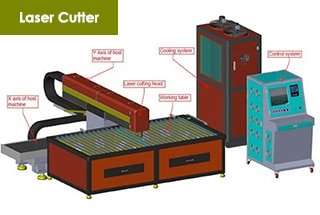
Have you ever wondered how modern industries achieve such precise and efficient production? This article explores the world of fiber laser cutting machines, revealing their benefits and guiding you on how to choose the perfect one for your needs. Learn how this technology can revolutionize your business and ensure long-term success.

After years of development, fiber laser cutting machines have significantly improved the production efficiency for various industries and are becoming increasingly popular in various industries.
The optical fiber laser cutting machine utilizes laser technology for processing and production, which is a non-contact method.

Compared to traditional methods, fiber laser cutting machines do not cause material deformation or damage, and provide fast and precise processing.
As a result, more and more companies are choosing to invest in fiber laser cutting machines.
The purchase of a fiber laser cutting machine is a crucial decision for many businesses.
However, with the growing number of fiber laser cutting machine brands, the prices in the market can vary widely.
This can make it difficult for buyers to make a confident decision.
Choosing the wrong equipment that does not meet your needs can result in not only a waste of initial capital investment, but also missed opportunities during the company’s growth period.
For companies with limited funds, making the wrong choice in fiber laser cutting machine can even lead to significant losses or bankruptcy.
Therefore, it is important to thoroughly research and choose the right equipment when purchasing a fiber laser cutting machine. This investment will benefit your business for at least 10 years.

You understand the significance of 10 years for a company’s growth.
Since many enterprises may be purchasing a fiber laser cutting machine for the first time and may not be familiar with the technology, this article will provide basic information to give a preliminary understanding of the machine, and then delve into how to choose the right fiber laser cutting machine.

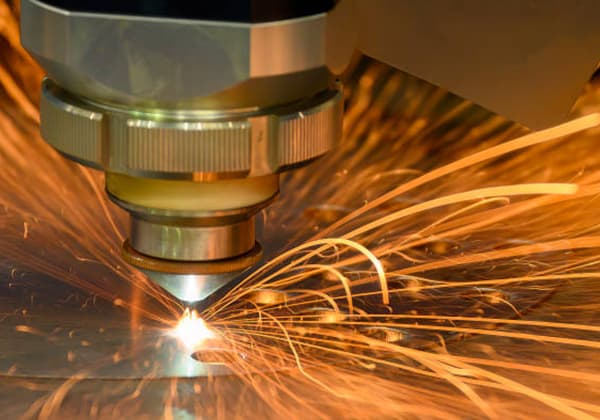
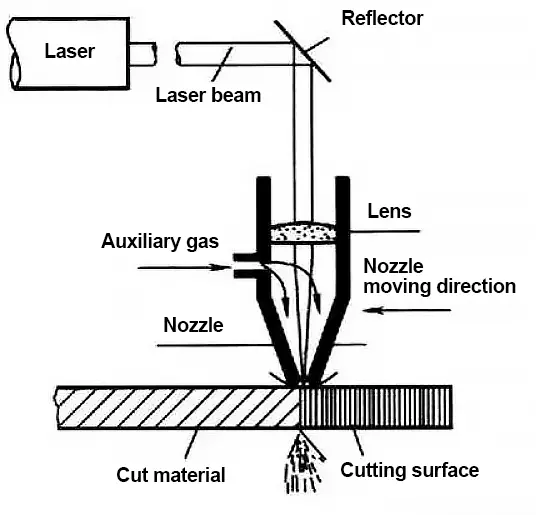
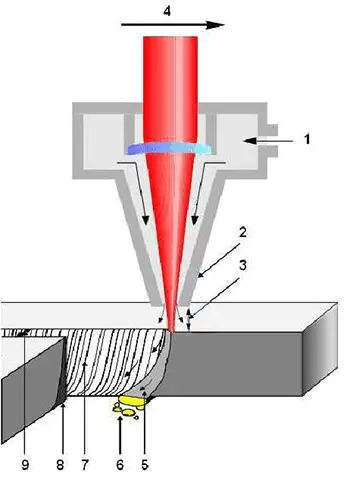
Laser cutting involves directing a highly focused and intense laser beam onto the workpiece, causing the material to rapidly melt, vaporize, ablate, or reach ignition, and then blowing away the molten material with the help of a high-speed air flow that is coaxial with the beam. This process is used to cut the workpiece.
Laser cutting is a type of thermal cutting method.
The following illustration shows the principle of laser cutting:
Laser cutting can be classified into four categories: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting cutting, laser oxygen cutting, and laser scribing and fracture control.
(1) Laser Vaporization Cutting:
The high-energy density laser beam heats the workpiece, causing its temperature to rapidly increase and reach the boiling point of the material in a short time. The material begins to vaporize and form steam, which is expelled at high speeds and forms a notch on the material.
Laser vaporization cutting requires a large power and power density due to the heat of vaporization of materials. It is mostly used for cutting thin metal materials and non-metallic materials such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic, and rubber.
(2) Laser Melting Cutting:
During laser melting cutting, the metal material is melted by the laser heat, and a non-oxidizing gas (Ar, He, N, etc.) is then injected through a nozzle that is coaxial with the beam to discharge the liquid metal and form a notch with the help of the gas’s strong pressure.
Laser melting cutting does not require complete vaporization of the metal and uses only 1/10 of the energy required for vaporization cutting. It is mainly used for cutting materials or active metals that are not easily oxidized, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and their alloys.

