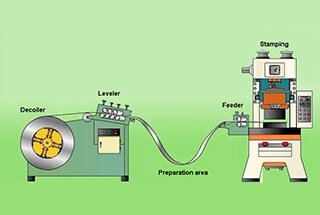
Ever wondered how massive metal parts are shaped with pinpoint precision? Enter the world of the Four-Column Hydraulic Press. This powerful machine uses hydraulic pressure to mold materials like metal and plastic. Discover its inner workings and learn how it revolutionizes manufacturing processes. Ready to explore?

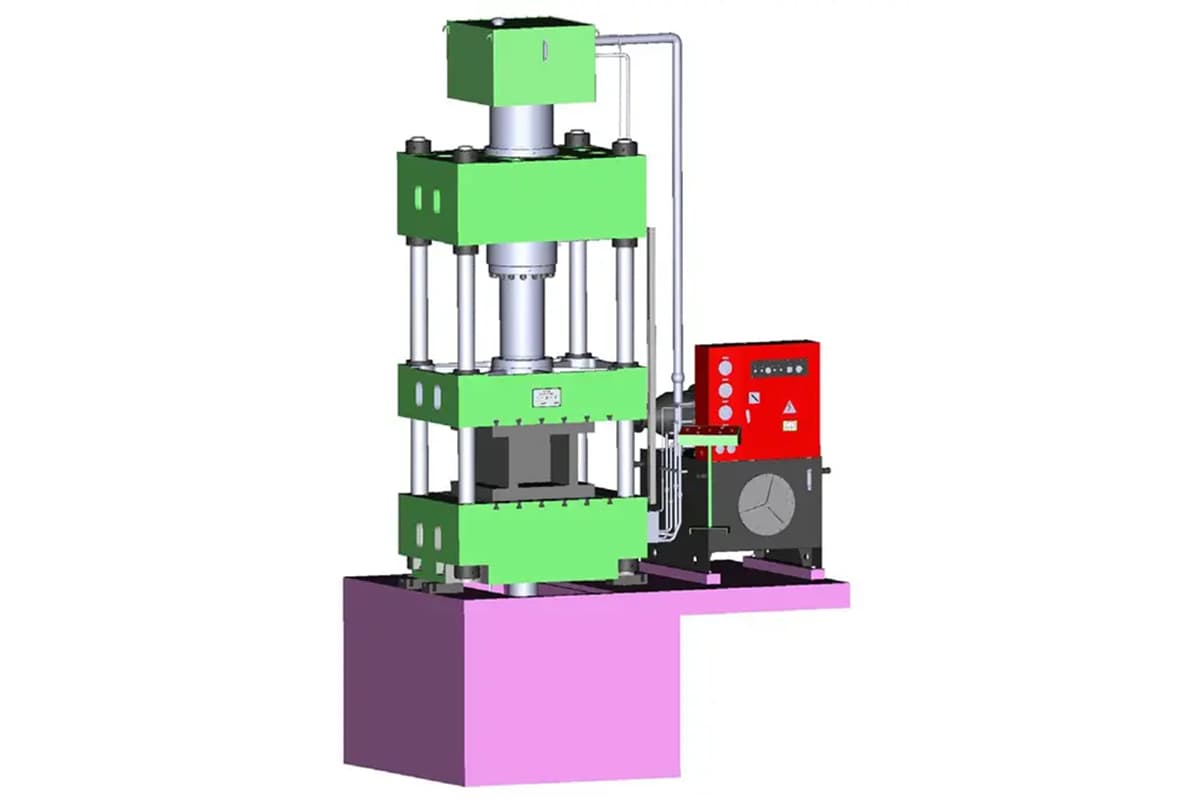
A Four-Column Hydraulic Press is a sophisticated industrial machine designed for precision material forming and processing. This versatile equipment utilizes hydraulic power to generate substantial compressive forces, typically ranging from 20 to 2000 tons or more. The press derives its name from its distinctive structure, featuring four robust cylindrical columns that guide the movement of the upper platen and ensure precise alignment throughout the pressing operation.
