Choosing the right hydraulic press can be daunting given the wide range of options. What are the critical factors to consider for your specific needs? This article guides you through the key aspects such as production requirements, accuracy, and cost-efficiency. By the end, you’ll understand how to select the ideal hydraulic press for your operations, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Dive in to learn what to look for and how to make an informed decision.


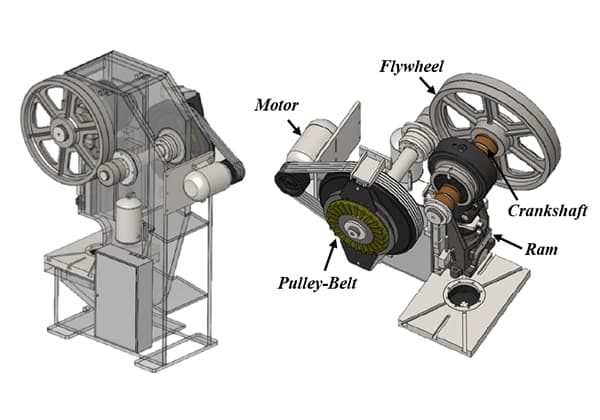
In the past, the term “stamping” was often confused with “blanking.” A few years ago, mechanical and screw presses were the primary tools used for stamping. However, this has changed with the advent of hydraulic presses.
Hydraulic presses were first introduced in the late 1930s and have since become a common tool in forming processes such as punching, forging, riveting, embossing, shearing, and crimping. Some hydraulic presses are even used for blanking and stamping.
To determine if a hydraulic press is suitable, it is important to first understand the definitions of stamping, blanking, and deep drawing.
Blanking
Blanking involves cutting, shearing, and punching a plate into the desired shape. The material can be a single sheet of thin plate or a continuous, long strip of plate.
Stamping
Stamping encompasses the processes of blanking, as well as forming, bending, flanging, and punching. A press that performs these processes can be referred to as a forming press.
Deep Drawing
Deep drawing involves positioning the blanking piece in the die and using the press to stamp it while the blank holder controls the metal flow to form a cavity in the workpiece. Generally, deep drawing refers to a workpiece whose depth of the drawn or concave part exceeds half of its diameter.
Generally, mechanical presses have a simple structure and are fast and efficient, making them suitable for mass production and simple blanking and forming processes. On the other hand, hydraulic presses are better suited for small to medium-sized batch production with just-in-time requirements, variable shapes, and more stringent accuracy requirements for slider speed, pressure, and position. These presses are processed in a specific order.