(3) Laser Oxygen Cutting:
The principle of laser oxygen cutting is similar to oxyacetylene cutting, using laser as a preheating heat source and an active gas such as oxygen as the cutting gas. The injected gas reacts with the cutting metal to produce an oxidation reaction and release a large amount of heat.
At the same time, the molten oxide and melt are blown out of the reaction zone to form a notch in the metal.
Laser oxygen cutting requires only 1/2 of the energy used in melting cutting and has a much higher cutting speed compared to laser vaporization cutting and laser melting cutting. This method is mainly used for cutting easily oxidized metal materials such as carbon steel, titanium steel, and heat-treated steel.
(4) Laser Scribing and Fracture Control:
Laser scribing involves scanning the surface of brittle materials with a high-energy density laser, heating and evaporating the material into a small groove, and then applying pressure to cause the brittle material to crack along the groove. Q-switched lasers and CO2 lasers are commonly used for laser scribing.
Controlled fracture uses the steep temperature distribution generated by laser grooving to produce local thermal stress in brittle materials, leading to the materials breaking along small grooves.

Compared to other thermal cutting methods, laser cutting is known for its fast cutting speed and high-quality results.
Some key advantages of laser cutting include:
(1) Excellent Cutting Quality:
Laser cutting provides better cutting quality due to its small laser spot, high energy density, and fast cutting speed.
Table 1 compares laser cutting, oxyacetylene cutting, and plasma cutting methods. The cutting material used was a 6.2mm thick low carbon steel plate.
Table 1 Comparison and calibration of laser cutting, oxyacetylene cutting and plasma cutting methods
| Cutting method | Slit width | Width of heat affected zone / mm | Slit shape | Cutting speed | Equipment cost |
| Laser cutting | 0.2-0.3 | 0.04-0.06 | Parallel | Fast | High |
| Oxyacetylene cutting | 0.9-1.2 | 0.6-1.2 | Relative parallel | Slow | Low |
| Plasma cutting | 3.0-4.0 | 0.5-1.0 | Wedge and inclined | Fast | Medium and high |
(2) High Cutting Efficiency
Laser cutting machines are equipped with multiple NC worktables due to the transmission characteristics of lasers, allowing for a fully numerical controlled cutting process.
During operation, different shapes can be cut by simply changing the NC program, allowing for both two-dimensional and three-dimensional cutting.
(3) Fast Cutting Speed
With a 1200W laser, a 2mm thick low carbon steel plate can be cut at a speed of 600cm/min, while a 5mm thick polypropylene resin board can be cut at a speed of 1200cm/min.
The material does not need to be clamped or fixed during the cutting process, saving time and reducing the need for tooling and fixtures.
The speed of laser cutting can be referred to this article.
(4) Non contact cutting

