In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, choosing the right industrial robot can make or break your business. With a dizzying array of options available, how can you ensure you’re making the best decision? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the top four industrial robot manufacturers, exploring their unique strengths, technologies, and market positions. Get ready to discover valuable insights that will help you select the perfect robotic solution for your needs.

In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, industrial robots have become an indispensable asset for businesses seeking to enhance productivity, precision, and competitiveness. However, with the myriad of brands and models available, selecting the optimal robot for specific applications can be a complex process requiring careful consideration of technical specifications, performance capabilities, and integration potential.
This comprehensive analysis focuses on the four dominant industrial robot manufacturers that collectively command over 70% market share in China’s robotics sector: FANUC, KUKA, ABB, and YASKAWA Electric. Each of these industry leaders has carved out unique technological niches and expertise, making a nuanced understanding of their offerings crucial for informed decision-making in robotic system implementation.
ABB, renowned for its advanced control systems, offers robots with exceptional precision and adaptability, particularly suited for complex assembly and material handling tasks. KUKA’s strength lies in system integration and on-body production, providing innovative solutions for automotive manufacturing and other high-volume production environments. FANUC, leveraging its expertise in CNC systems, excels in developing robots with superior motion control and repeatability, ideal for machining and fabrication processes. YASKAWA, with its mastery of servo motors and motion controllers, delivers robots known for their speed, efficiency, and reliability across a wide range of applications.

The industrial robotics landscape is evolving rapidly, with manufacturers constantly pushing the boundaries of automation technology. Whether you’re in automotive manufacturing, electronics production, or logistics operations, selecting the right industrial robot is crucial for optimizing your processes and maintaining a competitive edge. This comprehensive guide examines the leading industrial robot manufacturers, providing in-depth analysis of their core competencies, cutting-edge technologies, and market positioning.
Each brand featured here has demonstrated excellence in specific areas of robotics, from collaborative robots (cobots) to heavy-duty industrial manipulators. We’ll explore their unique offerings, technological innovations, and how they address the diverse needs of modern manufacturing and logistics environments. Additionally, we’ll provide insights into their market presence and industry-specific solutions to help you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational requirements and long-term automation strategy.
As you read through this curated list of top industrial robot manufacturers, consider factors such as:
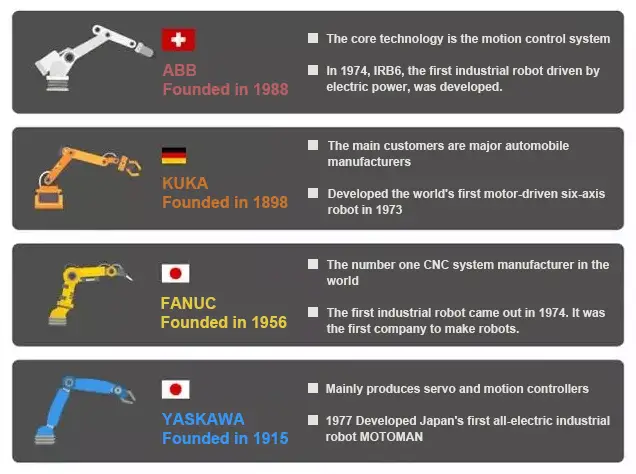
| Company | Country | Business | Advantage | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KUKA | Germany | Welding equipment, robot body, system integration, logistics automation | KUKA, known as the ‘purest’ robotics company, has its core customers in the automotive industry including Mercedes-Benz and BMW, and serves a wide range of industries in high-end manufacturing. Its robots use an open operating system and North America is its largest market globally. | Automotive Manufacturing |
