Ever wondered how robots are revolutionizing industries? From welding and cutting to assembling and sorting, industrial robots are transforming manufacturing processes with unmatched efficiency and precision. This article explores 13 essential applications of industrial robots, showcasing their impact on productivity and safety. Dive in to discover how these advancements can streamline operations and reduce labor costs in various sectors.

At present, the manufacturing industry is experiencing a surge in automation and intelligence, with the rapid development of industrial robots leading to increased maturity in their application in the processing and manufacturing fields.
It should be noted that these are not the only applications of industrial robots.
The possibilities for industrial robots are only limited by one’s imagination.

Arc welding robots are categorized into two main types: melting electrode welding and non-melting electrode welding. These robots possess unique characteristics, such as the ability to perform long-term welding operations, high productivity, and consistent high-quality and stability in welding processes.

The spot welding robot operates by following the actions, sequences, and parameters outlined in its programmed instructions. The entire process is fully automated and includes a communication interface with external devices.
This interface enables the robot to receive control commands from a higher-level master computer or management system, allowing it to perform its work.

Laser welding is known for causing minimal deformation to the workpiece being welded, resulting in virtually no joint gap and a high ratio of weld depth to width. This results in a higher quality weld compared to traditional welding methods.
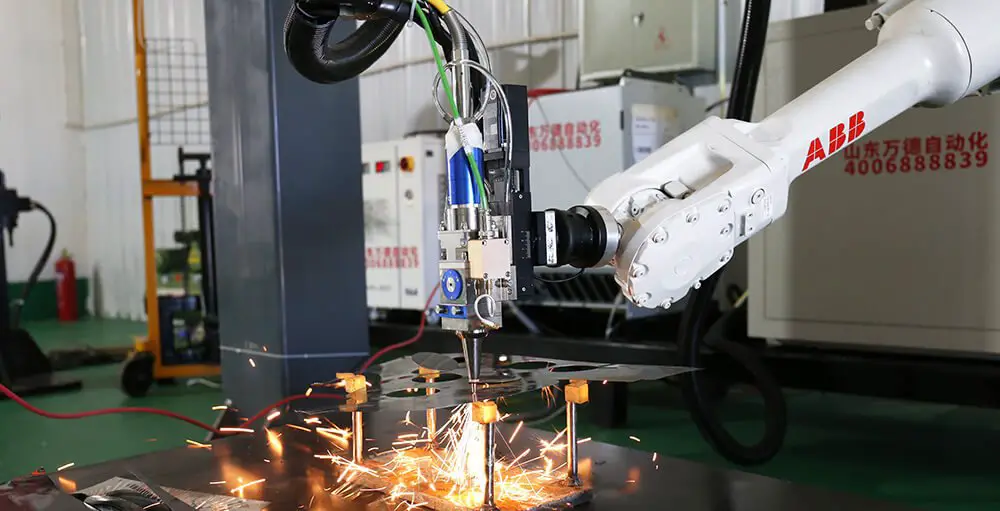
Robotic laser cutting systems are characterized by two key features: the ability of industrial robots to freely and flexibly carry out complex 3D curve processing trajectories, and the use of flexible, long-distance transmitting laser fibers as the transmission medium, which does not limit the robot’s range of motion.
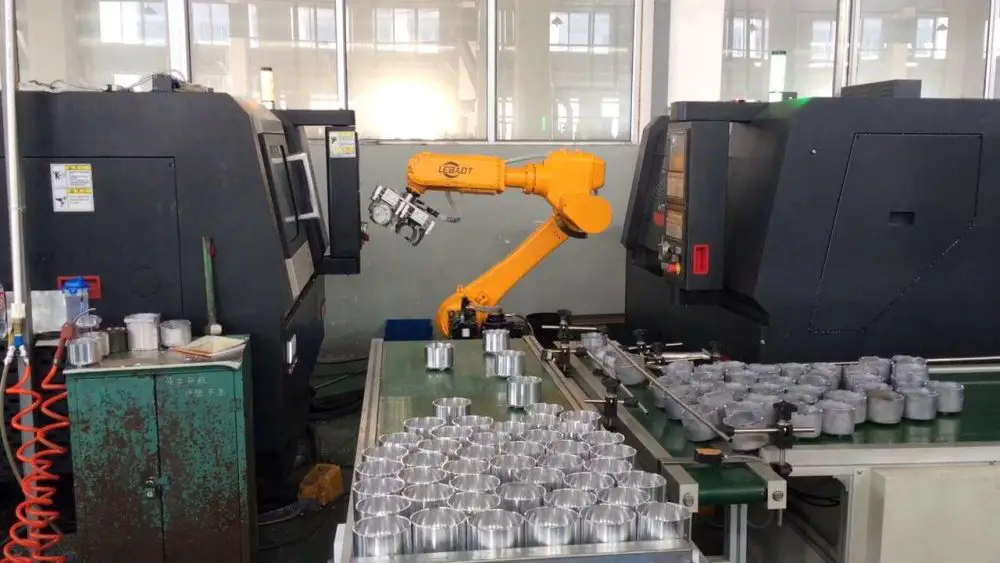