In laser cutting, the cutting torch does not come into contact with the workpiece, resulting in no tool wear.
To cut parts with different shapes, it is not necessary to change the “tool,” only the output parameters of the laser.
Additionally, the laser cutting process has the benefits of low noise, minimal vibration, and a lack of pollution.
(5) Wide Range of Cut Materials
Laser cutting offers a greater variety of materials to cut compared to oxyacetylene and plasma cutting, including metal, non-metal, metal matrix composites, non-metal matrix composites, leather, wood, and fiber.
However, the laser cutting adaptability of these materials varies due to their differing thermophysical properties and laser absorptivity.
(6) Shortcoming
The limitations of laser power and equipment size limit laser cutting to medium and small thickness plates and pipes.
Additionally, the cutting speed decreases significantly as the thickness of the workpiece increases. The cost of laser cutting equipment is high and requires a large initial investment.

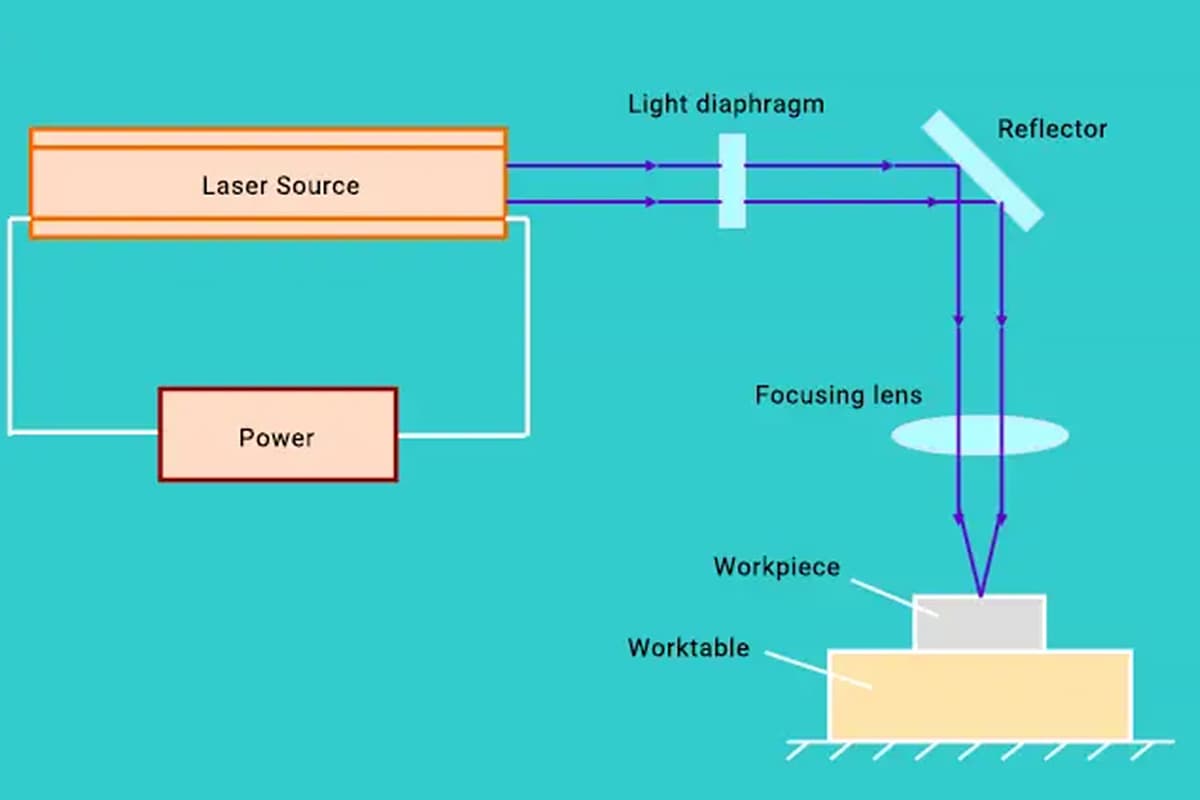
The laser cutting machine focuses the emitted laser into a high-powered laser beam through its optical path system.
The laser beam then heats the surface of the workpiece to its melting or boiling point. Simultaneously, high-pressure gas that is coaxial with the beam removes the molten or vaporized metal.
By adjusting the relative position between the beam and the workpiece, the material is finally cut into the desired shape.

