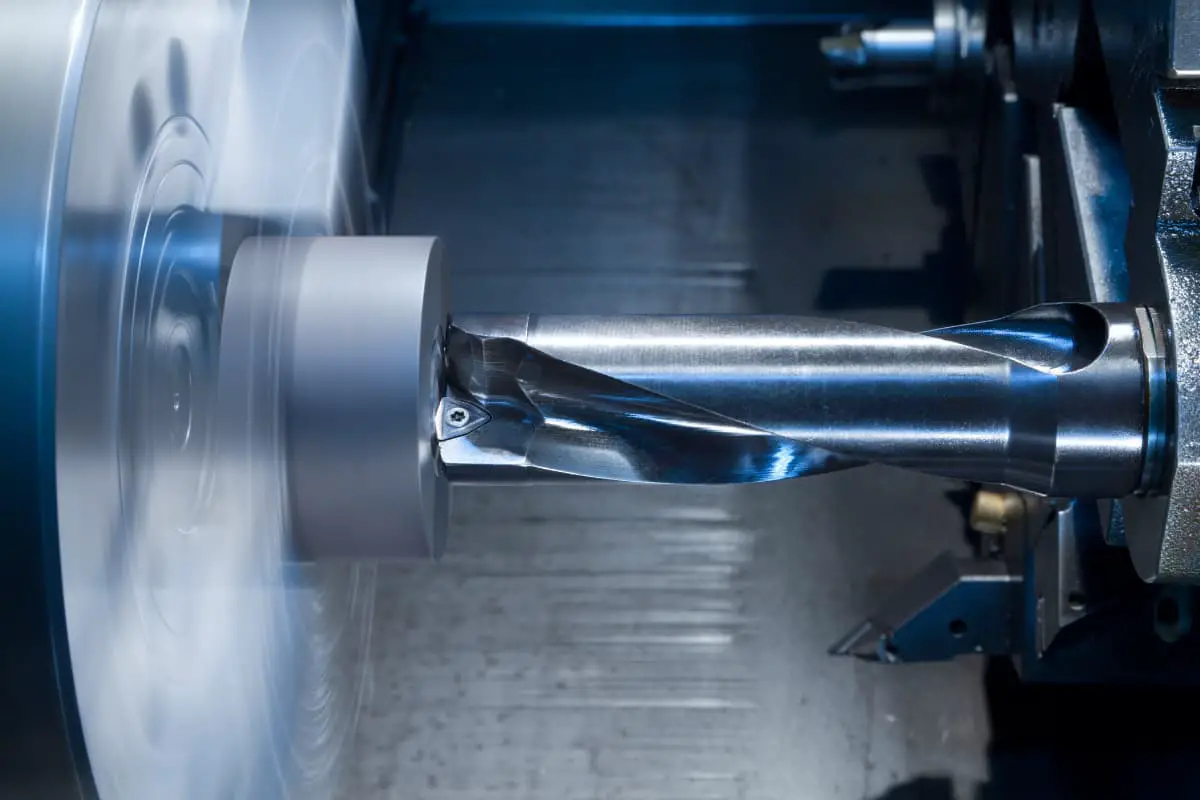
Imagine cutting through metal with the precision and speed of a laser. High-speed cutting, a cutting-edge machining technology, achieves just that. This article dives into the essence of high-speed cutting, detailing its efficiency, precision, and applications in industries like aerospace and automotive. Discover how this technology enhances manufacturing processes, reduces energy consumption, and ensures high-quality finishes, transforming modern production.

Cutting machining remains the most prominent method of mechanical processing, holding a significant role in mechanical manufacturing.
With the advancement of manufacturing technology, cutting machining technology underwent substantial progress towards the end of the 20th century, ushering in a new era characterized by the development of high-speed cutting, the creation of new cutting processes and methodologies, and the provision of comprehensive technological packages.
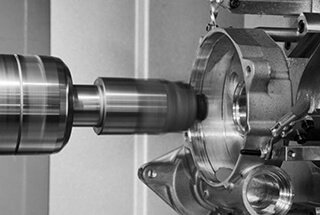
High-speed cutting, a rapidly emerging advanced manufacturing technology with improved processing efficiency and quality, is gaining increasing recognition and attention from more and more technicians in industrially developed countries today.
High-speed machining is a relative concept and lacks a consensus definition. It is generally considered as a modern processing technology that uses superhard material tools to greatly increase the cutting speed and feed rate, thus enhancing material removal rate, processing precision, and surface quality. The essence of high-speed machining lies in speed and accuracy.
Due to the diversity of tool materials, workpiece materials, and processing technologies, it is challenging to provide a definite definition of the speed range for high-speed cutting. Currently, it is generally considered high-speed machining if the spindle speed is over 10,000m/min or 5-10 times the ordinary cutting speed.
During high-speed machining, not only is the cutting speed significantly increased, but the speed of machine tool transport components is also much higher than conventional cutting, saving not only cutting time but also dramatically reducing auxiliary processing time.
Characteristics of High-Speed Cutting include:
With increased automation, auxiliary time and idle travel time have been greatly reduced, and the effective cutting time accounts for the major part of the workpiece’s in-process time. The cut time depends on the feed speed and feed size. Although high-speed cutting has a smaller cutting depth, the high spindle rotation speed and fast feed rate result in a higher metal removal rate per unit time, naturally enhancing processing efficiency.
High-speed cutting has a high material removal rate and accordingly reduces cutting forces. For the same cutting layer parameters, the unit cutting force of high-speed cutting is small, resulting in minimal force deformation of the workpiece during cutting, which helps ensure processing precision.
3) High processed surface quality.
During high-speed cutting, the cutting force is small, amplitude fluctuations are minimal, and the excitation frequency related to the spindle is far from the inherent frequency of the cutting process system, so vibrations are not easily generated.
During high-speed cutting, the metal removal rate per unit power significantly increases. Because of the high removal rate, low energy consumption, and short processing time, the utilization rate of energy and equipment is improved.
Currently, high-speed machining technology is primarily used in the aerospace industry, automotive industry, mold industry, and the processing of complex surfaces and difficult-to-machine materials. High-speed cutting technology is mainly applied in the aerospace industry where aircraft parts are usually manufactured as a whole, with a very high metal removal rate (generally over 70%).
In the automotive manufacturing industry, to meet the market’s personalized demands, production has gradually transitioned from mass production to diversified batch production.
For mold manufacturing, when high-speed, high-feed, and low-cutting depth processing methods are adopted, the processing of hardened steel mold cavities can achieve better surface quality, reducing or even eliminating the need for EDM and grinding, which offers significant advantages in reducing preparation time, shortening the process flow, and cutting processing time.