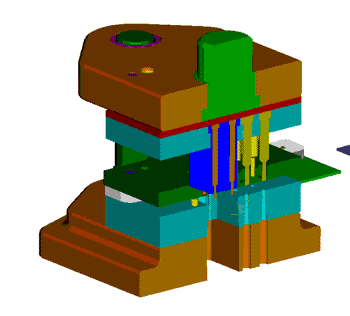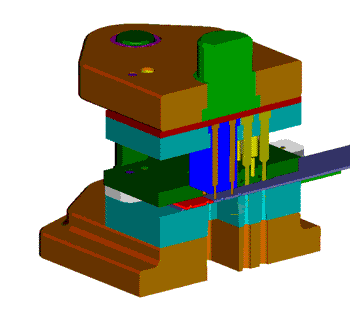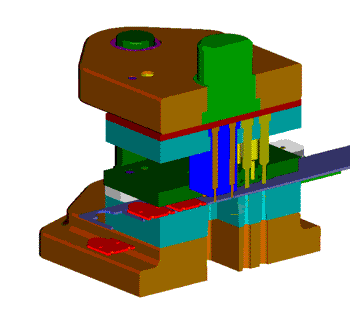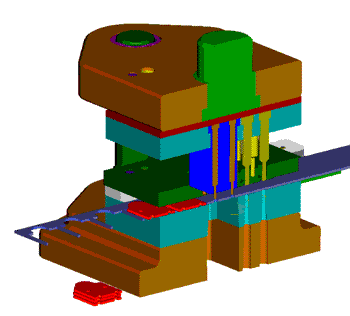
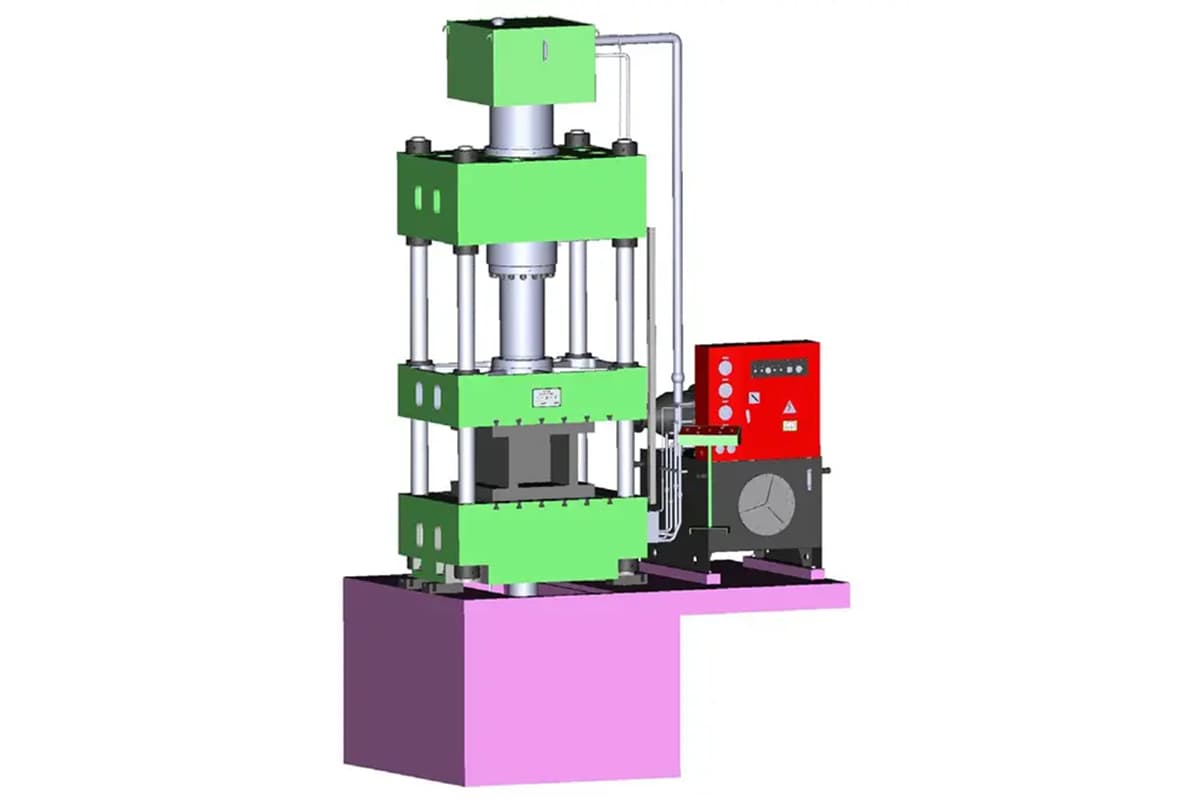
The hydraulic press is commonly used for blanking small to medium-sized parts with low production demands, typically producing 20-40 pieces per minute. The structure of the press is chosen based on the size of the workpiece, the pressure load (centered or eccentric), and the forming mode. It can be a C-shaped frame, double column, or four column press and must be sturdy enough to withstand the impact and vibration of the blanking process.
A single column press with a C-shaped frame may cause angular wave deformation during stamping. On the other hand, the four column press has a tendency for the force’s action point to deviate from its geometric center, while the double column press has a stable structure, accurate action, and minimal deflection, making it suitable for processing with eccentric loads.
Designers often make the blanking press twice as heavy as the standard configuration to improve its stability and reduce the impact of blanking.
Ideal Use of Hydraulic Press for Blanking
The hydraulic press is ideal for the blanking process when it meets the following requirements:
The production pace is slow, with 60 strokes per minute for processing small parts (1-2 inches) and 30-40 strokes per minute for processing large parts (3-15 inches).
For a diverse range of products, a complex program setting is often required, which can be easily set with the hydraulic press.
When frequent changes of JIT parts are required, the setting can be quickly changed using a hydraulic press.
The benefits of using a hydraulic press can be determined by knowing if the slider’s stroke range and pressure control adjustment meet the processing requirements. When designing the press, if the stroke range is set, a hydraulic press should be chosen. The preload of the hydraulic press is also easy to set, as it is used to counteract the impact of the workpiece weight or emergency stop.