See also:
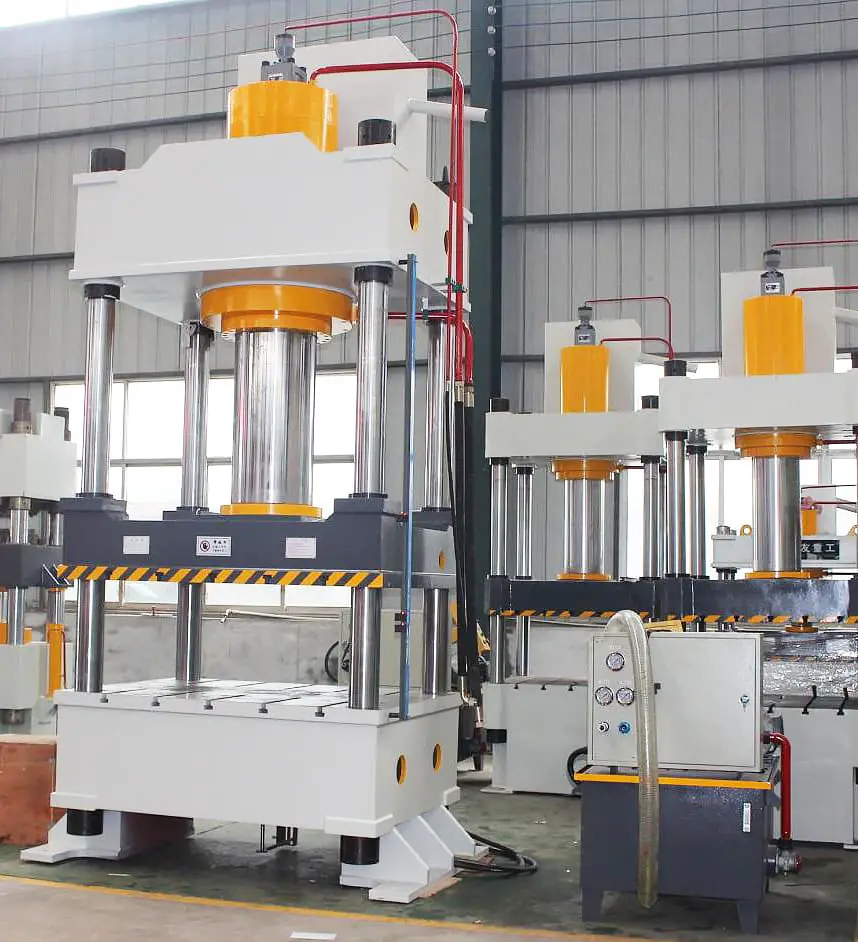

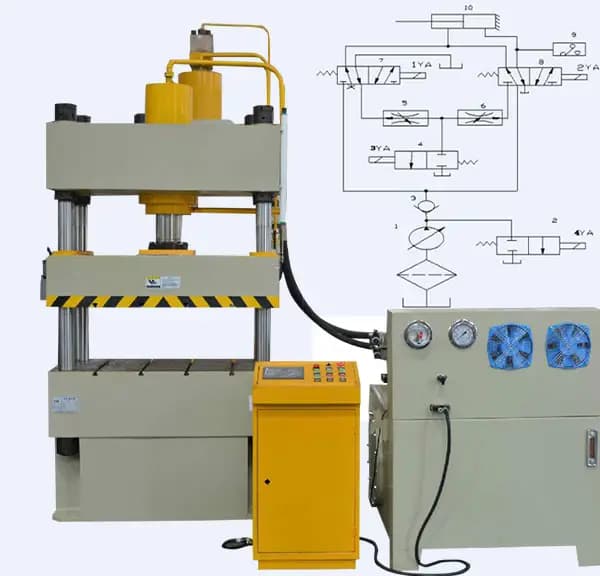
The hydraulic transmission system of a Four-Column Hydraulic Press consists of five key components: the power mechanism, control mechanism, executive mechanism, auxiliary mechanism, and working medium.