Structural steel
Cutting with oxygen results in improved outcomes. When oxygen is utilized as the processing gas, the cutting edge will have a slight oxidation.
For plates with a thickness up to 4mm, high-pressure cutting can be performed using nitrogen as the processing gas, which will prevent oxidation of the cutting edge.
For plates thicker than 10mm, using special laser plates and oiling the workpiece surface during processing will yield good results.
Stainless steel
Oxygen can be used if the oxidation of the cutting end face is acceptable. Using nitrogen results in cutting edges that are free of oxidation and burrs, and no additional treatment is necessary.
Applying a coating of oil to the surface of the plate will enhance the perforation effect without compromising the quality of the processing.
Aluminium
Although aluminum has high reflectivity and thermal conductivity, it can still be cut with a thickness less than 6mm, depending on the alloy type and the capability of the laser. When cutting with oxygen, the cutting surface will be rough and hard.
However, using nitrogen results in a smoother cutting surface. Pure aluminum is difficult to cut due to its high purity, and can only be cut with the installation of a “reflection absorption” device on the system. Without this device, the reflection will damage the optical components.
Titanium
Titanium plates are cut using argon and nitrogen as the processing gases. Other parameters can be referred to those used for nickel chromium steel.
Copper and brass
Both brass and copper have high reflectivity and excellent thermal conductivity. Brass with a thickness less than 1mm can be cut using nitrogen, while copper with a thickness less than 2mm can be cut using oxygen as the processing gas.
However, both brass and copper can only be cut if a “reflection absorption” device is installed on the system; otherwise, the reflection will damage the optical components.

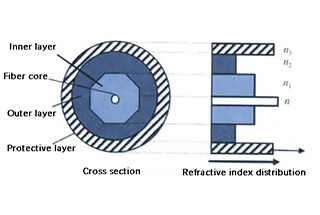
The fiber laser cutting machine uses a fiber laser generator as its light source. The fiber laser is a new type of laser that has been developed globally.
The high-energy-density laser beam is focused onto the surface of the workpiece, causing the area illuminated by the ultra-fine focus spot to instantly melt and vaporize. The numerical control mechanical system moves the spot to achieve automatic cutting.
Compared to the traditional gas and solid-state lasers, fiber lasers have significant advantages and have become a major player in high-precision laser processing, lidar systems, space technology, laser medicine, and more.
The optical fiber laser cutting machine can perform both flat and angled cuts, producing neat and smooth edges. It is ideal for high-precision cutting of metal plates.
Additionally, by incorporating a mechanical arm, the machine can perform three-dimensional cutting, eliminating the need for a five-axis laser.
In comparison to conventional carbon dioxide laser cutting machines, the fiber laser cutting machine requires less space and gas consumption and has a higher photoelectric conversion rate.
It is a new energy-saving and environmentally-friendly product, and is considered one of the world’s leading technologies.
Most laser cutting machines are either operated through NC programs or integrated into cutting robots.
As a precise machining method, laser cutting can cut almost all materials, including both two-dimensional and three-dimensional cuts of thin metal plates.
The laser cutting forming technology is also widely applied in the field of non-metallic materials.

The optical fiber laser cutting machine is widely used across various manufacturing and processing industries, including sheet metal processing, aviation, aerospace, electronics, electrical appliances, subway accessories, automobiles, grain machinery, textile machinery, engineering machinery, precision accessories, ships, metallurgical equipment, elevators, household appliances, craft gifts, tool processing, decoration, advertising, metal external processing, and kitchenware processing.
Different cutting and blanking methods each have their limitations and are best suited for specific applications in industrial production. The development and use of laser cutting machines is a major advancement and innovation in modern industrial production.
The fiber laser cutting machine is a high-tech device that combines advanced fiber laser technology, numerical control technology, and precision machinery technology. It uses a cutting-edge fiber laser to produce a high-energy-density laser beam.
The beam is focused onto the surface of the workpiece through the cutting head, forming a small spot with a diameter as small as 0.1mm. The area illuminated by the ultra-fine focus instantly melts and vaporizes, forming a hole.
The numerical control mechanical system moves the laser spot’s irradiation position, causing the hole to continuously form a narrow gap and achieve automatic cutting.

