기계가 완벽한 모터를 어떻게 선택하는지 궁금한 적이 있나요? 이 글에서는 다양한 기계 작업에 적합한 서보 모터를 선택하는 흥미로운 과정을 소개합니다. 엔지니어가 기계의 효율성과 정밀도를 보장하기 위해 사용하는 계산과 기준을 자세히 알아보세요.

주어진:
서보 모터와 감속 기어, 구성품 회로도는 다음과 같습니다:
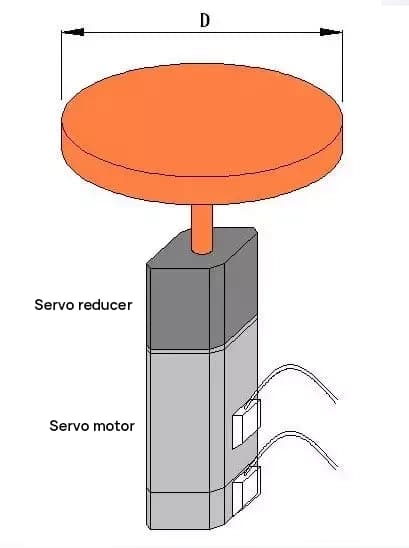
디스크 회전에 대한 관성 모멘트 계산하기
JL = MD2/8 = 50 * 502 / 8 = 15625 [kg-cm2]
기어 감속비가 1:R이라고 가정하면 서보 모터 샤프트에 반영되는 부하 관성은 15625/R입니다.2.
부하 관성은 로터 관성 J의 3배 미만이어야 한다는 원칙에 따라M 모터의
400W 모터를 선택한 경우 JM = 0.277 [kg-cm2],
그럼 15625 / R2 < 3*0.277, R2 > 18803, R > 137,
출력 속도 = 3000/137 = 22 [rpm],
요구 사항을 충족하지 않습니다.
500W 모터를 선택한 경우 JM = 8.17 [kg-cm2],
그럼 15625 / R2 < 3*8.17, R2 > 637, R > 25,
출력 속도 = 2000/25 = 80 [rpm],
요구 사항을 충족합니다.
이러한 유형의 전송은 저항이 최소화되므로 토크 계산이 무시됩니다.
주어진:
각 컨베이어 벨트 바퀴의 무게를 무시합니다,
이러한 부하를 구동하기 위한 모터의 최소 전력 요구 사항은 얼마입니까?
구성 요소의 개략도는 다음과 같습니다:
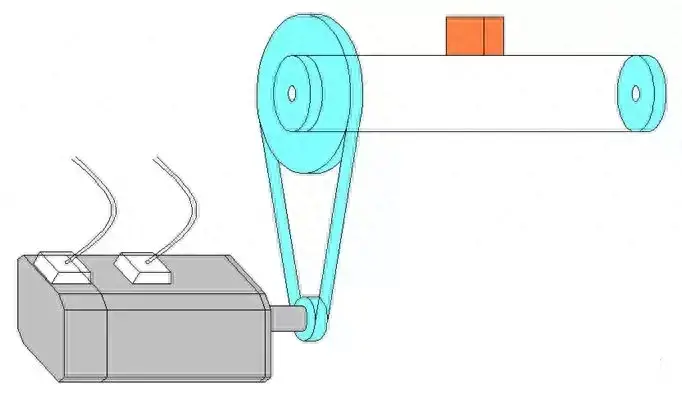
1. 모터 샤프트에 반영된 부하 관성 계산하기:
JL = M * D2 / 4 / R12
= 50 * 144 / 4 / 100
= 18 [kg-cm2]
부하 관성은 모터 로터 관성(JM)의 3배 미만이어야 한다는 원칙에 따라, 부하 관성은 모터 로터 관성(JM)의 3배 미만이어야 합니다:
JM > 6 [kg-cm2]
2. 모터 부하를 구동하는 데 필요한 토크를 계산합니다:
마찰을 극복하는 데 필요한 토크입니다:
Tf = M * g * µ * (D / 2) / R2 / R1
= 50 * 9.8 * 0.6 * 0.06 / 2 / 10
= 0.882 [N-m]
가속에 필요한 토크입니다:
Ta = M * a * (D / 2) / R2 / R1
= 50 * (30 / 60 / 0.2) * 0.06 / 2 / 10
= 0.375 [N-m]
서보 모터의 정격 토크는 T보다 커야 합니다.f보다 커야 하며, 최대 토크는 Tf + Ta.
3. 필요한 모터 속도 계산하기:
N = v / (πD) * R1
= 30 / (3.14 * 0.12) * 10
= 796 [rpm]
주어진:
부하 요구 사항을 충족하는 최소 전력의 서보 모터를 선택하세요,
구성 요소 다이어그램은 다음과 같습니다:

1. 모터 샤프트로 변환된 부하 관성 계산
모터 샤프트로 변환된 무게의 하중 관성
JW = M * (PB / 2π)²
= 200 * (2 / 6.28)²
= 20.29 [kg-cm²]
나사의 회전 관성
JB = MB * DB² / 8
= 40 * 25 / 8
= 125 [kg-cm²]
총 부하 관성
JL = JW + JB = 145.29 [kg-cm²]
2. 모터 속도 계산
필요한 모터 속도
N = V / PB
= 30 / 0.02
= 1500 [rpm]
3. 모터 부하를 구동하는 데 필요한 토크 계산
마찰을 극복하는 데 필요한 토크
Tf = M * g * µ * PB / 2π / η
= 200 * 9.8 * 0.2 * 0.02 / 2π / 0.9
= 1.387 [N-m]
무게가 가속할 때 필요한 토크
TA1 = M * a * PB / 2π / η
= 200 * (30 / 60 / 0.2) * 0.02 / 2π / 0.9
= 1.769 [N-m]
나사가 가속할 때 필요한 토크
TA2 = JB * α / η
= JB * (N * 2π / 60 / t1) / η
= 0.0125 * (1500 * 6.28 / 60 / 0.2) / 0.9
= 10.903 [N-m]
가속에 필요한 총 토크
TA = TA1 + TA2 = 12.672 [N-m]
4. 서보 모터 선택
서보 모터의 정격 토크
T > Tf 및 T > Trms
서보 모터의 최대 토크
T최대 > Tf + TA
마지막으로 ECMA-E31820ES 모터가 선택되었습니다.