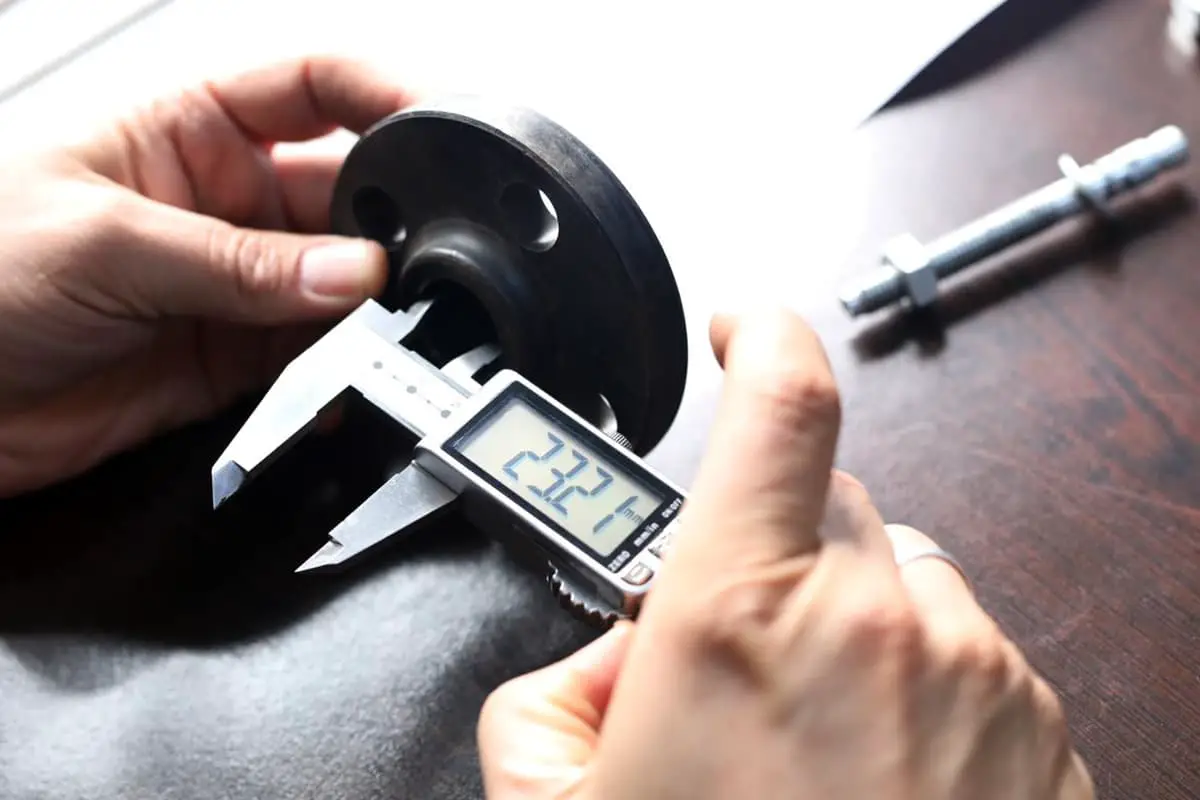
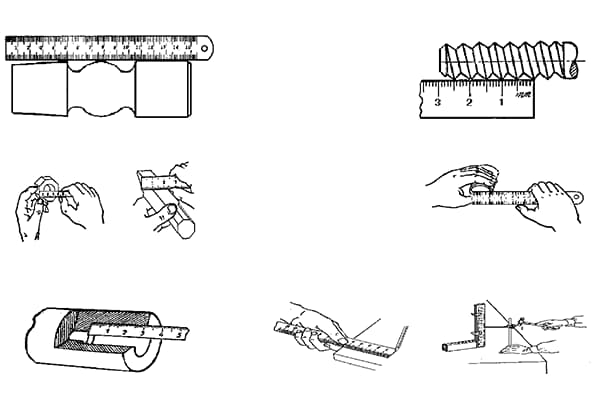
Have you ever struggled to measure the inside dimensions of an object with precision? The inside micrometer, a versatile tool for internal measurements, is essential for achieving high accuracy in mechanical processing. This article will guide you through its structure, technical data, and proper usage, ensuring you can confidently measure inner diameters and distances between parallel planes. By the end, you’ll understand how to handle and maintain this instrument to get reliable results every time.