| ABB | Switzerland | System integration business offerings include power products, power systems, low voltage products, discrete automation, motion control, and process automation. | The powerhouse of motors and automation equipment, ABB boasts exceptional advantages, robust system integration capabilities, and superior core technology in motion control. China has become the company’s second-largest market globally. | Electronic and electrical, logistics handling |
| FANUC | Japan | CNC system, automation, robot | FANUC focuses on the field of CNC systems and is known for its standardized programming and user-friendly operation. The company has the ability to produce core components in-house, which leads to strong profitability, except for the reducer. | The automotive industry, electrical and electronic |
| YASKAWA | Japan | Electric motor equipment, motion control, servo motor, robot body | Japan’s first company to produce servo motors, YASKAWA is a typical integrated robotics enterprise with close coordination among its various business departments. The company’s key components, such as servos and controllers, are self-sufficient and cost-effective. | Electronic and electrical, transportation |

Country: Switzerland
Founded: 1988
About the company:
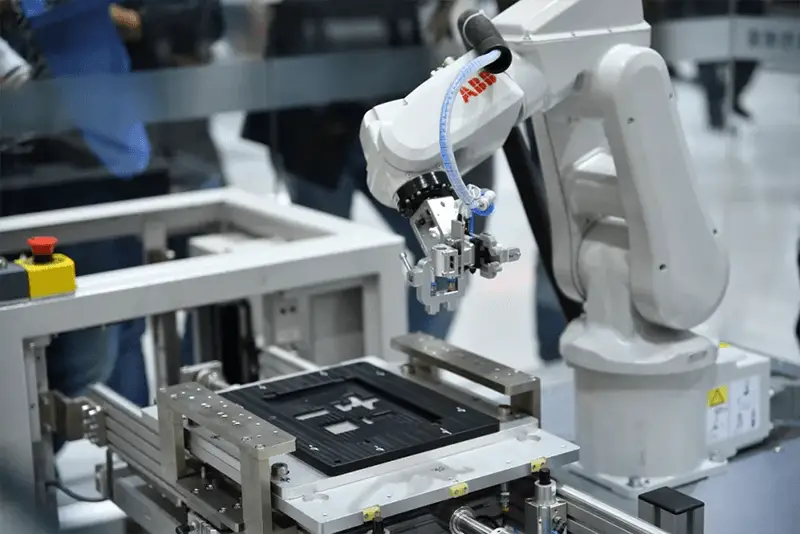
ABB, headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, is a renowned company operating in five key areas: power products, discrete automation, motion control, process automation, and low voltage products. It is known for its expertise in power and automation technology and places a strong emphasis on the robustness of its robots. ABB is recognized for the accuracy of its six-axis robots, even if its single-axis speed may not be the fastest.

Core areas
ABB is renowned for its expertise in advanced motion control technology, which forms the core and most challenging aspect of robotics. The company’s strength in this domain enables it to continuously enhance robot performance across critical parameters such as precision, speed, cycle time, and programmable flexibility. This results in significant improvements in production quality, efficiency, and reliability across diverse industrial applications.
Technology: Sophisticated algorithms drive performance at a premium
ABB, headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, is a global leader in power and automation technology. The company operates across five major business segments: power products, discrete automation, motion control, process automation, and low voltage products. ABB’s core competency lies in its cutting-edge motion control systems, which are widely recognized as the most complex and crucial aspect of advanced robotics.
ABB’s proprietary motion control technology significantly enhances robot performance through improvements in path precision, dynamic motion speed, optimized cycle times, and highly programmable designs. This translates to substantial gains in production quality, operational efficiency, and long-term reliability. The company’s state-of-the-art control cabinets are equipped with RobotStudio software, offering advanced 3D simulation capabilities and real-time online functionality. These systems support a wide array of industrial bus interfaces and seamlessly integrate with various welding and cutting power supplies, as well as PLCs from multiple manufacturers. The control cabinets feature fully adjustable parameters, including current, voltage, speed, and oscillation, enabling the creation of complex, application-specific motion trajectories.
While ABB robots equipped with these high-performance control systems command a premium price point and often have longer lead times compared to other major brands, the company’s unwavering focus on overall robot design quality and performance makes it a preferred choice for industries demanding uncompromising reliability and precision.
