Ever wondered why your machinery bearings heat up, leading to costly downtimes? High bearing temperatures can shorten bearing life and spike maintenance expenses. This article dives into common causes, like poor lubrication and inadequate cooling, and offers practical solutions to keep your equipment running smoothly. From selecting the right grease to ensuring proper cooling, you’ll learn essential tips to maintain optimal bearing temperatures and prevent unexpected shutdowns. Keep reading to safeguard your machinery’s performance and longevity.

Sometimes bearings experience elevated temperatures, which may not necessarily indicate a bearing issue but could also be symptomatic of a broader machine problem.
Let’s refocus on our primary topic.
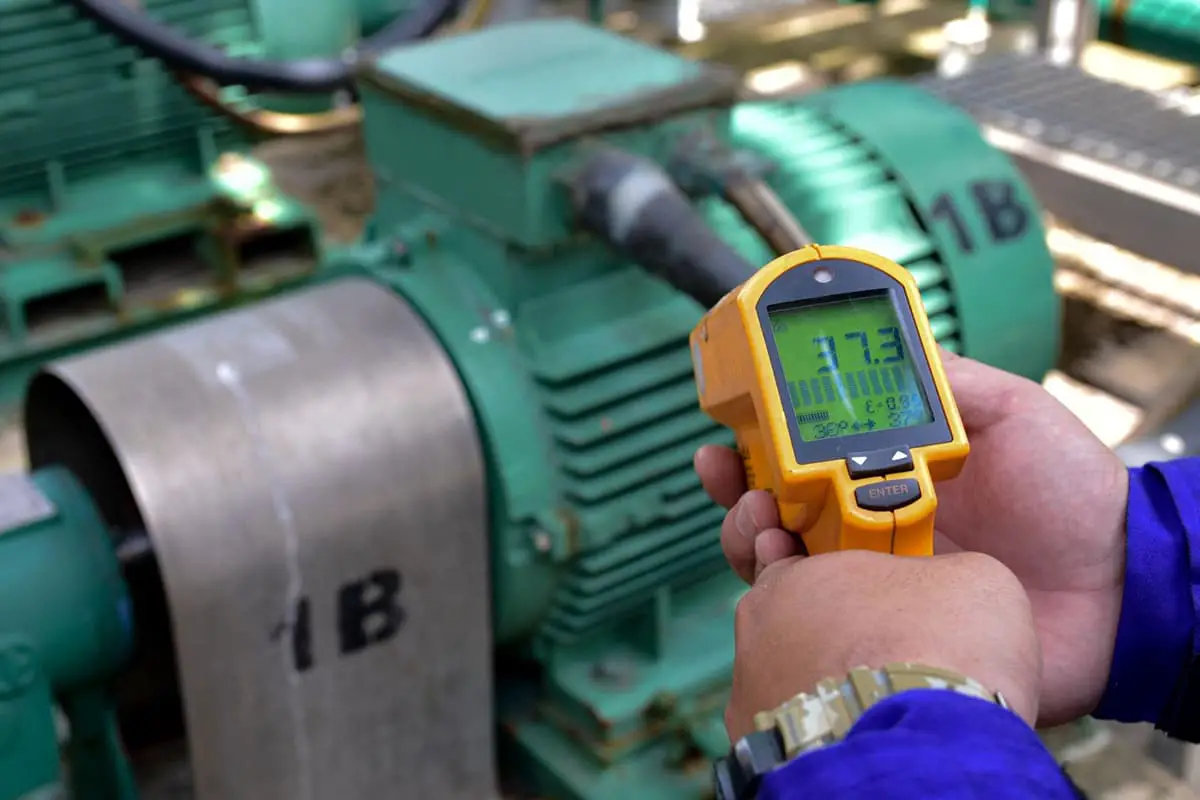
Excessive bearing temperature is a prevalent and potentially hazardous failure mode in rotating equipment. It can significantly reduce bearing service life and escalate maintenance costs.
When temperatures rise rapidly and surpass established thresholds, it can trigger unscheduled outages or necessitate load shedding operations. These disruptions can have substantial impacts on operational efficiency and economic performance.
