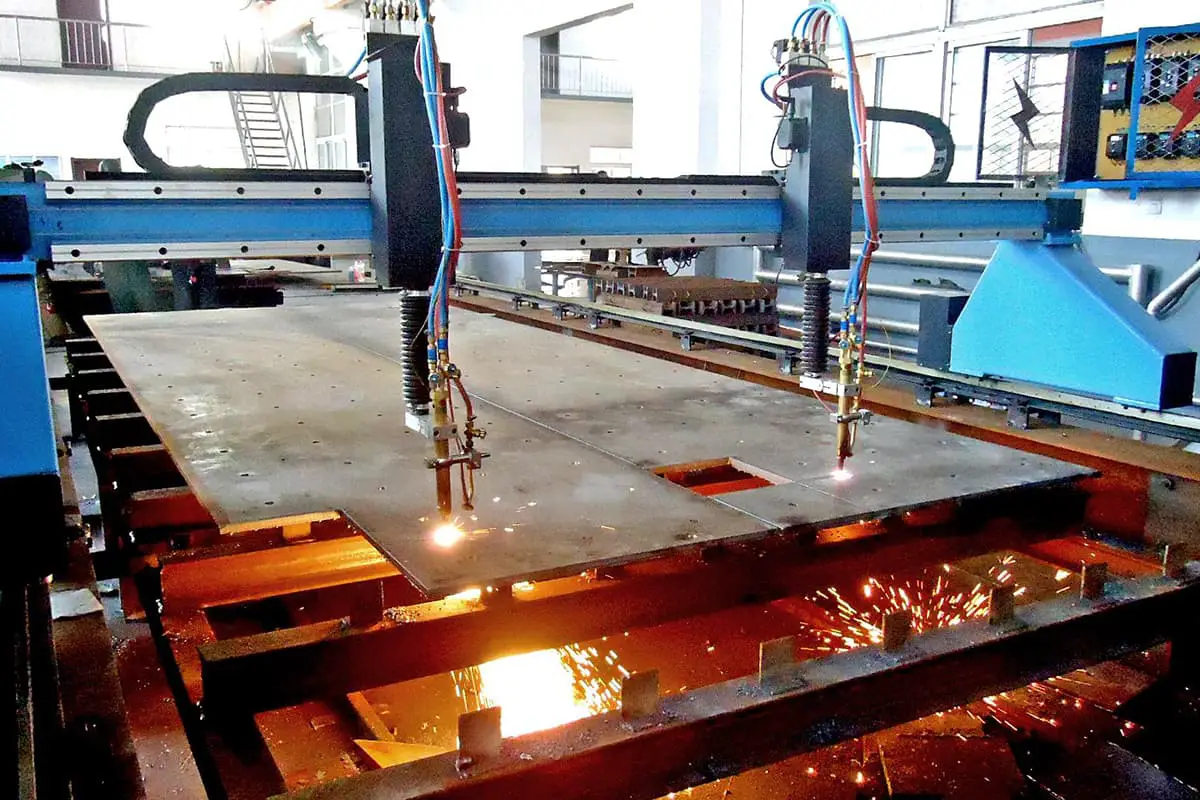
Cutting metal efficiently and cost-effectively is crucial in manufacturing. But which method should you choose: gas or plasma cutting? This article breaks down the costs, efficiency, and quality of each technique, offering a clear comparison to help you make an informed decision. By the end, you’ll understand the financial and operational impacts of both methods, ensuring you select the best option for your needs.

| Sheet Thickness(mm) | 16 | 18 | 20 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 50 |
| Use Probability(%) | 14 | 9 | 12 | 27 | 9 | 13 | 15 | 1 |
Analysis of plate thickness usage reveals that 50mm sheets have a very low utilization rate, primarily confined to frame construction. Cutting 50mm plates requires a 600A plasma power supply, which comes at a significant cost premium compared to the 440A alternative (850,000 CNY vs. 630,000 CNY).
Given the low usage rate of 50mm plates and the substantial price difference between 600A and 440A plasma systems, it is recommended to opt for the 440A plasma equipment. This decision balances capability with cost-effectiveness, aligning with the workshop’s actual cutting requirements.

Current Equipment Status:
Equipment Upgrade Options:
Despite a marginal price difference of 80,000 CNY, investing in new equipment is recommended for several reasons:
Furthermore, the new equipment would complement the existing 2013 CNC plasma/flame cutter, providing redundancy and increased capacity for the workshop. This strategic investment aligns with industry best practices for maintaining competitive manufacturing capabilities and ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
The cutting speed in metal fabrication processes is inversely proportional to the sheet thickness, with thicker materials requiring slower cutting speeds to maintain quality and precision. This relationship is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring consistent cut quality across varying material thicknesses.
Based on comprehensive analysis of cutting speeds across different sheet thicknesses, the following average speeds have been determined:
1. CNC Flame Cutting: Approximately 320 mm/min
2. CNC Plasma Cutting: Approximately 1800 mm/min (for 440A plasma system)
It’s important to note that these speeds are averages and can vary based on factors such as:
For optimal efficiency, fabricators should consider these average speeds as benchmarks, adjusting parameters based on specific job requirements and regularly calibrating their equipment to maintain peak performance.
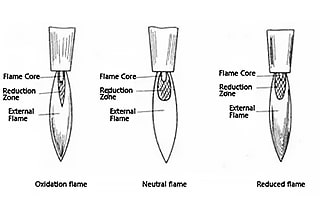
Both CNC flame cutting and plasma cutting can meet the requirements for surface smoothness, but they differ in dimensional accuracy and edge quality.