The fiber laser cutting machine can be classified based on power into:
If classified based on the cutting materials, common types in the market are:
It’s important to consider the material being used when selecting the equipment, as different materials will require different equipment.
If classified based on usage, the fiber laser cutting machine can be divided into:
This classification is more straightforward, as it mainly refers to different processing materials.
Additionally, the fiber laser cutting machine can also be classified based on the equipment’s structure, which can be mainly divided into:
The fiber laser cutting machine has several advantages, including:
(1) Excellent beam quality – The smaller focus spot and finer cutting lines result in higher work efficiency and better processing quality.
(2) Extremely high cutting speed – The cutting speed is twice that of a CO2 laser cutting machine with the same power.
(3) High stability – The machine uses the world’s top imported fiber laser, which has stable performance and key components that can last up to 100,000 hours.
(4) High electro-optic conversion efficiency – The fiber laser cutting machine has a photoelectric conversion efficiency of about 30%, which is three times higher than a CO2 laser cutting machine, making it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
(5) Very low use cost – The power consumption of the machine is only 20-30% of similar CO2 laser cutting machines.
(6) Very low maintenance costs – The machine doesn’t require a laser working gas and has optical fiber transmission without a reflector, saving on maintenance costs.
(7) Easy operation and maintenance – Optical fiber transmission eliminates the need to adjust the optical path.
(8) Super flexible light guide effect – The small size and compact structure make it easy to meet the requirements of flexible processing.
However, compared to a carbon dioxide laser cutting machine, the cutting range of a fiber laser is relatively narrow. Due to the wavelength, it can only cut metallic materials, and non-metallic materials are not easily absorbed, limiting its cutting range.

The fiber laser cutting machine has several advantages compared to YAG solid-state laser cutting, including:
(1) Cutting speed – The cutting speed of the fiber laser cutting machine is 4-5 times faster, making it suitable for mass processing and production.
(2) Use cost – The use cost of the fiber laser cutting machine is lower than that of the YAG solid-state laser cutting machine.
(3) Photoelectric conversion efficiency – The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the fiber laser cutting machine is about 10 times higher than that of YAG.
While the fiber laser cutting machine may have a higher price than the YAG laser cutting machine, it is still less expensive than a carbon dioxide laser cutting machine.
Despite the high price, the fiber laser cutting machine has the best performance-to-price ratio of the three.
| Technique | Slit(mm) | Deformation | Accuracy | Graphic change | Speed | Cost |
| Laser cutting | Small 0.1-0.3 | Small | High 0.2mm | Very easy | Slow | High |
| Plasma cutting | Small | Big | High 1mm | Very easy | Fast | Low |
| Waterjet | Big | Small | High | Easy | Fast | High |
| Die cutting | Small | Big | Low | Hard | Fast | Low |
| Sawing | Big | Small | Low | Hard | Very Slow | Low |
| Wire cutting | Small | Small | High | Easy | Very Slow | High |
| Gas fuel cutting | Very Big | Very Big | Low | Easy | Slow | Low |
| EDM | Small | Small | High | Easy | Very Slow | Very High |