The power mechanism, which generates the hydraulic energy, typically employs one or more hydraulic pumps. The selection of pumps depends on the required actuator movement speed and pressure range:
The control mechanism regulates the flow, pressure, and direction of the hydraulic fluid, typically using valves and electronic controls. The executive mechanism, usually comprising hydraulic cylinders, converts hydraulic energy into mechanical force and motion. The auxiliary mechanism includes components such as filters, heat exchangers, and accumulators to maintain system efficiency and longevity. The working medium, typically hydraulic oil, transmits power throughout the system.
The four-column design ensures uniform pressure distribution and maintains parallelism between the ram and the bed, crucial for precision forming operations. This press type excels in various metal forming processes, including:
Beyond metalworking, the Four-Column Hydraulic Press is versatile enough for:
The press’s ability to deliver precise, controlled force over a large area makes it indispensable in modern manufacturing processes where accuracy and repeatability are paramount.
Initially, the hydraulic press used water as its working medium. However, to enhance lubrication and reduce corrosion, a small amount of emulsified oil was added to form an emulsion as the working medium.
Later in the late 19th century, oil presses with mineral oil as the working medium emerged. This type of oil has excellent lubrication properties, resistance to corrosion, and a moderate viscosity, which enhances the performance of the hydraulic press.

During the second half of the 20th century, a new type of water-based emulsion was developed. Unlike the original “oil in water” emulsion, this new form was an “oil in water” emulsion.
The external phase of the “oil in water” emulsion is oil, which offers lubrication and corrosion resistance properties similar to oil. However, its oil content is low, making it less prone to combustion.
Despite its benefits, the cost of the water-based emulsion is relatively high, which has limited its widespread use.
The working medium used in the hydraulic press serves a dual purpose: it not only transmits pressure but also ensures that the machine’s working parts are sensitive, reliable, long-lasting, and have minimal leakage.
The basic requirements for the working medium of the hydraulic press are as follows:
The Four-Column Hydraulic Press, also known as simply the Hydraulic Press, is a machine powered by liquid pressure, which is based on Pascal’s law. There are many different types of hydraulic presses available.
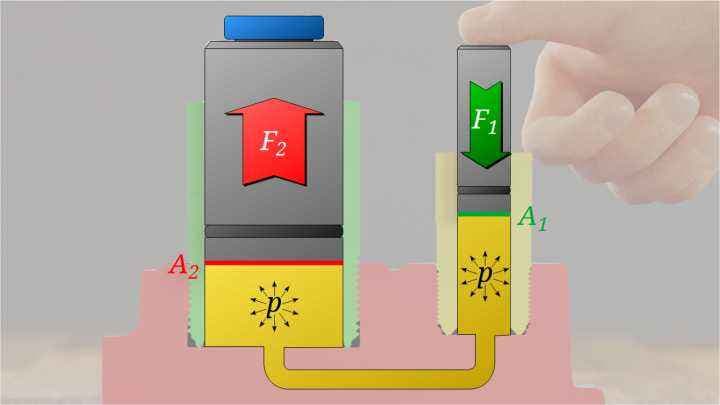
The applications of hydraulic presses vary based on the specific requirements. There are two main types of hydraulic presses based on the type of liquid used for pressure transmission.
The hydraulic press generates a substantial total pressure, making it a common choice for forging and stamping operations.
The forging hydraulic press can be further divided into two types: die forging hydraulic press and free forging hydraulic press. The die forging hydraulic press requires a mold, while the free forging hydraulic press does not.