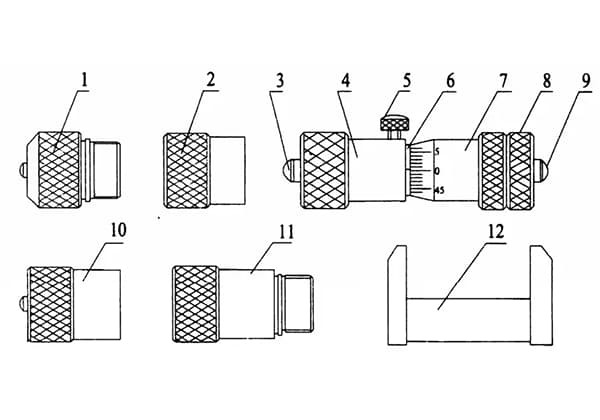
The Inside Micrometer is a universal internal dimensional measurement tool that uses the principle of a screw pair to read the distance between the spherical measuring surfaces at both ends of the main body. It is especially suitable for measuring the inner diameter, groove, and distance between two parallel planes in mechanical processing. The accuracy level measured is generally IT8-IT10 as specified in GB/T1800.3-1998.
The center of the measuring head of the inside micrometer is set with a hard alloy sheet, which extends the service life of the inside micrometer.
The driving mechanism of the inside micrometer is composed of a micrometer screw and a threaded shaft sleeve fixed in the fixed sleeve; the differential, calibration nut, and micrometer screw are fastened together as moving parts; The measuring head, threaded shaft sleeve, fixed sleeve, etc. are connected as a fixed part. The inside micrometer has a compact structure and stable and reliable measurement accuracy.
All accuracy indicators meet national standards.
Users can choose the appropriate micrometer based on their measurement needs or place special orders according to their requirements. The specific specifications and graduation values are shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| Series and indicators | Lower limit of measurement | |||
| 50 | 150 | 250 | Individual inner diameter | |
| Measuring range of micrometer head | 13 | 25 | 50 | 25 |
| Graduation value | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Specification (measurement range) | 50-250 50-600 50-1000 50-1500 | 150-1500 150-2000 150-3000 | 250-2000 250-3000 250-4000 250-5000 250-6000 | 50-75 75-100 275-300 |

| Technical data | ||||||
| Measuring range | 50~75 | 75~125 | >125~200 | >200~325 | >325~500 | >500~600 |
| Graduation value | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Indication error | ±0.006 | ±0.006 | ±0.008 | ±0.010 | ±0.012 | ±0.016 |
| Measure the spherical radius of the surface | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| The range of the micrometer screw is 13 | ||||||
| Check the size and deviation of the card board by 50 ± 0.002 | ||||||
Observe whether there are any defects on the appearance of the Inside Micrometer that may affect the measurement. Clean the measuring contacts, measuring heads, and measuring heads, rotate the differential to check if it rotates flexibly, and check if the locking device is firmly fixed.
Before using the Inside Micrometer, use the calibration clamp to calibrate the zero position of the micrometer head (combination of 3-9 components), and apply even force.
If there is a slight error, first tighten the locking screw and then loosen the calibration nut to align the zero position of the differential cylinder with the longitudinal line of the fixed sleeve, and finally tighten the calibration nut.
When connecting the connecting rod to the Inside Micrometer during use, first unscrew the nut on the threaded shaft sleeve, and then tighten the right end of the connecting rod to the left end of the threaded shaft sleeve.