Choosing a laser cutting machine can be a challenging task, much like deciding what to have for lunch. Understanding your needs is key to finding the right product.
Just like everyone has different tastes, everyone’s needs are different. What works best for you is what you should choose.
Before buying a laser cutting machine, consider the following factors:
The purchase cost is a significant factor in the investment of enterprise development. While growth requires fresh resources, it shouldn’t be done without consideration. This is where skills and research come into play.
If your budget allows, you can opt for top imported brands, such as the world’s top ten laser cutting machine brands.
However, most enterprises have budgets that may not support the purchase of these large brands. The technology behind laser cutting machines, especially metal laser cutting machines, has seen rapid development in recent years.
Nowadays, laser cutting technology has reached a level of maturity and stability. When cost is a concern, choosing a Chinese brand laser cutting machine is also a wise choice.
This way, you can obtain a suitable machine at a lower purchase cost.
When choosing a fiber laser cutting machine, consider factors such as your business scope, the thickness of cutting materials, and the materials you will be cutting. Then, determine the power and workbench size needed for the machine.
Power is a crucial factor affecting the price of a fiber laser cutting machine, with higher power resulting in a higher price and increased work efficiency.
A common misconception is that the higher the power, the better the machine will be for cutting, regardless of the thickness of the plate. This is not necessarily true.
High power is ideal for cutting thick plates, while medium power is better suited for cutting medium-thin plates. The quality of the cut depends on the optical quality of the machine, not just the power.
Many manufacturers, both big and small, are trying to increase their power, but this does not always equate to better performance.
In some cases, a machine with a power of 8000W may have a better cutting effect than one advertised as 15000W or 20000W.
For cutting thick plates, high power is necessary. If the power is too low, the plates will not be cut.
Currently, fiber laser cutting machines on the market have power ranging from 500W to 20,000W and the worktable size can be customized according to the customer’s needs.
To choose a fiber laser cutting machine with high cost-performance, it is important to evaluate your output demand and select a machine that meets your personal needs.
For instance, if you need to cut 1-8mm carbon steel plates, a 1000W laser cutting machine would be sufficient. If you frequently cut 8mm thick plates, a 1500W machine would be more efficient. For cutting thin plates, 1000W is enough.
For processing aluminum alloys, a fiber laser cutting machine is recommended.
For specific cutting parameters, refer to the laser cutting machine cutting parameters table.
Cutting parameter table of laser cutting machine
| Metal / laser power (W) | 1000W | 1500W | 2000W | 3000W | 4000W | 6000W | 8000W | 12000W |
| Carbon steel (mm) | 1-8 | 1-12 | 1-16 | 1-20 | 1-22 | 1-22 | 1-22 | 1-25 |
| Stainless steel (mm) | 1-4 | 1-4.5 | 1-6 | 1-8 | 1-10 | 1-16 | 1-20 | 1-25 |
| Aluminum alloy (mm) | 1-2 | 1-3 | 1-4 | 1-6 | 1-8 | 1-14 | 1-16 | 1-25 |
| Brass (mm) | 1-2 | 1-3 | 1-4 | 1-6 | 1-8 | 1-14 | 1-16 | 1-25 |
Compared with other cutting systems, such as CO2 laser and plasma cutting machines, fiber laser cutting machines offer higher cutting accuracy and efficiency, with notable advantages including high precision (±0.02mm), stability, and efficiency.
Fiber laser cutting machines have the advantage of high stability and a long service life. With proper operation and regular maintenance, the main parts of the machine experience minimal wear and tear.
The main expenses are electricity, gas, and general consumables, which are relatively low costs.
As we all know, the high precision and high efficiency of the optical fiber laser cutting machine are powerful tools in the metal processing industry.
However, these technical advantages focus on the accessories of the equipment.
Even if the same fiber laser cutting machine uses different accessories, the final cutting result can vary.
Therefore, it is crucial for users to choose cost-effective accessories when purchasing a fiber laser cutting machine.
A laser cutting machine typically consists of six core components:
The configuration of the core components of a fiber laser cutting machine has a major impact on its price, particularly the quality and brand of the laser source. This significantly determines the base price of the machine.
Here’s a guide on how to select the core components of a fiber laser cutting machine.
The performance and quality of a laser cutting machine largely depend on the quality of its optical components.
Many people believe that power consumption is a key factor in determining the machine’s efficiency, but the most critical factor is not power but optical quality.
The fiber laser, as the head accessory of the fiber laser cutting machine and its core “power source,” determines the optical quality.
The best fiber lasers on the market include German IPG with a photoelectric conversion rate of about 40%, UK SPI, USA n-light, and China’s Raycus and Max laser.