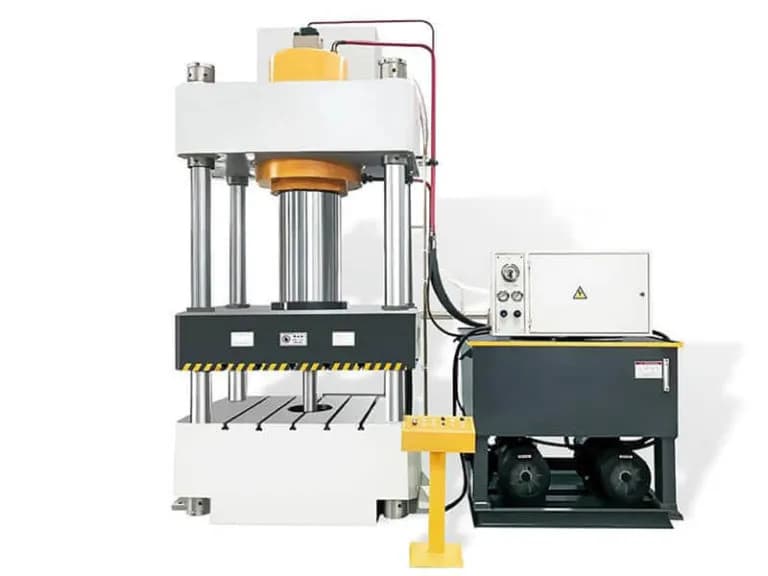

The Four-Column Hydraulic Press is a sophisticated piece of machinery comprising two primary systems: the main structural assembly and the hydraulic control system.
The main structural assembly consists of:
The hydraulic control system includes:
This versatile machine excels in various forming processes, including:
The four-column design offers superior guidance and parallelism compared to C-frame presses, ensuring uniform pressure distribution across the work surface. This makes it ideal for applications requiring high precision and repeatability.
The press features an integrated power unit and a centralized electrical control system. It offers three primary operating modes:
Advanced models may incorporate CNC controls, real-time force monitoring, and data logging capabilities for enhanced process control and quality assurance.
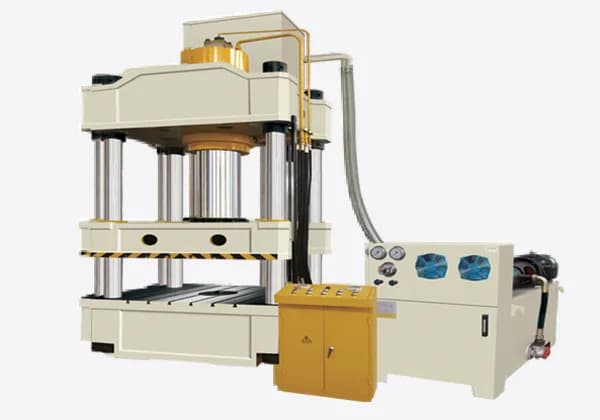

The structural design of hydraulic presses encompasses several configurations, including double column, four column, eight column, welded frame, and multi-layer steel strip winding frame. For medium and small vertical hydraulic presses, a C-frame design is also common.
C-frame hydraulic presses offer enhanced accessibility with three open sides, facilitating ease of operation. However, this design compromises overall structural rigidity. In contrast, welded frame hydraulic presses used for stamping operations provide superior rigidity. These presses feature open front and back sides while maintaining closed left and right sides, striking a balance between accessibility and structural integrity.
In a vertical four column free forging hydraulic press, the oil cylinder is securely mounted in the upper beam. The plunger is rigidly connected to the movable beam, which is guided by the columns and translates vertically in response to hydraulic pressure. The press incorporates movable worktables that can traverse horizontally. The upper and lower anvils are installed beneath the movable beam and on the working table, respectively. The frame, composed of upper and lower beams and columns, bears the working forces generated during operation.
For larger and medium-sized free forging hydraulic presses utilizing pump accumulator systems, a three-cylinder configuration is typically employed to achieve three-stage working force capabilities. This design enhances versatility and power modulation. The main working cylinder is complemented by a balance cylinder and a return cylinder, which apply upward forces to facilitate controlled movement and cycle completion.
These advanced structural designs and hydraulic systems enable precise force control, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced productivity in various metal forming and forging applications.