When using the Inside Micrometer to measure the aperture, support the measuring surface of the measuring contact on the measured surface, adjust the differential, and swing the measuring surface on one side of the differential cylinder in the radial section of the hole to find the maximum size, and then swing it in the axial section of the hole to find the minimum size. This adjustment needs to be repeated several times.
Finally, tighten the locking screw, remove the Inside Micrometer, and read the measurement. When measuring the distance between two parallel planes, swing the Inside Micrometer in multiple directions and take the smallest size as the measurement result.
The Inside Micrometer can not only be used with a connecting rod for internal diameter and internal dimensional measurement but the micrometer head (combination of 3-9 components) can also be used as a single Inside Micrometer.
When using the Inside Micrometer, select the appropriate connecting rod from the provided connecting rod comparison table to form the required size to reduce cumulative errors. Also, connect the largest connecting rod to the micrometer head, and then sequentially connect to the measuring contact to reduce the bending of the axis after connection.
When using the Inside Micrometer to measure the aperture, at least one cross-section should be measured in two perpendicular directions. For deep hole measurements, the number of supporting faces should be appropriately increased.
Pay attention to the influence of temperature during measurement and prevent heat transfer from the hand or other heat sources. Especially for large-size measurements, special attention should be paid.
The support position of the Inside Micrometer during measurement should be correct. When measuring with a long-length Inside Micrometer, support it at 0.211L on both ends of the full-length size. This reduces deformation and minimizes measurement errors.
After measurement, the Inside Micrometer should be placed flat to avoid deformation of the instrument.
During use, be careful not to bump the micrometer. Before assembling the connecting rod, wipe clean all contact surfaces and measuring surfaces. After use, apply rust-proof oil to each measuring surface, and store them in a box.
The connecting rod comparison table is attached below.
Except for the (50-70) mm measurement range, all other components are connected to the micrometer head with a connecting sleeve.
| Comparison Table for Extension Rod of (50-600) mm Inner Diameter Micrometer | |||||||||
| Measuring range mm | Micrometer head 50mm | Measuring contact 13mm | Measuring head 20mm | Extension rod NQ1 13mm | Extension rod NQ2 25mm | Extension rod NQ3 50mm | Extension rod NQ4 100mm | Extension rod NQ5 150mm | Extension rod NQ6 200mm |
| 50~63 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 63~70 | 1 | ||||||||
| 70~83 | |||||||||
| 83~95 | 1 | ||||||||
| 95~108 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 108~120 | 1 | ||||||||
| 120~133 | – | – | 1 | ||||||
| 133~145 | 1 | ||||||||
| 145~158 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 158~170 | 1 | ||||||||
| 170~183 | 1 | – | 1 | – | – | – | 1 | – | – |
| 183~195 | 1 | ||||||||
| 195~208 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 208~220 | 1 | ||||||||
| 220~233 | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| 233~245 | 1 | ||||||||
| 245~258 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 258~270 | 1 | ||||||||
| 270~283 | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| 283~295 | 1 | ||||||||
| 295~308 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 308~320 | 1 | ||||||||
| 320~333 | 1 | – | 1 | – | – | 1 | – | – | 1 |
| 333~345 | 1 | ||||||||
| 345~358 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 358~370 | 1 | ||||||||
| 370~383 | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| 383~395 | 1 | ||||||||
| 395~408 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 408~420 | 1 | ||||||||
| 420~433 | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| 433~445 | 1 | ||||||||
| 445~458 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 458~470 | 1 | ||||||||
| 470~483 | 1 | – | 1 | – | – | 1 | – | 1 | 1 |
| 483~495 | 1 | ||||||||
| 495~508 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 508~520 | 1 | ||||||||
| 520~533 | – | – | – | 1 | |||||
| 533~545 | 1 | ||||||||
| 545-558 | – | 1 | |||||||
| 558~570 | 1 | ||||||||
| 570~583 | – | – | 1 | ||||||
| 583~595 | 1 | ||||||||
| 595~608 | – | 1 | |||||||