Robotic loading and unloading systems are known for their high efficiency, stability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance. They can be utilized for a diverse range of products, allowing users to quickly adjust product structures and expand production capacity. This results in a significant reduction in the labor intensity for industrial workers.
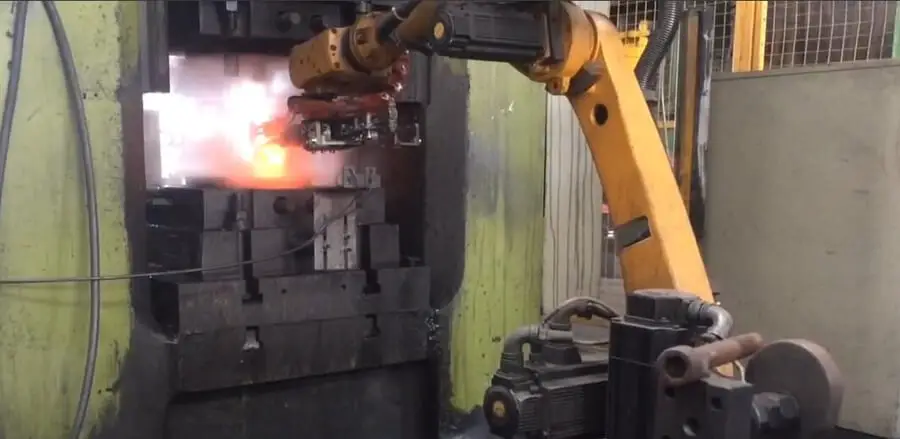

The forging robot is automated through the use of advanced computer control and programming. It is capable of fully replacing manual labor in the continuous and repetitive tasks of loading, turning, and unloading in the forging production process. This leads to a reduction in labor intensity and danger, as well as an increase in the degree of automation and efficiency in the production process.
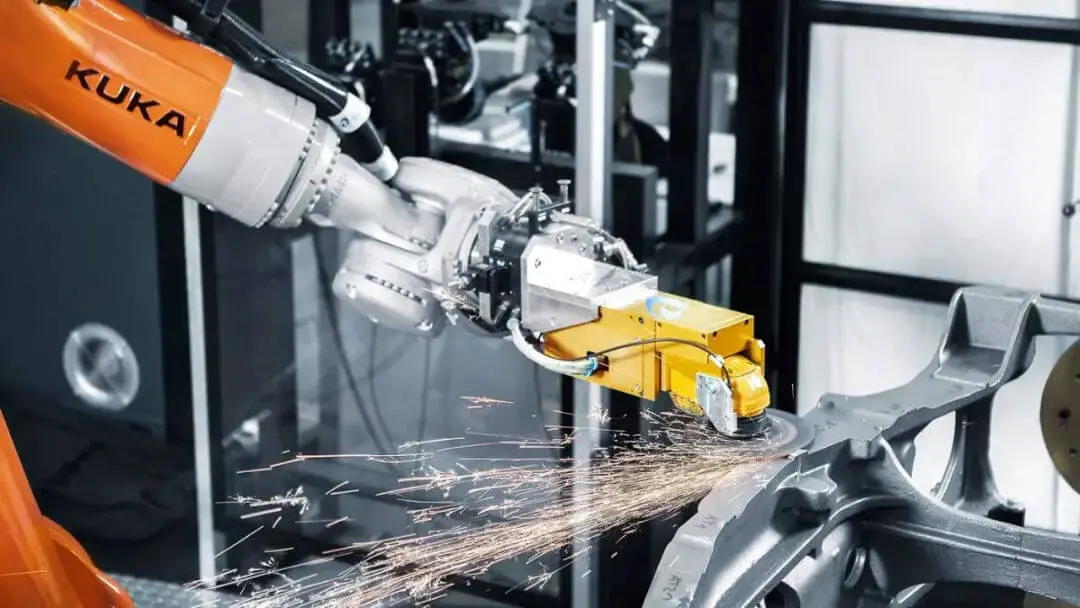