During feeding, when two pieces of material are fed to the die or when parts are discharged from the die, the device may fail to eject the machined parts, resulting in the pressing of two pieces. In this case, a mechanical press may be damaged, while the hydraulic press will not be damaged as it has an overload protection function that limits the maximum pressure.
Hydraulic presses are widely used in stamping processing and come in various configurations. The most commonly used configurations are:
Note that there are few double column presses with a working pressure above 5000 tons.
Selection of Hydraulic Press for Stamping
The hydraulic press should be selected for stamping when the following requirements are met:
Due to the ease of setup, the hydraulic press can be quickly configured to meet JIT requirements and change dies frequently.
The feeding method can be manual or automatic, depending on the processing batch. For small batch production (less than 100,000 pieces per year), manual feeding is used, while for mass production, some or all use an automatic feeding mechanism.
If eccentric pressure is required, a double column press should be selected.
If a hydraulic pad is needed for material support or automatic discharge, a hydraulic press should be selected.
When different processing speeds or position control of the slider are required, with high position accuracy and sustained pressure, a hydraulic press should be selected.
When the hydraulic press needs to be re-installed for another project, such as when the production line changes, it can be easily reset as the maximum pressure can be used at any stage of the stroke.
The hydraulic press is used for deep drawing due to its ability to accurately control the slider speed, allowing the metal material to flow without tearing during the drawing process. It is suitable for deep drawing processes with low output, frequent die replacement, a need for various drawing speeds, large pressure changes of the hydraulic pad, and high pressure regulation requirements.
The hydraulic press is recommended for deep drawing in the following cases:
When the workpiece design is complex and the required processing procedures are also complex, the simple adjustment of the hydraulic press is suitable for this situation.
The hydraulic press can be used when a single press is needed to complete processing or for multi-step drawing and shaping processes. It is also suitable for single-line production of deep drawing and/or reverse drawing, and due to its pressure stroke limit, it is suitable for finishing processing.
The hydraulic press can maintain maximum pressure unchanged during the drawing process, reducing the tonnage requirements of the press.
Conclusion
When considering the purchase of a hydraulic press, in addition to evaluating the factors discussed in this post, such as safety, ease of maintenance, installation cycle, and cost, it is important to provide the press supplier with detailed requirements for the press’s performance.
The manufacturer needs to know the following key factors: production rate, budget, mold design, workpiece structure, number of mold changes, overall dimensions of the press, and the purpose of the project.
The advancement of technology highlights the importance of close communication and contact with different press manufacturers in order to make a correct and wise choice. Only through this communication can the correct selection and optimal use of a press be ensured.
Hydraulic press equipment is widely used in various industries for its high degree of automation and precision. The hydraulic system is a crucial component that determines the overall quality of the hydraulic press.
When purchasing a hydraulic press, it’s important to consider all parts of the hydraulic system, including the hydraulic pump, hydraulic valve, and oil cylinder, as their quality directly affects the stability of the press’s performance.
The main components of the hydraulic pump station are the hydraulic pump, hydraulic valve, oil circuit block, motor, and oil pipe. Any malfunction in any of these parts can severely impact the functionality of the hydraulic press, so it’s important to exercise caution when selecting this equipment to avoid careless mistakes.
The hydraulic pump serves as a stable source of power. It is recommended that the displacement of the pump be moderate and not overly large. If the displacement is too large, it can cause the hydraulic oil that meets the requirements for equipment operation to enter the oil return pipe through the overflow valve.
This overflow will result in pressure loss below the specified pressure, leading to an increase in system temperature and negatively impacting the performance of the equipment.
To prevent pressure loss in the system, it is advisable to choose the hydraulic pump wisely.

The quality of the oil cylinders and molds is also crucial. High-quality components can be used for a longer period of time, whereas low-quality components will require more frequent replacements, leading to higher costs.
It’s important for users to conduct thorough research and make informed purchasing decisions. There are many manufacturers of hydraulic presses, and some may compromise on quality for the sake of quantity.
It’s not wise to choose a manufacturer simply because of their low price. When purchasing a hydraulic press, it’s crucial to prioritize quality over price to protect your own interests. It’s recommended to choose carefully to ensure that you are getting a hydraulic press that meets your needs and will serve you well in the long run.