Consequently, it’s crucial to swiftly identify the root cause of the temperature anomaly and implement appropriate corrective measures. This proactive approach is essential to ensure continuous, safe operation of the equipment and minimize downtime.
In this discussion, we’ll conduct a comprehensive analysis of the causes behind bearing overheating and explore effective solutions to mitigate these issues.


1. Improper refueling quantity, too little or too much lubricating grease
The bearing box should be regularly lubricated according to the requirements of the work.
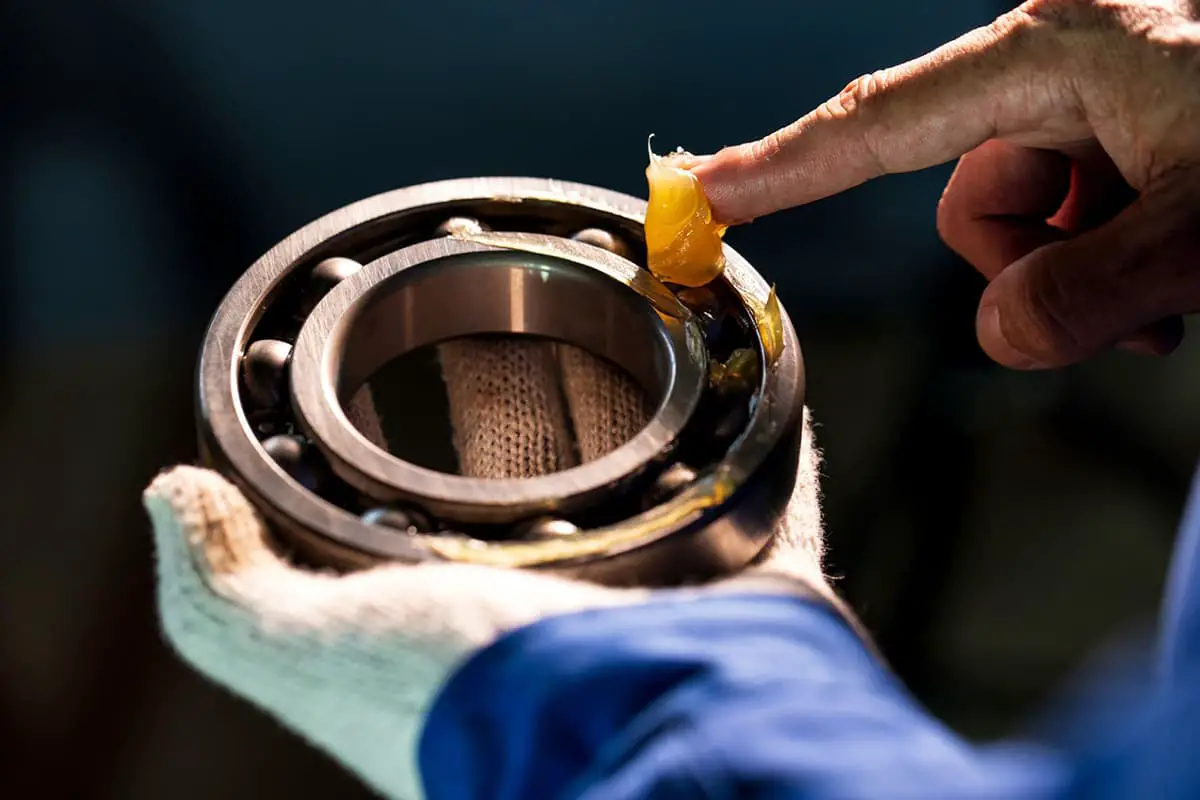
After lubricating the bearing, sometimes the temperature will increase due to over-lubrication. The phenomenon is that the temperature continues to rise, and after reaching a certain point (generally about 10℃ to 15℃ higher than the normal operating temperature), it will remain constant and then gradually decline.
2. The grease added to the bearing does not meet the requirements or is contaminated
If the lubricating grease selection is inappropriate, it is difficult to form a uniform lubricating film, which cannot reduce the internal friction and wear of the bearing.