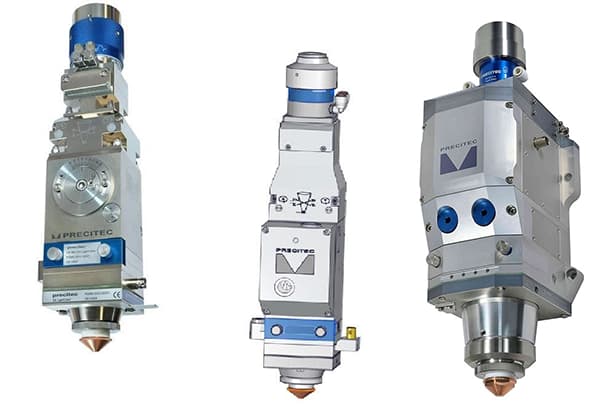
2) Cutting head
The cutting head of a laser cutting machine is a device that outputs a laser and is comprised of a nozzle, focusing lens, and focusing tracking system.
The cutting head of the laser cutting machine moves along the set cutting path, but the height of the laser cutting head must be adjusted and controlled based on the material, thickness, and cutting method.
The quality of the cutting head is primarily determined by the ability of the optical lens group to output high-quality laser and the presence of a precise adjustment system.
Prominent brands of cutting heads include Precitec and Raytools.

3) Control system
The control system is the primary operating system for the optical fiber laser cutting machine.
Its quality plays a crucial role in determining the stability of the machine’s performance.
The control system is responsible for guiding the movement of the X, Y, and Z axes of the machine tool and regulating the output power of the laser.
In China, the operating system of laser cutting machines is widely used with Cypcut and PA, and each company optimizes it to better suit its own equipment.
This optimization process occurs during proofing and testing and is relatively simple to operate.

4) Bed
The size of the bed on a laser cutting machine determines the capacity of work it can handle.
The bed size is a fixed characteristic and cannot be altered.
Before making a purchase decision, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the cutting workload you plan to undertake.
For instance, if you plan to handle large projects, it would be advisable to invest in a large format laser cutting machine.
A large machine tool can significantly reduce the time spent on loading and unloading and ultimately result in a considerable reduction in overall time cost.

The bed of an optical fiber laser cutting machine typically consists of a plate welding bed, pipe welding bed, or casting bed.
To reduce costs, most laser cutting machine manufacturers opt for a plate welding bed.
The thickness of the bed varies from 8mm to 16mm, depending on the laser cutting power. For ultra-high power fiber laser cutting applications, thicker steel plates are utilized.
While a plate welding bed is more commonly used, it may have a negative impact on the machine’s load-bearing capacity, stability, and cutting accuracy compared to a casting bed.
Therefore, if budget is not a concern, it’s recommended to choose a one-piece cast iron bed when purchasing an optical fiber laser cutting machine.
5) Motor
Step Motor:
The motor plays a crucial role in determining the cutting accuracy of an optical fiber laser cutting machine.
Some manufacturers opt for imported stepper motors, while others utilize stepper motors produced by joint ventures. Smaller enterprises often choose generic motors.
Servo Motor:
A servo motor is an engine that controls the operation of mechanical components in the servo system.
It is an indirect speed change device that works in conjunction with an auxiliary motor.
The servo motor can accurately control the speed and position accuracy and converts a voltage signal into torque and speed to drive the control object.
A high-quality servo motor can significantly enhance the cutting accuracy, positioning speed, and repeated positioning accuracy of a laser cutting machine.
6) Laser lens

The laser lens plays a role in determining the power of a fiber laser cutting machine. It can be either imported or domestically produced.
Domestically produced lenses can further be classified into those made with imported materials and those made with domestic materials.
There is a significant price difference between these options, and there is also a noticeable difference in terms of effectiveness and lifespan.

Once your requirements are determined, you can either visit the market or reach out to peers who have already purchased a laser cutting machine to evaluate its performance and basic specifications.
It’s advisable to communicate with several powerful sellers with favorable prices, and to conduct an on-site investigation later on.
During negotiations, it’s important to discuss the price, training, payment method, and after-sales service of the machine in greater detail.
In terms of the brand of fiber laser cutting machine, it’s recommended not to prioritize brand over performance.
If you must choose a brand, keep in mind that Trumpf is ranked No. 1 globally, and Hanslaser is ranked No. 1 in China.