When purchasing a hydraulic press, it’s important to determine the specifications based on your specific needs and to follow these general principles:
For crank presses, the closing height of the die should be between the large height of the die and the small height of the die. The size of the workbench should be greater than 50-70mm (on one side) of the mold base for installation, and the hole diameter of the base plate should be greater than the protruding size. The size of the missing die handle should match the size of the die handle hole for the workpiece or waste.

Hydraulic press, as a widely used piece of equipment in modern industry, is often evaluated based on quality, brand, and price when selected by enterprises and institutions. The brand effect has a significant impact on the price, and the same equipment can have a large price difference based on the trademark.
Therefore, many small and medium-sized enterprises prioritize hydraulic presses with high cost-performance, but they may overlook important details in the purchasing process. Here are some points to consider when purchasing a hydraulic press.
1. Parts
The hydraulic press is a machine made up of many parts and components.
It is uncommon for hydraulic press manufacturers to produce all parts of the hydraulic press in-house. Instead, some parts are purchased or outsourced, with only the key components being manufactured in-house and then assembled into a complete machine for sale.
Many users of hydraulic presses are aware of the common problem of oil leaks, which can be difficult to repair.
Attempts to fix the issue can either involve a lengthy disassembly process with a low probability of success, or a quick fix that may not address the root cause.
Is the technology of hydraulic press manufacturers not up to par, causing oil leaks? Or is it due to the unreliable quality of the parts leading to wear and oil leaks? The latter is more likely the case.
The quality of the components directly impacts the quality of the hydraulic press. To ensure high-quality parts, it is recommended to choose well-known brands, even if it means paying a higher price for the hydraulic press.
When choosing a hydraulic press, it is possible to judge the reasonableness of the price based on the components used. This can help eliminate concerns about potential quality issues affecting your work after purchase.
2. Configuration
The configuration of the hydraulic press is distinct from its components. The configuration can be categorized into high, medium, and low levels depending on the needs of various products, businesses, and organizations.
For example, a basic hydraulic press cannot be compared to a fully automatic one in terms of efficiency and ease of operation.
Therefore, when selecting a hydraulic press, it is crucial to understand the equipment configuration offered by the supplier.
The following factors directly impact the price of the hydraulic press:
Common quotations for hydraulic presses vary.
Many manufacturers may offer low prices in order to attract customers, but they often raise the prices during the negotiation process.
It is important to note that there may be a price difference between tax-included and tax-excluded equipment, between manual and PLC-controlled equipment, and between equipment with and without molds.
Additionally, some customers may request that the manufacturer cover the shipping costs, which will be calculated separately.
When choosing a hydraulic press, it is important to understand the full price offered by the supplier, including what is included and what is not included.
It is also recommended to compare prices from multiple companies to find the most cost-effective manufacturer.
Making direct inquiries without taking into account the specific configuration can lead to overspending and result in the selection of a less optimal option.

Qualification Analysis
Check for the availability of the business license, tax registration certificate, organization code, production license, and quality certificate. Evaluate the completeness of the enterprise’s production life, registered capital, and quality supervision system.
Assess the Enterprise’s Production Strength
Request the enterprise to provide photos of their processing equipment, production site, finished products, and semi-finished products under production to gauge their strength.
Inquire about the Manufacturer’s Sales Performance
Determine if the manufacturer has at least five years of sales contracts and if they have provided large hydraulic presses, hydraulic presses, and presses to military enterprises and state-owned listed enterprises.
It is generally believed that these performance indicators suggest good production capacity and quality of the enterprise.
Technical Evaluation
Analyze the technical proficiency of the equipment manufacturer’s business personnel. Business personnel from strong production enterprises are usually well-trained, and large enterprises have stringent requirements for their business personnel. They typically require them to have a considerable diploma and proficiency before engaging in business and economic work.
Avoid Pursuing Low Prices Blindly
Low-priced equipment usually indicates a problem. Inquire about the market price of first-line state-owned enterprises. Usually, 80% of state-owned enterprises’ equipment prices are considered the best cost-effective options.
Analyze the Conversation Feeling
Powerful manufacturers and business personnel are often confident and professional. For example, they may not be flexible on price, payment methods, and manufacturing period.
Small manufacturing units, on the other hand, may be more willing to compromise to secure an order, but once the contract is signed and the advance payment is made, they may not uphold their end of the agreement.
Therefore, it is crucial to follow these six points and choose a reliable hydraulic press manufacturer.