It’s noteworthy that ABB’s expertise in power electronics, particularly in inverter technology, has led to its widespread adoption in power stations and inverter installations across China, further solidifying its reputation in the energy sector.
Domestic market analysis
ABB’s strategic approach in the Chinese market emphasizes forging strong partnerships with key players in the 3C (Computer, Communication, and Consumer Electronics) and home appliance industries, including collaborations with industry giants such as Huawei, Changhong, and Topstar. These partnerships underscore the critical importance of the 3C sector to ABB’s growth strategy and highlight the company’s role as an innovation leader and trendsetter in this rapidly evolving industry.
Looking ahead, ABB is poised to integrate advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT connectivity, and big data analytics into its product portfolio. The company is increasingly focusing on developing application-specific solutions and strengthening its relationships with system integrators to enhance the development of comprehensive, integrated automation solutions tailored to the unique needs of the Chinese market.

Country: Germany
Founded: 1898
About the company:
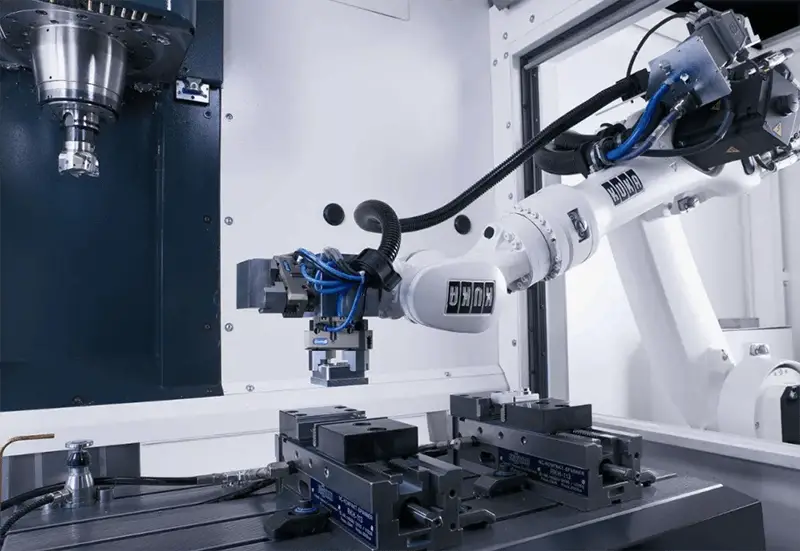
KUKA, founded in Augsburg, Germany in 1898, initially focused on interior and urban lighting. However, it quickly expanded into other areas. Its primary customer base is the automotive industry, and KUKA is dedicated to providing advanced automation solutions for various industrial processes, including brain surgery and radiography in hospitals.

Core areas
KUKA robots are extensively deployed across diverse industries, including automation, metal processing, food production, and plastics manufacturing. Their versatility extends to crucial tasks such as material handling, precision processing, spot welding, and arc welding. KUKA’s advanced robotic systems are particularly renowned for their adaptability in complex manufacturing environments, offering solutions for both high-volume production and customized applications.
Technology: User-friendly operation with reliability considerations
The acquisition of KUKA by Midea marked a significant milestone in the robotics industry. In terms of market positioning, KUKA is often equated to BMW in the automotive world, while ABB is likened to Mercedes-Benz, both representing premium segments of industrial robotics. While KUKA robots are known for their high-end capabilities, industry data suggests a higher return rate compared to competitors like ABB and FANUC. Some reports indicate a higher frequency of technical issues with KUKA robots, which merits consideration in long-term reliability assessments.
Despite these challenges, KUKA maintains a strong market presence, particularly in domestic sales. This is largely attributed to the ease of secondary development and integration of their robotic systems. A standout feature is KUKA’s user-friendly human-machine interface (HMI), which significantly reduces the learning curve. Operators with minimal technical background can become proficient in basic robot operations within a day – a stark contrast to some Japanese robot brands known for more complex control systems and steeper learning curves.