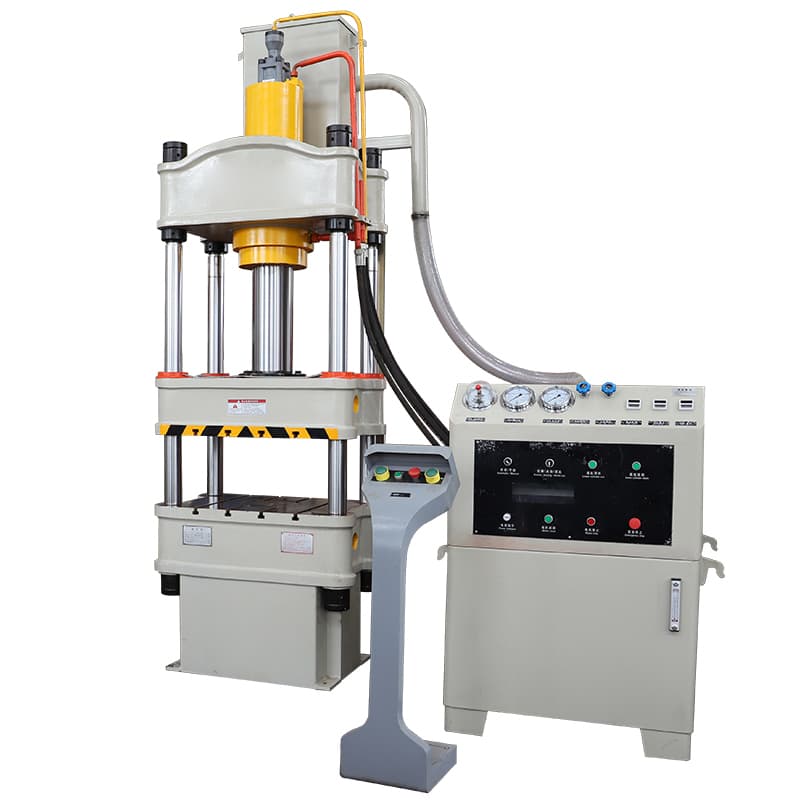

The four column hydraulic press is equipped with an independent power system and electrical control unit, offering centralized button control for three operational modes: adjustment, manual, and semi-automatic. The press allows for precise customization of working pressure, pressing speed, stroke length, and the range of no-load rapid descent and deceleration to meet specific pressing process requirements. Additionally, the machine is capable of performing ejection processes.
The press features three process modes: standard pressing, ejection, and drawing, each with two process control options: constant pressure and constant stroke. The constant pressure forming process includes programmable ejection delay and automatic retraction post-pressing.
At the heart of the machine’s control system is a state-of-the-art PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), ensuring high-precision operations. The mobile work platform is driven by a frequency conversion controller, enhancing energy efficiency and speed control. The YH25-315D “T” type moving action platform represents an advanced design, significantly improving the automation capabilities of the hydraulic press series, boosting production capacity, and reducing operator fatigue.
Utilizing hydraulic fluid as an energy transfer medium, the press incorporates an advanced master-slave cylinder hydraulic circuit, which contributes to superior thermal management with low oil temperatures. The press achieves impressive performance metrics:
The structural design of the press features a robust four-column, three-plate configuration. Vertical accuracy of the movable plate is maintained by four precision guide sleeves. This design ensures exceptional parallelism between the upper and lower working faces, with a maximum deviation of less than 0.08 mm at any point, guaranteeing high-precision forming operations.
There are numerous types of hydraulic presses available in the market, each designed to be suitable for processing different parts and materials.
Many large-scale material processing and metal material production facilities now commonly use the four column hydraulic press because it is cost-effective and user-friendly.
So, what are the advantages of the Four-Column Hydraulic Press?
The pressure generated by the Four-Column Hydraulic Press is stable, which reduces die wear and leads to more precise product formation under numerical control. The forgings produced are of high quality, with minimal flash and small tolerances, resulting in high accuracy.
This hydraulic press allows for less cutting processing and eliminates the need for additional turning, milling, and planing processes. For instance, the tooth shape of cylindrical gears and bevel gears can be directly formed and produced.
The motor of the hydraulic press is digitally controlled, and the user can input simple displacement and speed parameters to achieve intelligent flexible process curve numerical control. This eliminates the need for the user to compile the process curve, making it extremely convenient to use.
Pressure numerical control ensures that the mold will not be overworked, worn, or damaged.
