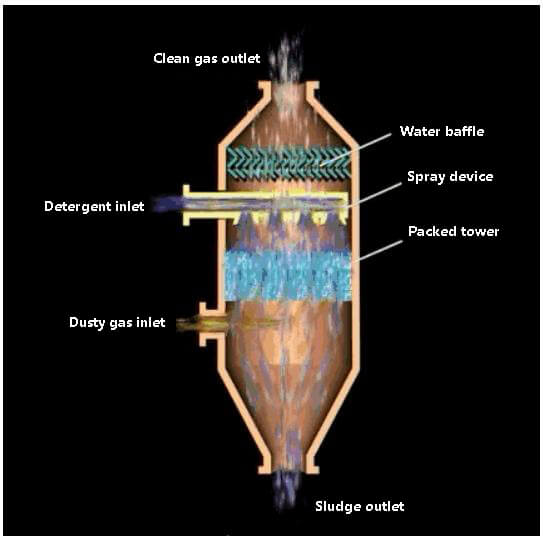
Packed tower
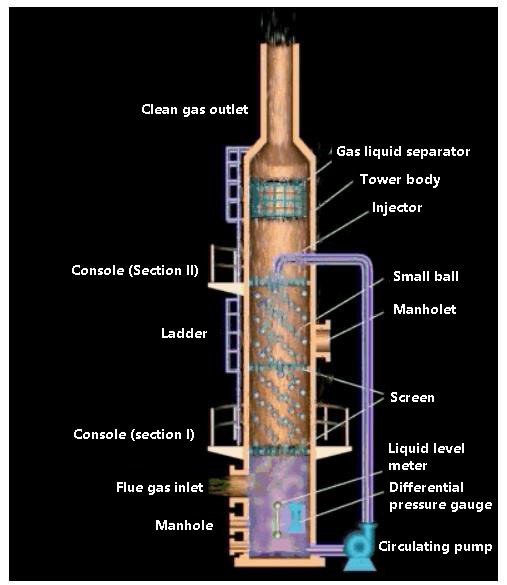
Turbulent ball tower
Foam wet dust remover, such as foam precipitator and cyclone dust trap.
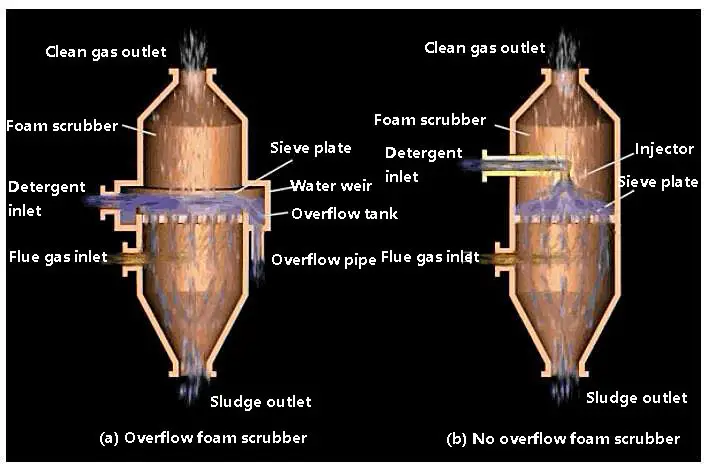
Foam washing dust remover
The venturi scrubber is known for its high dust removal efficiency for fine dust and its ability to cool high-temperature gas.
As a result, it is frequently employed for cooling and dust removal of high-temperature flue gas, such as that generated by iron-making blast furnaces and steel-making electric furnaces. It is also used for the purification of various furnace flue gases in nonferrous smelting and chemical production.
The venturi scrubber has the advantages of a simple structure, small size, flexible layout, low investment cost, but it can result in large pressure loss.
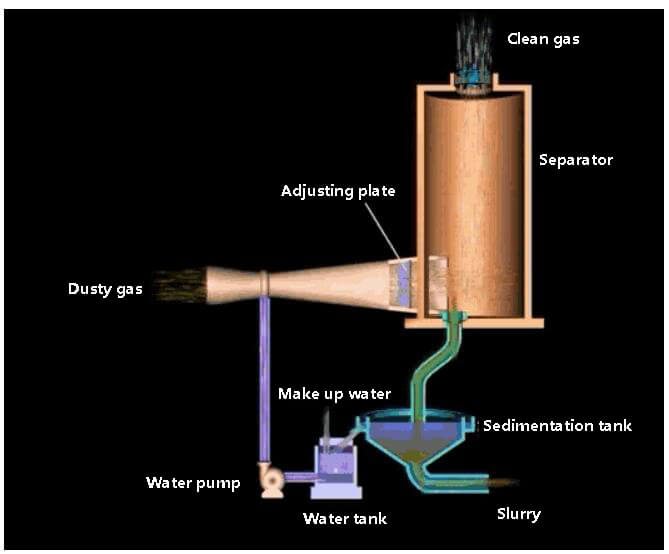
Venturi scrubber