KUKA’s expertise shines particularly in the heavy-duty robotics segment. For robots with payloads of 120 kg or more, KUKA and ABB dominate the market share. In the ultra-heavy-load category of 400-600 kg payload capacity, KUKA leads in sales, showcasing their engineering prowess in handling demanding industrial applications.
Domestic market analysis
KUKA is actively expanding its service network across China, with a strategic focus on penetrating the southwestern regions. The company is aligning its future growth strategy with the burgeoning automotive equipment sector, leveraging its strengths in heavy-duty robotics and automation solutions. The Midea acquisition has reshaped both KUKA’s market positioning and Midea’s industrial portfolio, creating ripple effects throughout the robotics industry. The synergy between Midea’s manufacturing scale and KUKA’s technological expertise promises intriguing developments in industrial automation and smart manufacturing solutions.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1956
About the company:
FANUC was founded in 1956 and introduced its electro-hydraulic stepper motor just three years later. As microelectronics, power electronics, and computing technology rapidly advanced in the 1970s, FANUC decided to pivot from its successful electro-hydraulic stepper motor products. In 1976, the company successfully developed a CNC system and later teamed up with Siemens to create a high-level CNC system. Today, FANUC is recognized as one of the world’s leading companies in the design and manufacture of CNC systems.

Core areas
ANUC is a globally recognized professional manufacturer of CNC systems. Its industrial robots are unique in comparison to those of other companies, characterized by their convenient process control, smaller base size for the same type of robot, and distinctive arm design.
Technology: very high accuracy, but not overload
FANUC is a globally recognized professional manufacturer of CNC systems, and its industrial robots stand out from those offered by other companies. The company’s journey in CNC systems started in 1956 when a group of innovative Japanese technologists established a research team in response to the advent of the 3C era. Their efforts resulted in the development of highly precise industrial robots, with reports indicating that FANUC’s multi-functional six-axis small robots have repeatable positioning accuracy of ±0.02mm.
FANUC’s industrial robots are unique in their convenient process control, smaller base size for the same type of robot, and innovative arm design. Additionally, the company has integrated blade compensation, a feature used in CNC machine finishing, into its robots, enabling them to perform inward cuts during the finishing process. This cannot be achieved without secondary development in YASKAWA robots.
While FANUC is well-known for its accuracy, it has limitations in terms of robot stability. If its robots operate at full load and reach 80% speed, an alarm will be triggered, indicating limited overload capacity. As a result, FANUC excels in light-load, high-precision applications, which explains the success of its miniaturized robots (weighing less than 24 kilograms).
Domestic market analysis
FANUC’s strategy is distinct from others as it focuses on entering markets with high demand, particularly the Chinese market which has significant growth potential. In China, 55% of FANUC’s industrial robot sales are used in the general manufacturing industry, with the top three industries being home appliances, logistics, and electrical and electronics. FANUC is currently the largest robot brand in terms of total market sales, relying on an open market approach instead of relying on the sales of a few large customers.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1915
About the company:
Founded in 1915, YASKAWA is Japan’s largest industrial robotics company and is headquartered in Kitakyushu Island, Fukuoka. In 1977, the company made history by developing and producing Japan’s first fully electrified industrial robot, utilizing its own motion control technology. Since then, YASKAWA has continued to innovate and develop various automated robots for tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, and handling, solidifying its position as a leader in the global industrial robot market.