The deburring robot is the result of a combination of various disciplines, including mechanical and precision machinery, microelectronics and computers, automatic control and drive, sensors and information processing, and artificial intelligence. It represents the latest advancements in these fields.
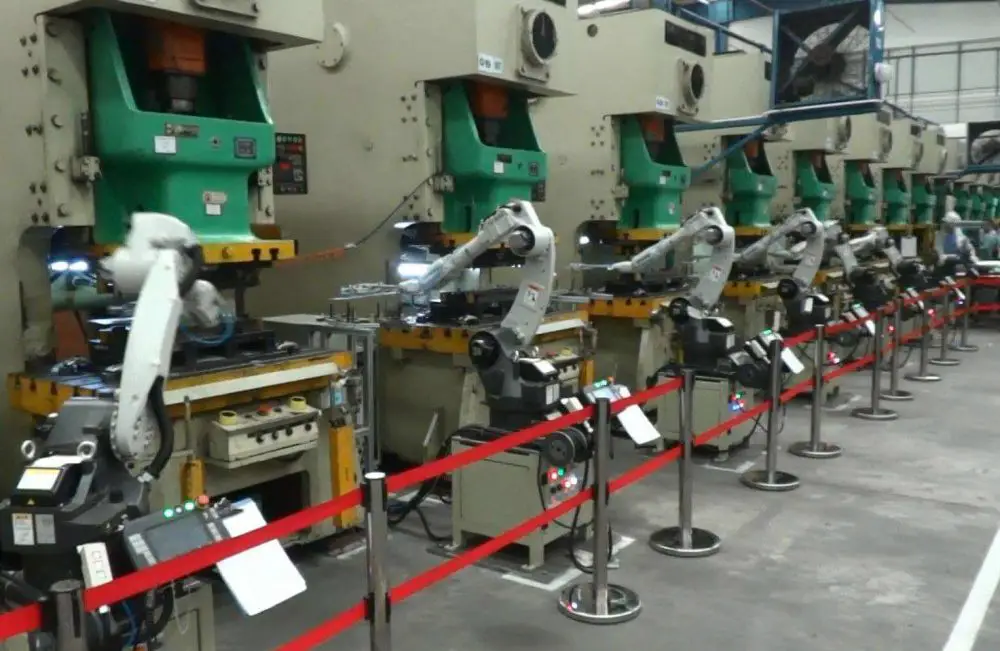

Stamping robots, used in manipulators, enhance automation in the transfer of materials, loading and unloading of workpieces, tool changes, and machine assembly. This results in increased labor productivity, reduced production costs, and a faster pace of industrial production mechanization and automation.

The use of robots in gluing and dispensing has significantly improved efficiency, saving a considerable amount of manpower and reducing labor costs. The investment in this technology will typically be recouped within a year of operation, and the robot will continue to function for at least ten years with proper maintenance.
As high-volume, fully automated gluing lines become more prevalent, the market outlook and development potential for gluing systems are expected to grow.

Assembly robots are a crucial component of flexible automated assembly systems and consist of a robot operator, controller, end-effector, and sensing system. The operator structures come in various types, including horizontal joint, right angle coordinate, multi-joint, and cylindrical coordinate.
The controllers typically utilize multi-CPU or multi-stage computer systems to control motion and perform motion programming. The end-effectors are designed to adapt to different assembly objects, such as grippers and wrists.
The sensing system collects information regarding the interaction between the assembly robot, its environment, and the assembly object.