After-sales service is often overlooked and undervalued. People tend to prioritize price over service.
Regardless of how advanced a laser cutting machine is, customers will encounter various issues during usage.
In such cases, it’s crucial for the seller to provide timely solutions to the customer.
Having professional and prompt after-sales service is extremely important for laser cutting machine manufacturers.
They should offer a one-stop service that includes pre-job training during machine operation, as well as maintenance and commissioning of mechanical equipment.
Ultimately, time is money, and any delay can result in a loss for the user.
What is the most critical consideration for users when purchasing laser equipment?
Is it money or the market?
No, neither is the most important factor.
While capital and market are important considerations, they are not the most critical factors.
The key to success in the market is choosing the right processing equipment that is suitable for the development of your business and market.
With advancements in technology and the market, the power of laser cutting machines is increasing, and there are more and more manufacturers.
However, the professional quality of sales personnel is inconsistent, which can lead to misunderstandings for customers when choosing a laser cutting machine.
Our recommendations are as follows:
Myth 1: When power and configuration are similar, the lower-priced option is preferred.
(1) Domestic laser:
The prices of different brands vary greatly even with the same power.
(2) Imported laser vs. domestic laser:
While the configurations may seem similar, there is a significant difference in practice.
If the price is low, the corresponding input cost is also low, and the configuration and raw materials differ, which can affect the stability of the equipment.
While choosing a lower-priced option may seem like a cost-saving measure, frequent problems during actual use can result in greater actual losses, making the cost savings negligible.
Myth 2: For plates of the same thickness, laser cutting machines with different powers have the ability to cut, so choose the one with low power.
For instance, both a 2000W+ power laser and a laser with lower power can cut 10mm carbon steel.
However, this does not mean that it’s advisable to choose the lower power laser.
The efficiency of cutting 10mm carbon steel varies between different power ranges, and the power should be chosen based on factors such as budget, capacity requirements, product characteristics, and others.
Myth 3: Want to buy a universal machine.
Many people who purchase only one laser machine hope that it will have all functions, including the ability to cut pipes and plates, as well as handle other specialized parts.
However, in an attempt to meet these varied functional requirements, the main functions of the equipment may be compromised.
As a result, while all functions may be available, they may not be performed optimally.
It’s important to note that a laser cutting machine is a general-purpose machine, not a universal machine.
Myth 4: Payment by installment.
Many customers consider in-plant installment as a crucial factor when selecting equipment, but the actual down payment for in-plant installment is often high, which increases financial pressure.
Given the current state of the financial market, it’s recommended to choose the financial leasing method instead:
(1) The minimum down payment for finance lease is 10%.
(2) All finance-leased equipment is insured and will be compensated in the event of damage caused by natural or man-made disasters (for example, in the case of equipment being damaged by flooding, compensation will be provided).
(3) The quality and service are overseen by a third party, which can prevent unattended issues.
(4) Utilizing financial products can improve an individual or enterprise’s reputation.
As the enterprise grows and needs to purchase larger and more equipment in the future, the loan amount will be higher and easier to handle, providing an additional financing channel for the enterprise.
Myth 5: The higher the power, the thicker the cutting thickness.
While a higher power laser cutting machine may indicate the ability to cut thicker plates, it does not guarantee that the cutting quality will meet the requirements of practical production applications.
Factors such as material properties, cutting efficiency, and cooling technology can impact the cutting quality.
Laser cutting equipment is designed for processing sheet metal and excels at cutting medium to heavy plates.
Plates that are too thick fall into the category of machining and require specialized machining equipment.
Myth 6: With the same brand and power, the faster the cutting speed, the better.
The fastest linear cutting speed of lasers from the same brand and with the same power should be consistent in theory.
If a laser’s specifications claim a cutting speed that exceeds the fastest speed in the market, it may be fraudulent.
Myth 7: What is imported is the best.
Laser cutting machines have been developed in China for decades and their product quality has been proven in the market.
Additionally, there are more mature suppliers of corresponding parts in China, which offers advantages in terms of cost-performance, performance, and service.
There are many factors to consider when selecting a laser cutting machine, such as the maximum size and material of the workpiece to be processed, the maximum thickness to be cut, and the size of the raw material format, as well as future development plans.
For example, one should consider the maximum workpiece size after technical modification, the most material-saving format size of the materials provided by the steel market, loading and unloading time, etc.
With the above introduction on how to select a fiber laser cutting machine, you should now have a better understanding of how to choose a machine that is suitable for your needs.
If you still have any questions, please feel free to leave us a message in the comments section.