Flame cutting typically achieves a dimensional accuracy of ±2mm, with difficulties in consistently attaining ±1mm tolerance. The kerf (cut width) is generally wider compared to plasma, but the cut edge exhibits minimal bevel or inclination, satisfying most structural steel fabrication requirements.
Plasma cutting, on the other hand, offers superior dimensional accuracy. While the maximum error can reach 2mm, fine-tuning process parameters (such as cutting speed, amperage, and torch height) allows for relatively easy achievement of ±1mm tolerance. This precision makes plasma cutting advantageous for applications requiring tighter tolerances.
However, plasma cutting tends to produce a more pronounced bevel angle on the cut edge, especially in thicker materials. For instance, when cutting 50mm thick plates, the edge inclination often exceeds acceptable limits for precision fabrication. In contrast, 30mm thick plates typically meet inclination requirements, demonstrating the thickness-dependent nature of plasma cut quality.
The choice between these methods depends on specific project requirements:
Ultimately, the selection should balance factors including material thickness, required tolerances, production volume, and downstream fabrication processes to optimize overall manufacturing efficiency and quality.
The hourly usage cost in continuous cutting mode:
Electricity usage 55 degrees 60 CNY + main consumable parts cost 120 CNY + other consumable usage costs 2.4 CNY + air 6 cubic meters 6 CNY + oxygen 5 cubic meters 18 CNY + dust removal 2.2 degrees of electricity 2.42 CNY = hourly usage cost 209.42 CNY.
| Project | Electricity Cost | Wear Parts | Air | Oxygen | Others | Dust Removal | Total |
| Amount | 60 | 120 | 6 | 18 | 2.4 | 2.42 | 209.42 |
Cost per hour in continuous uninterrupted cutting mode:
Propane CNY30 + Oxygen CNY56 + Electricity usage (3 units) CNY3.3 + Consumable components CNY3 = CNY92.3.
| Project | Electricity Fee | Propane | Oxygen | Fragile Parts | Total |
| Amount | 3.3 | 30 | 56 | 3 | 92.3 |
Note: The plasma cutting speed is 5.62 times that of flame cutting, and the cost is 2.27 times that of the flame.
Considering that most workpieces can be cut with a dual torch using CNC flame cutting, the efficiency of plasma is 2.81 times that of dual-torch flame cutting.
The cost of flame dual-torch cutting for continuous operation for one hour is 184.6 CNY, while plasma is 209.42 CNY.
According to the company’s standard working hour quota, the labor cost for a CNC cutting worker working continuously for one hour is 18 CNY.
| Equipment Price | 750000 (Plasma) | 170000 (Dust Removal Equipment) | |
| Residual Value Rate (0.95) | 712500 | 161500 | |
| Annual Depreciation Cost | 59375 | 13458 | |
| Monthly Depreciation Cost | 1979 | 1122 | |
| Daily Depreciation Cost | 66 | 37 | |
| Hourly Depreciation Cost | 8 hours | 8.25 | 4.67 |
| 16 hours | 4.13 | 2.31 | |
| Equipment Price | 190000(Flame) | |
| Salvage Value Rate (0.95) | 180500 | |
| Annual Depreciation Cost | 15041 | |
| Monthly Depreciation Cost | 1253 | |
| Daily Depreciation Cost | 42 | |
| Hourly Depreciation Cost | 8 hours | 5.2 |
| 16 hours | 2.6 | |
| Plasma | Amount | Flame | Amount |
| Electricity Cost | 60 | Electricity cost | 3.3 |
| Fragile Parts | 120 | Vulnerable parts | 3 |
| Air | 6 | Propane | 30 |
| Oxygen | 18 | Oxygen | 56 |
| Others | 2.4 | Labor | 18 |
| Dust Removal | 2.42 | ||
| Labor | 18 | ||
| Equipment Depreciation | 12.92 | Equipment Depreciation | 5.2 |
| Total | 239.74 | Total | 115.5 |
From the above table, it can be concluded that the total cost for one hour of continuous operation is 239.74 CNY for the plasma process, and 115.5 CNY for the CNC flame process.
Appendix: A comparison of time and cost between plasma and flame cutting for a framework.
| Item | Time (min) | Amount (CNY) | |
| Plasma Cutting | 76 | 297.8 | |
| CNC Flame Cutting | Single torch | 316 | 598.3 |
| Double torch | 158 | 299.2 | |
Chassis and Frame Production Capacity Estimation Table
| Chassis | Flame Cutting | 6.5 hours/set | 20 sets/month | 8×26=208h | 62.5% |
| Plasma Cutting | 1.2 hours/set | 11.5% | |||
| Framework | Dual Torch Flame Cutting | 2.63 hours/set | 100 sets/month | 126% | |
| Plasma Cutting | 1.57 hours/set | 75.5% |
Appendix
Comparison of Typical Sheet Thickness Between Plasma and Flame Cutting
| Plate Thickness (mm) | Speed (mm/min) | Cost (CNY/Meter) | Cutting Quality | ||
| 16 | Plasma | 3200 | 1.25 | Good(0.84) | |
| Flame | Single Torch | 400 | 4.81 | Good | |
| Double Torch | 800 | 4.80 | Good | ||
| 25 | Plasma | 2800 | 1.43 | Average(1.3) | |
| Flame | Single Torch | 320 | 6.0 | Good | |
| Double Torch | 640 | 6.0 | Good | ||
| 30 | Plasma | 2650 | 1.51 | Average(1.57) | |
| Flame | Single Torch | 300 | 6.40 | Good | |
| Double Torch | 600 | 6.39 | Good | ||
| 50 | Plasma | 700 | 5.71 | Poor(2.62) | |
| Flame | Single Torch | 200 | 9.60 | Good | |
| Double Torch | 400 | 9.56 | Good | ||