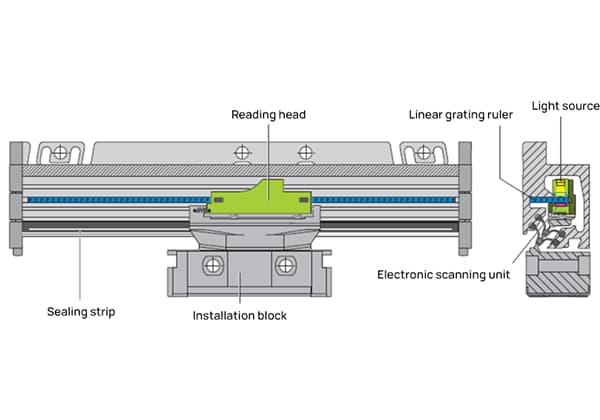
Robotic vision is a crucial aspect of any robotic system. It allows robots to acquire two-dimensional images of their environment through the use of vision sensors, which are then analyzed and interpreted by vision processors. The processed information is then translated into symbols, enabling the robot to recognize objects and determine their location.

Spraying robots, also referred to as spray painting robots, are industrial robots that can automate the process of spray painting or applying other coatings.
The main benefits of using spray painting robots include:
(1) Exceptional flexibility and a wide range of work capabilities.
(2) Improved spray quality and material utilization.
(3) Easy operation and maintenance, with offline programming capabilities that significantly reduce commissioning time in the field.
(4) High equipment utilization rate, with spray robots typically having a utilization rate of 90% to 95%.
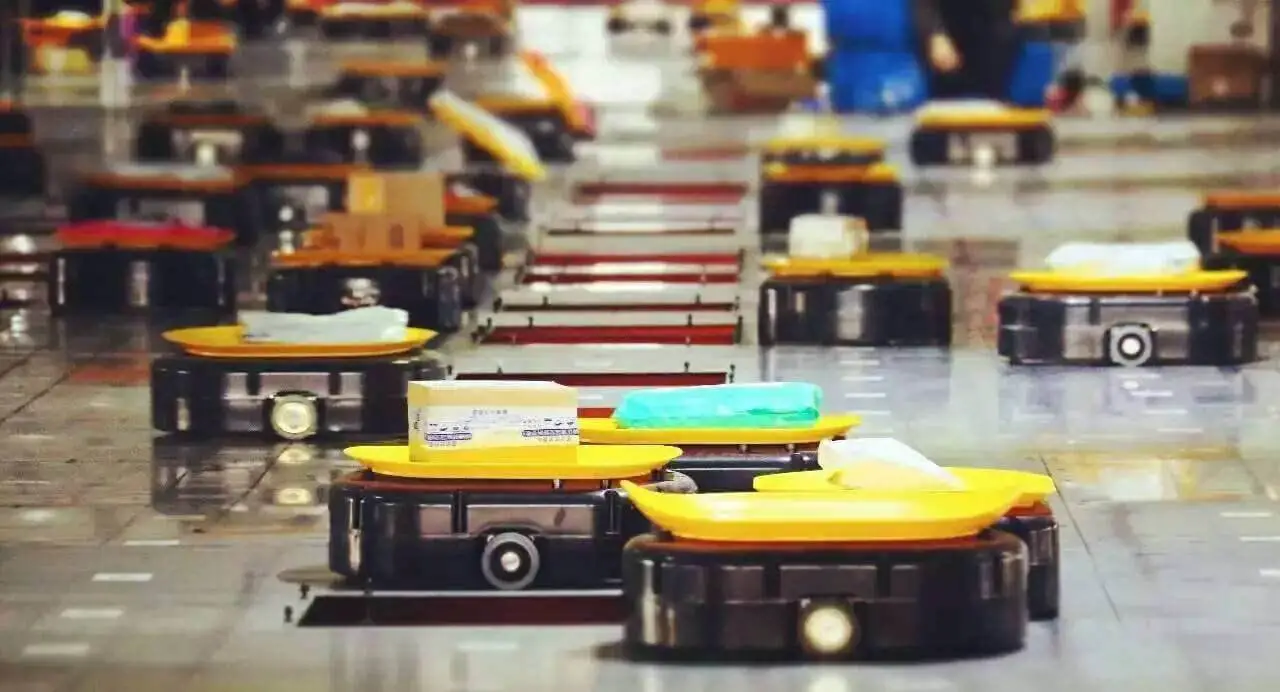

A sorting robot is a robot that utilizes sensors, objective mirrors, and electron optics systems to efficiently sort goods.
Automatic sorting robots have become widespread in their use. For example, Japan has developed an automatic apple dispenser that can sort up to 540 apples per minute based on color, shine, and size, and distribute them into different containers.