Core areas
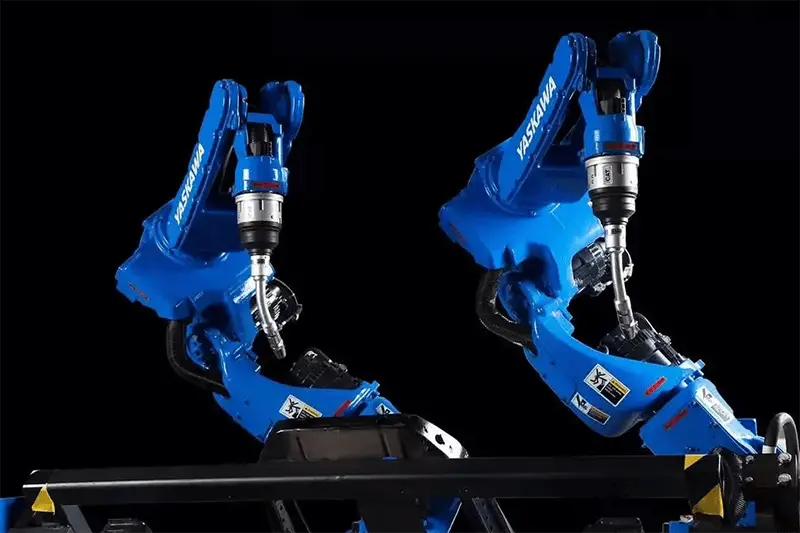
YASKAWA is a leading producer of servo and motion controllers, which are essential components for manufacturing robots. The company has designed and manufactured a variety of automated robots for tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, and handling.
YASKAWA’s core industrial robotics offerings include spot and arc welding robots, paint and processing robots, LCD glass plate transfer robots, and semiconductor chip transfer robots. Additionally, YASKAWA was one of the pioneers in introducing industrial robots into the semiconductor production industry.
Technology: good stability, but slightly less accuracy
With nearly a century of expertise in electric motor technology, YASKAWA has a global market dominance in the production of AC servo and inverter products. In 1977, the company made history by developing Japan’s first fully electric industrial robot, focusing on maximizing the motor’s inertia for increased stability and load handling capabilities. As a result, YASKAWA robots can operate at full speed and load without triggering an alarm and can even handle overload operation. This makes YASKAWA a popular choice in heavy-duty robotics applications, such as the automotive industry. However, compared to FANUC robots, YASKAWA robots have a lower level of precision. If precision is a requirement, customers tend to choose FANUC. However, YASKAWA offers a clear price advantage, with lower prices compared to the other major brands and a high price-performance ratio. For instance, YASKAWA’s welding robots with welding kits are priced between 130,000-140,000 and the company adopts a mass production approach, unlike Panasonic’s robots.
Domestic market analysis
Recently, YASKAWA has been actively expanding its presence in the domestic market through the construction of new robotics centers, increased investment in factories, and the formation of a joint venture with the United States to accelerate the localization of its services.
There is a large demand for robots in China and the United States is a significant player in the home appliance industry, providing YASKAWA with opportunities for growth in sales.
Despite challenges in the Japanese market for its service robots, particularly in the medical robotics sector, YASKAWA remains optimistic about the potential for new growth in the domestic service robot market.
As the market becomes increasingly competitive, it is becoming more common for major robotics companies to seek partnerships with larger application-based companies. This trend is expected to continue in the future.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1942
About the company:
Seiko Epson Corporation, founded in May 1942 and headquartered in Suwa, Nagano, Japan, is a well-known advanced company in the digital imaging field globally.
The Epson Group is committed to providing innovative digital imaging technologies and solutions to its customers through a culture of innovation and creativity that enhances its overall value as a company.
In recent years, the company has established production and R&D facilities in 32 countries across five continents and has business and service outlets in 57 countries around the world.
With 94 companies globally, the Epson Group employs over 72,000 people worldwide.
Epson China:
Seiko Epson Corporation has been present in China since the 1980s and has gone through three phases of development: trade exchanges, investment and factory construction, and expansion. Over the past 40 years, Epson has built a comprehensive network of manufacturing, sales, and service facilities.
Epson (China) Co., Ltd. was established in 1998, with its headquarters located in Beijing and twelve branches across the country. The regional headquarters is responsible for managing Epson’s investments and business development in China.