If the lubrication is insufficient, the bearing temperature will increase.
When different types of grease are mixed, a chemical reaction may occur, causing the grease to deteriorate, cake and reduce lubrication.
Contaminated grease will also increase the bearing temperature.
Dust falling into the process of adding grease causes grease pollution, resulting in deterioration of the grease inside the bearing box, destroying bearing lubrication and increasing temperature.
Therefore, suitable grease should be selected, and the bearing box and bearing should be cleaned during maintenance, and the oil pipeline should be checked for blockages.
Different types of grease should not be mixed.
If replacing other types of grease, the original grease should be cleaned first. Grease should be added regularly during operation and maintenance.
The grease should be properly stored and protected against moisture and dust.
3. Insufficient cooling
Check whether the pipeline is blocked and whether the temperature of the oil inlet and return water exceeds the standard.
If the cooler is unsuitable, the cooling effect is poor and cannot meet the use requirements, it should be replaced or a new cooler should be installed in parallel.
Also, check the insulation and sealing of the core barrel of the axial flow pilot fan.
4. Check the coupling alignment and bearings after confirming that there is no such problem
The alignment of the coupling must meet the process standards. The thermal expansion of the equipment in operation should also be considered when aligning the axial flow fans, hydraulic couplers, etc.
Due to the thermal expansion of the induced draft fan side, the temperature of the bearing box rises.
As the temperature of the fluid coupling increases during operation, the bearing box expands and the bearing temperature increases.
Therefore, when aligning, the motor should be higher, and the size of the reserved amount depends on the characteristics of the equipment and the temperature parameters in operation.

During the disassembly of the bearing housing, the initial step is to assess the condition of the lubricant. Look for signs of deterioration, caking, contamination, or any other abnormalities. This evaluation provides crucial insights into potential causes of bearing damage.
Next, conduct a thorough inspection of the bearings for indications of scoring, wear patterns, and surface finish quality. Examine the inner and outer rings, rolling elements, and cages for defects such as cracks, corrosion, flaking, pitting, overheating marks, or discoloration.
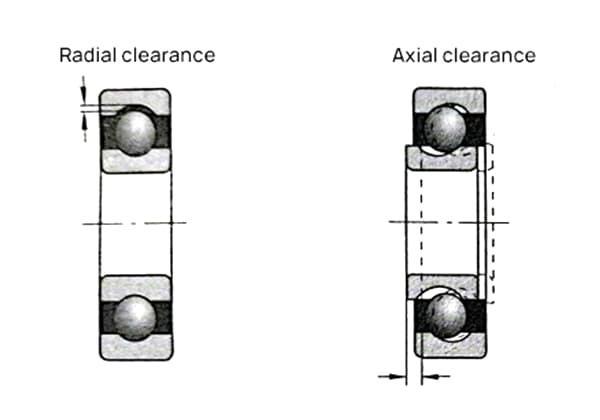
Measure the bearing clearance to ensure it falls within specified tolerances. Inspect the bushings for wear, pitting, or peeling. If any of these issues are detected, replacement with new bearings is necessary to maintain optimal performance and reliability.
Proper fitting of bearings is critical during installation. Ensure precise matching between the bearing’s inner diameter and the shaft, as well as the outer diameter and housing.
An excessively loose fit can lead to creep, causing relative motion between mating surfaces. This phenomenon results in wear on contact areas, potentially damaging the shaft or housing. Additionally, wear debris accumulation within the bearing can increase heat generation, vibration, and ultimately lead to bearing failure.
Conversely, excessive interference can cause the outer ring to contract or the inner ring to expand, reducing the bearing’s internal clearance. This alteration in geometry can significantly impact bearing performance and lifespan.
When determining the appropriate fit, consider factors such as:
Optimal internal clearance is crucial for bearing performance and longevity. Insufficient clearance can result in:
Conversely, excessive clearance can:
It is essential to select the appropriate and verified bearing clearance based on specific equipment requirements and operating conditions. Factors to consider include:
Regular monitoring and adjustment of bearing clearance throughout the equipment’s lifecycle can significantly enhance performance, efficiency, and reliability.