The Four-Column Hydraulic Press has several energy-saving features, including no clutch friction energy consumption, no flywheel idle energy consumption, and the high efficiency of the motor. These features make the servo press both efficient and energy-saving.
The equipment of the Four-Column Hydraulic Press does not have any wearing parts, making it more durable. The motor rotor does not have windings, conductors, or permanent magnets, making it stronger than a permanent magnet servo motor. It is solid and reliable, as well as resistant to impacts. The maintenance-free equipment saves maintenance personnel and reduces the amount of time required for maintenance.
The body of the Four-Column Hydraulic Press is equipped with a tonnage meter that allows for the adjustment and testing of the mold under pressure control. The mold can be adjusted slowly and without stopping the machine, eliminating the need for special mold adjustment and test equipment and personnel. This saves on mold adjustment labor and reduces the amount of time required for the task.
The operation of the Four-Column Hydraulic Press is controlled by high-speed computer intelligence, allowing for full automation without the need for manual operation.

For typical parts such as automobile engine brackets and radiator brackets, hydroformed parts are 20% to 40% lighter compared to stamped parts. For hollow stepped shaft parts, the weight reduction can be as much as 40% to 50%.
Hydroforming parts typically only require one set of dies, while stamping parts often require multiple sets of dies. For example, the number of hydroformed engine carrier parts can be reduced from 6 to 1, and the number of radiator bracket parts can be reduced from 17 to 10.
For example, with the radiator bracket, the heat dissipation area increased by 43%, the number of solder joints was reduced from 174 to 20, the number of processes was reduced from 13 to 6, leading to an increase in productivity by 66%.
For instance, the rigidity of the radiator bracket formed through hydroforming can be increased by 39% in the vertical direction and 50% in the horizontal direction.
According to statistical analysis of hydroforming parts in use, the production cost of hydroformed parts is 15% to 20% lower compared to stamped parts, and the cost of dies is 20% to 30% lower.


Common faults and maintenance techniques for four-column hydraulic presses: Precision parts often feature in the hydraulic transmission system.
While hydraulic transmission in machinery is known for its convenience and labor-saving benefits, it is also prone to damage.
The main cause of this is a lack of understanding of its working principle and structural characteristics, resulting in an inadequate understanding of preventative maintenance techniques.
There are three primary factors that contribute to problems in the hydraulic system: contamination, overheating, and air ingress.
These three factors are closely related and can lead to additional problems if any one of them occurs.
Practice has shown that 75% of the issues in the four-column hydraulic press system can be attributed to these three factors.
The cleanroom should have clean floors, closed doors and windows, and maintain a temperature of approximately 20°C.
Other common maintenance:
After identifying the characteristics of the oil used, such as viscosity, density, vapor pressure, air solubility, bulk modulus, anti-combustibility, temperature range, pressure range, lubricity, and compatibility, and selecting or equipping the hydraulic oil based on specific requirements, the issue of the working medium in the hydraulic system can be resolved.
However, improper usage can still alter the properties of the oil. For instance, it is commonly believed that the viscosity of oil at a certain temperature and pressure is constant, regardless of activity. In reality, the viscosity of the oil will significantly decrease after excessive shearing.
For hydraulic oil that has been in use for an extended period, the temperature range is determined by its oxidation and thermal stability.
Therefore, the hydraulic oil should be stored, transferred, and filled at a temperature below its initial oxidation temperature for a long time, and prevent contamination during storage, transfer, and filling.
Regular sampling and inspection of the oil should be conducted and a regular oil change schedule established.
Ensure adequate oil storage in the tank to facilitate heat dissipation in the hydraulic system and maintain the system’s sealing.
Immediately clean up any leaks that occur.

Common faults and protection techniques for four-column hydraulic presses: Precision parts often feature in the hydraulic transmission system.
While hydraulic transmission in machinery is known for its convenience and labor-saving benefits, it is also prone to damage.
This is due to a lack of understanding of its operating principle and structural characteristics, resulting in an inadequate understanding of how to prevent and protect it.
The hydraulic system has three primary factors that contribute to problems: contamination, overheating, and air ingress.
These three factors are closely related and can lead to additional problems if any one of them occurs.
Practice has shown that 75% of the issues in the hydraulic system can be attributed to these three factors.
Action failure
Sliding block crawling
Downward with pressure
Troubleshooting: adjust the pilot valve and use the pressure no more than 1MPa.
Cylinder port (or piston) seal ring leaks oil
Troubleshooting: check the sealing ring and replace it if damaged.
Troubleshooting: adjust the pressure value
Troubleshooting: check valve port and re fit
There is air in the oil passage of the pressure gauge.
Troubleshooting: loosen the connector to bleed when pressing up.
Troubleshooting: check whether the pipeline is loose, and if it is loose, clamp it firmly.
Troubleshooting: replace the pressure gauge.
Pressure compensation variable pump flow is too small.
Troubleshooting: adjust according to the requirements of the oil pump.
Troubleshooting: if the oil output from the oil drain of the oil pump is greater than 4L / min, it should be removed for maintenance.
Troubleshooting: check the corresponding links of each part.
Pressure drop
Troubleshooting: check whether the sealing fastener of the corresponding valve is damaged, and replace it if damaged.
Repair and weld the leaking pipeline and check whether the pressure commissioning is normal.
Troubleshooting: replace the sealing ring.
The above information provides a general overview of the situation. When a fault is identified during actual use, it is important to first analyze the cause before conducting any troubleshooting steps.

In China, the selection of a hydraulic press should be based on the nature of the production process, batch size, mold conditions, accuracy requirements, and other factors due to the variety of hydraulic press models and their differing levels of stiffness, accuracy, and usage methods.
The four-column hydraulic press is a widely used piece of equipment in industrial production, but it can be difficult to find a high-cost-effective option.
For those who frequently use and operate a four-column hydraulic press, it can be challenging to find a suitable piece of equipment.
It is recommended that purchasing partners determine their specifications based on their actual needs and follow the following principles:
① Before making a purchase, it is important to determine the shape and raw materials to be pressed, the desired output, and any special requirements for the four-column hydraulic press. The manufacturer should then be consulted to provide the appropriate model.
② When choosing a four-column hydraulic press, it is important to ensure that the pressure is adequate to improve the equipment’s lifespan and support future development. The nominal pressure should be higher than the actual working pressure.
③ The output of the four-column hydraulic press is not only dependent on the model, but also on the hydraulic system of the equipment. A fast system is important.
④ The stroke of the four-column hydraulic press should be sufficient to accommodate the size of the molded product and allow for easy removal from the mold.
The quality of a four-column hydraulic press not only impacts its lifespan, but also affects production efficiency.
After determining the desired equipment model, it is advisable to reach out to multiple companies to gather information on hydraulic press prices, parameters, delivery methods, and other relevant details.
It is also recommended to visit the processing factory for an on-site investigation to assess the production scale, actual processing capacity, and the company’s technical capabilities in order to determine the quality of the equipment being produced.
(1) The appearance design of the four-column hydraulic press should be reasonable, with a uniform and smooth paint job and a smooth surface without pitting.
(2) During equipment testing, check for any abnormal noises or mechanical vibrations.
Test the pressure effect of the four-column hydraulic press and ensure that it operates smoothly during the test run.
See also:
Many people do not have a clear understanding of the four-column hydraulic press. Installation and commissioning are crucial for the performance and efficiency of the equipment.
It’s important not to sacrifice after-sales service in the pursuit of a low price or assume that it is included with a high-priced piece of equipment. It should be specified in the contract as a separate clause.
When considering purchasing a hydraulic press, in addition to evaluating the aforementioned factors, it’s important to provide the press supplier with detailed requirements for performance, including safety, maintainability, installation cycle, and cost.
For the manufacturer, the key considerations include: production cycle, budget, mold design, workpiece structure, number of mold changes, external dimensions of the press, and the purpose of the project.
The advancement of science and technology highlights the importance of keeping close contact and communication with various hydraulic machinery manufacturers in order to make an informed and wise decision. This is the best way to ensure the selection of a high-quality hydraulic press.