Epson’s operations in China primarily consist of information technology products such as printers, scanners, projectors, electronic components, and industrial robots. These products are popular among Chinese consumers due to their high quality, energy efficiency, and environmentally friendly features.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1955
About the company:
Yamaha Engine Co., Ltd., established on July 1, 1955, is a professional manufacturer of motorcycles. Since 1960, the company has expanded its product line to include motorboats, outboard engines, and automobile engines.
Yamaha Engine Co., Ltd. has been ranked among the top 500 companies in the world several times. With factories and operating institutions worldwide, the company invested $1 billion in the Zizhu Science Park in Minhang District, Shanghai in 2006 to establish Yamaha Engine Trading (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., which primarily sells Yamaha products manufactured in China to overseas markets.
In 2006, Yamaha Engine intensified its research and development of the Yamaha Electric Bicycle and has recently begun selling it across all provinces in China. In addition to its motorcycle business, Yamaha Engine has diversified into other industries, including the boat business, power product business, automobile engine business, intelligent chemical plant equipment business, aviation business, and PAS business, extending its reach from land to sea and even to the sky.
Today, Yamaha Engine Co., Ltd. is not only involved in the motorcycle industry but also in a variety of other industries.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1896
About the company:
Kawasaki Heavy Industries began producing industrial robots in Japan in 1969, marking the start of commercial mass production of these machines. With over 50 years of experience in the field of robotics technology, Kawasaki uses advanced methods to continuously develop high-quality and first-class industrial robots and provide high-value added projects and services.
The Robotics Business Department, based in Akashi, Japan, has offices and service centers throughout the country to support customers with technical assistance. Kawasaki’s subsidiaries and dealers in overseas markets are also dedicated to meeting the sales, service, and engineering needs of their customers.
In 2006, Kawasaki Robotics (Tianjin) Co., Ltd. was established in the Tianjin Economic and Technological Development Zone in China and is fully owned by Kawasaki Heavy Industries. It is responsible for sales, after-sales service (maintenance, repair, etc.), and technical support of Kawasaki’s industrial robots in China.
Kawasaki robots are used in various industries, including logistics, beverages, food, fertilizers, solar energy, and coal tiles. The company offers a wide range of palletizing and handling robots, as well as professional after-sales services and advanced technical support tailored to meet the specific needs of their customers’ workshops.
In addition, Kawasaki has a well-stocked inventory of parts, ensuring timely delivery of required accessories to customers. The company also has display spraying robots, welding robots, and testing rooms for spraying, providing customers with various related services.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1928
About the company:
Nachi is a comprehensive manufacturing company that produces a wide range of products, from raw materials to machine tools. With its expertise in machining, unmanned robots, bearings, hydraulic parts, and other functional components, Nachi has made significant contributions to the growth of the manufacturing industry.
The company is dedicated to enhancing its product line with high precision and powerful features, and to strengthening its brand. As a hub for manufacturing, sales, and technical engineering services, Nachi has established the “Nachi China Business Center.”
Nachi BUERYUE (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd., Nachi’s core subsidiary in China, provides world-class products and services to the Chinese manufacturing sector and conducts business operations. The Zhangjiagang Base, which is set to be completed next year, will feature an exhibition hall, the Nachi Galaxy China, displaying Nachi products and their industrial chains.
In addition to precision cutting tool grinding services, Nachi’s manufacturing plants also produce cutting tools, ball bearings for automobile air conditioners, hydraulic motors and stations, and functional parts for automobile drive systems.
Nachi is continuously exploring ways to establish and grow its Chinese business. Nachi (China) Co., Ltd. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Japanese company located in Shanghai, with its main factory located in Toyama, Japan.
Since its establishment in 1928, Nachi has adhered to the philosophy of “contributing to the growth of the world’s manufacturing industry” and continuously combined its core technologies to drive research and development. Today, Nachi’s main products include bearings, cutting tools, machine tools, hydraulic equipment, automatic production robots, special steel, ultra-precision machinery for the IT industry, and environmental systems.
Nachi operates a Tokyo News Agency and has production bases in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Greater China, as well as permanent representative offices and sales outlets globally. This enables the company to stay up-to-date with market trends and provide prompt services to customers worldwide.
Nachi has established a trading company and production factory in Jiading, Shanghai, and is seeking talented individuals from the community to join its growing team. The company offers competitive salaries, benefits, and opportunities for personal development based on the candidate’s experience and capabilities.

Country: China
Founded: 1993
About the company:
Estun Automation, listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange with stock code 002747, was founded in 1993. The company operates according to the principles of “integrity, focus, and co-growth” and is dedicated to independently researching and developing core technologies, in order to establish a strong foundation for the company’s globalization and become an internationally respected enterprise.
Thanks to its focus on the full automation ecosystem, its R&D investment of around 10% of its annual revenue, and the strong support of the global resource platform established through international expansion, Estun has successfully developed three core businesses: industrial automation products, industrial robot products, and industrial digital products.
As one of the first Chinese companies to independently develop AC servo systems, the industrial automation product line offers a complete range of AC servo systems, frequency converters, PLCs, touch screens, visual products, and motion control systems, along with motion control solutions that feature the Trio control system and intelligent unit products that integrate robots. These solutions cater to customers’ automation needs, from single-axis to single-machine to complete units.
The industrial robot product line has grown rapidly with the support of the company’s independent core components, offering a comprehensive series of specifications, mainly comprising of six-axis robots with a load capacity range of 3kg to 600kg and over 54 types. These robots serve a variety of industries, including new energy, welding, metal processing, 3C electronics, engineering machinery, aerospace, and more.
In 2021, Estun entered the field of industrial intelligence and digital manufacturing, offering customers remote access platforms for automation equipment and digital value-added services, including equipment data acquisition and edge computing, operation monitoring, process quality monitoring, and digital management services to improve production efficiency and material consumption control.
Becoming an international Chinese enterprise is Estun’s core development strategy. In addition to subsidiaries in Hubei, Guangdong, and Shanghai, the company has wholly-owned or holding companies abroad, including Trio in the UK, Cloos in Germany, M.A.i in Germany, an Italian Research and Development Center, and Barrett in the US. Estun’s welding robots and rehabilitation robots have a leading position in the world, providing a strong foundation for the company’s international development strategy.
In the future, Estun will continue to prioritize creating value for customers and helping them grow, focusing on industry-specific solutions and featured products, serving prominent customers in the industry, making full use of the company’s motion control + robot synergies, and providing more competitive integrated automation solutions for the industry. The company will forge its own unique development path.

Country: Japan
Founded: 1921
About the company:
The Mitsubishi Electric Group offers a diverse range of high-quality products and services for various needs, including home, office, factory, and social infrastructure. Its business philosophy, “One Mitsubishi Electric,” aims to contribute to a better future for China and the creation of a better society.
To achieve this goal, the Mitsubishi Electric Group is committed to promoting its “One Mitsubishi Electric” initiative, which seeks to enhance its overall strength in China. In the future, the company will continue to listen to its customers’ needs and leverage its advanced technology and products to support the growth and development of Chinese society.
Mitsubishi Electric (China) Co., Ltd. (MEC), the Chinese head office of Mitsubishi Electric Co., Ltd., was established in 1997. MEC is responsible for formulating and executing China’s strategy, as well as managing enterprise risk, accounting and finance, human resources, public relations and publicity, legal affairs, information security, intellectual property, environmental protection, IT, production technology, research and development, and providing comprehensive support to group companies in China.
The company operates with a principle of “attention to the site and quick action,” which emphasizes understanding the situation on the ground and making rapid decisions and taking appropriate measures to respond.
Business Areas:
Industrial Automation:
Power Equipment:
Electromechanical Products for Rail Transit Vehicles:
Society & Public System:
Elevator & Escalator:
Household Air Conditioners:
Imaging Equipment:
Print Image Sensing:
Semiconductor & Devices:
Other Products:








