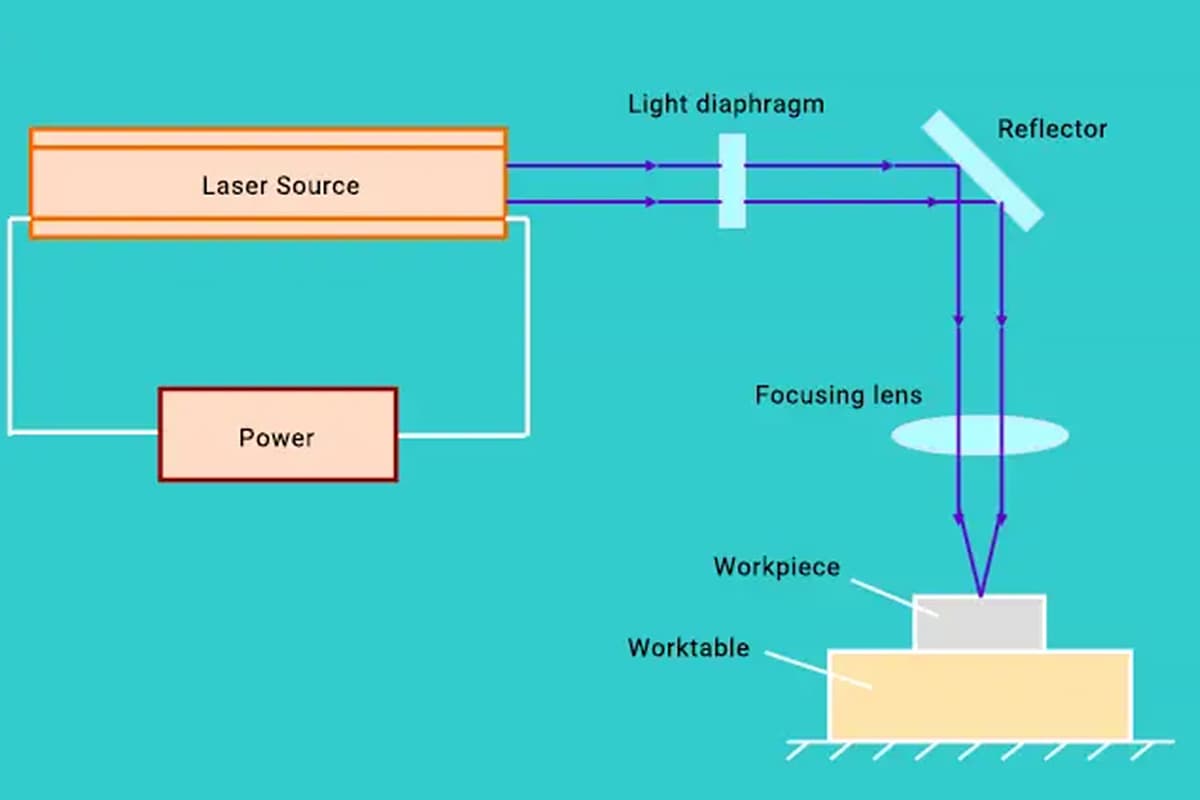
Have you ever wondered what makes a laser cutting machine tick? In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the inner workings of these high-precision machines that have revolutionized the metalworking industry. Our expert mechanical engineer will break down the key components, from the powerful fiber laser to the intricate cooling system, and explain how they work together to deliver unparalleled cutting performance. Get ready to gain a new appreciation for the technology behind these marvels of modern engineering!
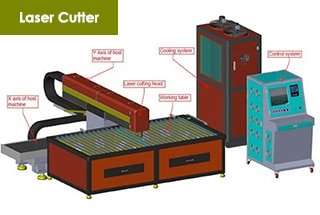
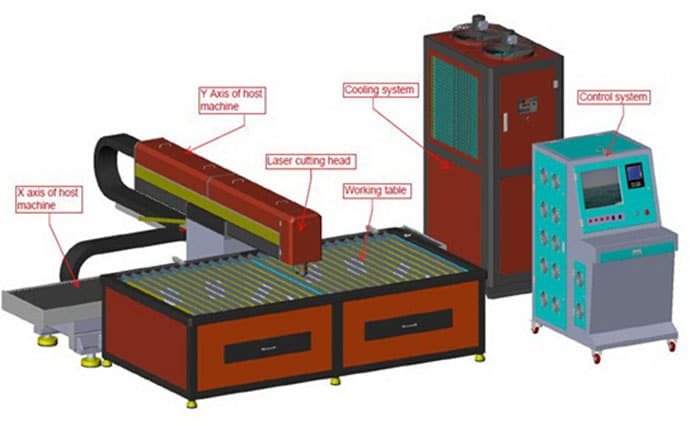
Laser cutting machines are complex systems composed of several key components, each playing a critical role in ensuring the machine’s operation, precision, and efficiency. Understanding these components is essential for selecting, operating, and maintaining a laser cutting machine effectively. Here are the primary components:
The fiber laser source is the core component of a laser cutting machine, responsible for generating the laser beam through diode emission and fiber amplification. This technology offers high conversion efficiency, longer service life, and lower maintenance costs. For example, IPG Photonics is known for its high-power fiber lasers, which are widely used in industrial applications due to their reliability and performance.
The laser cutting head focuses and directs the laser beam onto the material. It consists of a nozzle, focusing lens, and a focus tracking system. The head travels along a predefined cutting path and adjusts its height based on the material’s thickness and cutting method. RayTools and Precitec are notable manufacturers of high-quality laser cutting heads. For instance, the RayTools BM109 series is recognized for its precise focusing capabilities, which significantly enhance cutting accuracy.
The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system acts as the brain of the laser cutting machine. It controls the movement of the X, Y, and Z axes and the output power of the laser. The CNC system interprets CAD designs and converts them into precise cutting instructions, ensuring high precision and repeatability. Modern CNC systems, such as those from Siemens, offer advanced features like real-time monitoring and adaptive control, which improve cutting efficiency and accuracy.
Motors are vital for the motion system of the laser cutting machine. There are two main types:
The machine tool includes the bed, beam, worktable, and Z-axis system, all crucial for the machine’s stability and precision. Different configurations, such as gantry, cantilever, and beam types, cater to various industrial applications. For example, a gantry-type machine tool provides robust support for high-speed cutting, ensuring minimal vibration and high accuracy.
A cooling system, typically a water chiller, is essential for cooling the laser source, laser head, and other components. Effective cooling ensures stable performance and prevents overheating, which can damage the machine. For instance, a S&A CW-6200 water chiller can efficiently regulate the temperature of a high-power laser source, maintaining optimal performance even during prolonged operation.
The air supply system, comprising an air compressor, filter device, and air dryer, provides clean and dry air to the laser generator and optical path. Maintaining the optical path and mirrors with clean air is crucial for optimal performance. An Atlas Copco air compressor, combined with a high-efficiency air dryer, ensures that the compressed air is free of contaminants and moisture, protecting sensitive components.
Laser lenses, including full mirror, half mirror, and focusing lenses, are integral to the optical system. The quality of these lenses directly affects the laser’s output power and the machine’s overall performance. For example, II-VI Incorporated produces high-quality ZnSe focusing lenses that offer excellent transmission and durability, enhancing the cutting quality and extending the lens’s lifespan.
The power supply system connects the lasers, CNC machine tools, and other power systems, ensuring stable operation and preventing external power grid interference. A stable power supply is critical for maintaining consistent laser output and preventing fluctuations that could affect cutting quality.
The air compressor supplies and stores compressed air, while air-cooled dryers and filters ensure the air is clean and dry. This cleanliness is necessary for the proper functioning of the optical path and mirrors. For example, a Kaeser air compressor, paired with a desiccant air dryer, provides a reliable source of clean, dry air, which is essential for high-quality laser cutting.
An exhaust blower and dust collector are essential for removing debris and smoke generated during the cutting process. This ensures a clean working environment and compliance with environmental standards. A Donaldson Torit dust collector, for example, efficiently captures fine particles and fumes, protecting both the equipment and the operators.
Gas cylinders provide auxiliary gases, and the gas control system manages the gas flow during cutting. This system includes bottled gas, liquefied gas, and compressed air. Proper gas management is crucial for achieving clean cuts and preventing oxidation. For instance, using high-purity nitrogen as an auxiliary gas can prevent oxidation when cutting stainless steel, resulting in a smoother edge finish.
The control platform integrates all machine commands and settings, ensuring the laser cutter operates as expected for different materials and designs. Software interprets CAD designs and translates them into precise cutting instructions. Advanced control software, like those from Lantek, offers features such as nesting optimization and real-time monitoring, which enhance cutting efficiency and material utilization.
Understanding these components is crucial for anyone involved in the selection, operation, and maintenance of laser cutting machines, ensuring high accuracy, efficiency, and quality in various cutting applications.
The auxiliary equipment for laser cutters includes:
Let’s dive into it and I will split the laser cutter into 14 parts and explain each one in detail.

The mechanical part of the laser cutter is responsible for the movement in the X, Y, and Z-axes, including the cutting work platform. The stability of the machine tool is crucial for fiber laser cutting machines, as it directly impacts the cutting precision.
Currently, the most common machine tools in the market are the gantry type, cantilever type, and beam type.
Each type of machine tool has its own functions, such as beam type machine tools being mainly used by large manufacturers for material cutting, and 3D fiber laser cutting being mainly used in the automotive industry.
Motion control systems play a pivotal role in ensuring the precision and efficiency of laser cutting machines. These systems manage the movement and positioning of the laser beam relative to the workpiece, enabling accurate and intricate cuts.
Advanced motion control solutions employ polynomial corner blending and jerk control to maintain high accuracy, especially around corners, without compromising speed. For example, in the aerospace industry, these technologies are used to cut complex shapes from titanium sheets, ensuring smooth transitions and reduced mechanical stress, leading to improved cutting precision and smoother edges.
High-end laser cutting systems often integrate galvo scanners with linear motor stages. Galvo scanners steer the laser beam with high-speed mirrors, while linear motor stages move the workpiece in the X and Y axes. This combination allows for sub-micrometer precision and rapid acceleration, enhancing throughput and ensuring high-quality cuts. For instance, in the electronics industry, this technology is essential for cutting intricate patterns on printed circuit boards.
Gantry systems are a common configuration in laser cutting machines, featuring high-precision designs driven by linear motors in the XY axes. These systems provide dynamic stability and are essential for machining intricate designs such as stencils and printed circuit boards. They may utilize air-bearings, mechanical bearings, or hybrid designs, offering extreme mechanical stability and long travel ranges. In the automotive industry, gantry systems are used to cut precise shapes for body panels and other components.

A device that produces a laser light source is known as a laser generator. The laser generator is the main power source of laser equipment, similar to the engine in a car and is the most expensive component of fiber laser cutting machines.
Currently, the imported fiber laser generator brands in the market include German IPG, ROFIN, and British SPI, among others.
With advancements in technology, domestic laser brands such as Raycus and Max have also emerged, gaining recognition in the market for their high cost-performance ratio.
When comparing laser sources, it is essential to consider their efficiency, maintenance requirements, and cost. Fiber laser sources, such as those from Raycus and IPG, are known for their high efficiency, long service life, and low maintenance needs. For instance, fiber lasers can achieve an efficiency rate of up to 30-40%, significantly higher than the 10-15% efficiency typically seen in CO2 lasers. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and operational costs over time. CO2 laser sources, while versatile and capable of cutting a wide range of materials, generally have higher maintenance costs due to the need for regular alignment and cleaning of optical components. Fiber lasers are more suitable for metal cutting, offering superior performance and lower operating costs over time.

The laser lens is the most commonly used component in fiber laser cutting equipment. Various optical devices contain laser lenses, each serving a different purpose, such as full-reflection lenses, semi-reflection lenses, and focusing lenses.
The quality of the lens directly impacts the output power of the laser, thereby affecting the overall performance of the machine. While imported lenses have a longer lifespan and better cutting effect compared to domestic lenses, they are much more expensive.
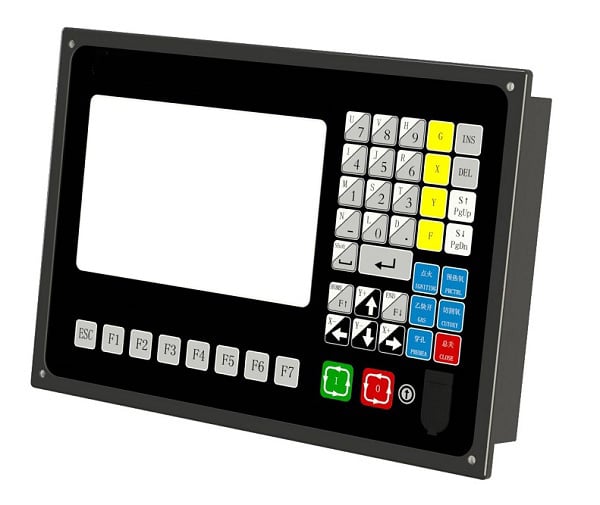

The control system is the primary operating system of the fiber laser cutting machine, which mainly controls the movements of the X, Y, and Z axes and regulates the output power of the laser. Its quality determines the stability of the machine’s operating performance.
The precision and cutting effect can be effectively improved through accurate control of the software.
The control panel is a crucial interface that allows operators to manage and control the laser cutting machine’s functions. It is designed to facilitate precise operations and ensure safety while interacting with the machine.
The control panel features buttons for maneuvering the laser lens assembly in various directions, such as left, right, up, and down. This capability is essential for accurate positioning, especially when setting up a new job or during maintenance. Operators must be cautious and avoid reaching into the laser cabinet while parts are in motion. Potential hazards include accidental burns from the laser beam or mechanical injuries from moving components. Ensuring the machine is powered down or in a safe mode before reaching inside can prevent these accidents.
The menu system, accessible through buttons like the “Z U” button, allows operators to perform various functions, including moving the honeycomb bed and setting autofocus. For example, to set up autofocus for a cutting job:
This process ensures the laser is correctly focused, leading to precise cuts and engravings.

The connection between the laser generator, the laser cutter, and the power supply system serves mainly to prevent interference from the external power network.
A regulated power supply prevents external power grid interference, maintaining the stability and precision of the laser cutting process. It ensures that the power supplied to the laser generator and other components is consistent and reliable.

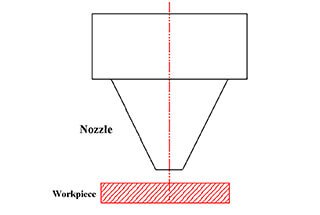
The cutting head is the laser output device of a fiber laser cutting machine, consisting of a nozzle, a focusing lens, and a focus tracking system.
The cutting head drive device, which consists of a servo motor, screw rod, or gear, moves the cutting head along the Z-axis as programmed.
However, the height of the laser cutting head must be adjusted and controlled depending on the material, thickness, and cutting method being used.
Laser cutting heads are vital components of a laser cutting machine, directing and focusing the laser beam onto the material being cut. Understanding the various parts and accessories of a laser cutting head is essential for achieving high-quality cuts and maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the machine.
The laser cutting head plays a critical role in the precision and quality of cuts. High-power laser cutting heads, like those from Germany Precitec, are designed for heavy-duty applications and offer advanced features such as auto-focus and collision protection. Auto-focus adjusts the focal length automatically for different materials and thicknesses, ensuring optimal cutting quality. Collision protection prevents damage to the cutting head by stopping the machine if it detects an obstacle. Raytools laser heads, commonly used in lower-power machines, are more cost-effective but may lack some of the advanced features found in higher-end models. The choice of cutting head should be based on the specific cutting requirements and the types of materials being processed.
Nozzle
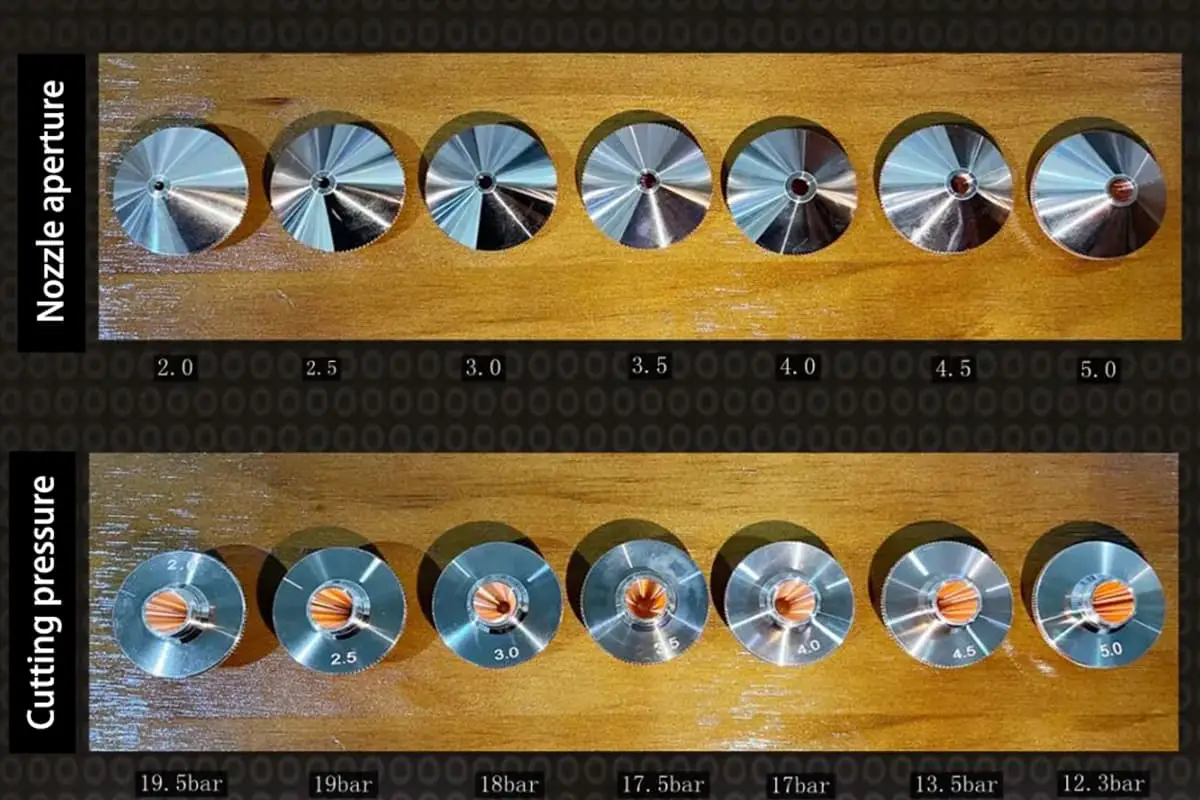
The nozzle directs the laser beam onto the material and aids in removing molten material and debris through the flow of assist gas (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or air). For instance, when cutting stainless steel, a small-diameter nozzle with nitrogen assist gas may be used to achieve a clean cut without oxidation.
Lenses
Lenses focus the laser beam to a fine point, increasing its intensity and enabling it to cut through the material. Different focal lengths, such as 2.5″ or 5″, are used depending on the material thickness and the required cutting precision. For example, a shorter focal length lens is ideal for cutting thin sheets of metal, while a longer focal length is better for thicker materials.
Protective Glass/Mirrors
Protective glass or mirrors shield the lens from contamination by debris and vapors generated during cutting. This prevents damage to the focusing lens, thus extending the lifespan of the laser cutting head. For instance, during the cutting of acrylic, protective glass helps maintain the clarity and effectiveness of the focusing lens.
Focus Tracking System
This system includes parts like servo motors and gears that enable the cutting head to move along the Z-axis according to the programmed cutting path. It ensures a consistent distance between the nozzle and the material, crucial for maintaining uniform cuts and preventing damage to the cutting head. For example, cutting uneven surfaces like corrugated metal requires an effective focus tracking system to maintain cut quality.
Height Sensor
Height sensors maintain a consistent distance between the nozzle and the material, ensuring optimal focus and preventing damage to the cutting head. This feature is particularly important for cutting materials with varying thicknesses, such as cutting a metal sheet with variable thickness across its surface.
Collimation Components
Collimation components straighten or collimate the divergent light transmitted from the laser source, ensuring the laser beam remains focused and directed accurately towards the material. For example, in fiber lasers, collimation is crucial for maintaining beam quality over long distances.
Ceramic Parts
Ceramic parts provide insulation and protection for the optical components, ensuring the longevity of the cutting head by withstanding high temperatures. These parts are essential in high-power applications where thermal management is critical.
Auto-Focusing Cutting Heads
These heads integrate sensors and motors to adjust the focus automatically, suitable for large and medium-sized platform cutting machines. They are capable of cutting thick materials like stainless steel and aluminum with good cutting quality.
Collimator Lens and Focusing Lens with Water Cooling
Some designs include water cooling for the collimator lens, focusing lens, and nozzle to enhance the cutting process and protect the components from overheating. This feature is crucial in high-power laser cutting applications to maintain optical performance.
Collision Protection Function
This feature prevents damage to the laser head when it collides with the workpiece, ensuring the longevity of the cutting head. For example, collision protection is essential when cutting complex shapes that may cause the head to come into contact with raised edges.
Sensors
Height sensors and capacitive sensors ensure the proper distance between the cutting head and the workpiece surface and detect the presence and position of the workpiece, providing feedback for precise alignment and positioning.

The process of controlling the whole cutting device.
The operating system of a laser cutting machine processes graphics and image files, converting them into precise control instructions. A user-friendly operating system with efficient nesting software can significantly enhance productivity and material utilization. When comparing operating systems, consider the ease of use, compatibility with various file formats, and the availability of advanced features such as real-time monitoring and adaptive control. Advanced nesting software optimizes material usage by arranging parts to be cut in a way that minimizes waste, thereby reducing costs.
High-performance motion controllers rely on fast and accurate closed-loop positioning stages that provide real-time position feedback. This feedback is essential for the precise triggering of the laser, ensuring cuts are made at the exact moments required for high-quality results. For example, in the medical device industry, real-time feedback is crucial for cutting tiny, precise components for surgical instruments.
The motor of the laser cutting machine is a crucial component of the motion system. The performance of the motor directly impacts the processing quality and production efficiency of the product.
Currently, the commonly used motors are the stepping motor and servo motor, which are selected based on the industry and processing object’s requirements.
Stepping motor: It has a quick start-up speed, responsive, and is suitable for engraving and cutting processing. They are affordable, with many brands offering different performance options.
Servo motor: It has a fast movement speed, smooth operation, high load-bearing capacity, and stable performance. It is ideal for industries and products with high processing requirements, providing smooth edge processing and fast cutting speed, though it is more expensive.
Servo motors are crucial for providing the necessary power and precision in laser cutting operations. Companies like Industrial Indexing Systems (IIS) offer advanced servo motors and controllers that meet the demanding requirements of laser cutting tasks. These motors ensure the finesse needed for intricate work while maintaining the strength for various cutting operations. Singular control solutions, such as those from Aerotech, combine high-precision motion control with position-synchronized laser triggering, ensuring consistent laser spot placement and superior part quality.
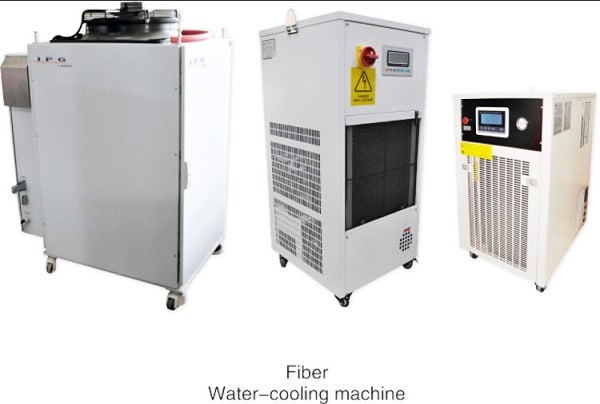

The Cooling System is used to cool the laser generator of a fiber laser cutting machine. The laser generator converts electrical energy into light energy, with a conversion rate of 20% in the case of a CO2 laser. The remaining energy is converted into heat.
The cooling water system removes the excess heat to keep the laser generator functioning properly.
The chiller also cools the external optical path reflector and focusing mirror to ensure stable beam transmission quality and prevent lens deformation or cracking due to overheating.
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining the optimal operating temperature of the laser source and other components. An effective cooling system not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the machine. When comparing chillers, consider the cooling capacity, energy efficiency, and compatibility with the laser cutting machine. Proper cooling is essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to decreased performance and potential damage to the laser components.
Water cooling is widely used due to its efficiency in heat dissipation. The system typically involves circulating water through the laser machine to absorb heat, which is then transferred to a radiator or heat exchanger where it is released into the atmosphere.
Laser chillers are specialized units designed to provide precise temperature control. They automate the cooling process and come in various types to suit different requirements.
When selecting a water chiller for a laser cutting machine, consider several factors to ensure optimal performance:
The chiller must have adequate cooling capacity to handle the heat load generated by the laser cutter. This is crucial for maintaining the operating temperature within the desired range.
The chiller should be compatible with the laser cutter’s specifications, including water flow rate and pressure requirements. Incompatibility can lead to inefficient cooling and potential damage to the machine.
Choosing energy-efficient chillers can reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Central chiller systems can be more efficient for facilities using multiple laser cutters.

The laser cutter’s working medium and auxiliary gas cylinders are included.
These gases serve as industrial supplements for laser oscillation and as auxiliary gases for the cutting head’s operation.

Provide and store compressed air.

The air supply system is used to provide clean and dry air to the laser generator and laser beam path, ensuring the normal operation of the pathway and reflectors.

The smoke and dust generated during the fabrication process must be filtered and treated to meet environmental protection standards.

Eliminate the leftover materials and wastes generated during processing.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
A laser cutting machine is composed of several essential parts, each crucial to its functionality and performance. The core component is the laser generator, also known as the laser source, which produces the laser beam used for cutting. Common types include CO2 lasers, YAG solid-state lasers, and fiber lasers, with fiber lasers being popular for their high efficiency and stability.
The laser cutting head is another vital part, containing a nozzle, focusing lens, and focus tracking system. It directs the laser beam precisely onto the material. The CNC system, or control system, manages the movement of the machine’s axes and regulates the laser’s power output, ensuring accurate and stable operation.
Motors, particularly servo motors and stepper motors, are integral to the motion system, enabling precise and smooth movements of the cutting head. The machine tool or bed frame provides the structural support and platform for material processing, with high precision and stability being crucial for accurate cutting.
Optical path components, including various mirrors and lenses, guide the laser beam to the cutting head. The quality of these optical components significantly affects the machine’s performance. A cooling system, often involving a water chiller, maintains the proper temperature of the laser generator and other critical parts, ensuring efficient operation.
The air supply system, comprising an air compressor, air storage tank, and gas cylinders, provides the necessary gases for laser operation and cutting processes. An exhaust and dust collection system, including an exhaust blower and dust collector, removes debris and filters smoke and dust, maintaining a clean working environment.
Finally, the power supply ensures stable electricity flow to the laser generator and CNC system, preventing interruptions and ensuring consistent performance. Auxiliary equipment such as stabilizers, gas storage tanks, and slag dischargers also play essential roles in supporting the overall functionality of the laser cutting machine. Together, these components enable the machine to perform precise and efficient cutting operations across various applications.
To maintain the laser cutting head effectively, several key steps and best practices must be followed, ensuring the longevity and precision of the laser cutting machine. Daily maintenance involves cleaning the protective lens with isopropanol or analytical alcohol (with a purity above 99.5%) to prevent water marks, and inspecting the lens holder and sealing ring, replacing the ring if damaged. Additionally, check the nozzle before each cutting operation to ensure it is clean and intact, and verify that the laser beam is centered by using scotch tape on the nozzle and adjusting the alignment if necessary.
Regular maintenance should include weekly cleaning of the cutting head and its components, using dustproof gloves, finger cots, long-fiber absorbent cotton swabs, ethanol, and a rubber air blower. The protective lens should be cleaned at least once a week, with the lens holder designed for easy maintenance. Ensure proper sealing between the QBH interface of the laser head and the optical fiber cable to prevent dust entry, and consider operating in a clean environment or using a breathing system.
Consumables such as the nozzle, ceramic ring, and protective lens should be replaced as needed, particularly if the nozzle is damaged or after a collision. Correct installation of the fiber head within the cutting head, ensuring it is horizontal and locked, is crucial. Proper sealing using qualified protective mirrors and sealing rubber rings, and installing a breathing system if necessary, will help maintain the cutting head’s integrity.
Adhering to equipment instructions and requirements, selecting the correct laser cutting process data parameters, and scheduling regular check-ups with a qualified technician are essential preventive measures. This includes inspecting the power output, cooling system, exhaust, and electrical connections. Additionally, ensure proper lubrication of moving parts, regular alignment checks, and maintenance of the filter and air system, such as cleaning dust collection baskets and replacing filter cartridges as specified.
By following these guidelines, the laser cutting head can remain in optimal condition, enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the laser cutting machine.
When purchasing a new laser tube for your laser cutting machine, several critical factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. First, evaluate the power rating of the laser tube, as this directly influences the machine’s ability to cut through various materials and thicknesses. Higher power tubes can handle thicker materials and achieve faster cutting speeds.
Next, consider the tube’s compatibility with your machine, ensuring that it fits within the existing setup and matches the machine’s specifications. The quality and type of the laser tube—whether CO2 or fiber—also matter, as each type has different operational costs, maintenance requirements, and cutting capabilities.
Durability and lifespan are important; high-quality tubes from reputable manufacturers typically offer longer service life and better performance consistency. Additionally, assess the cooling requirements of the laser tube, as proper cooling is essential to maintain performance and prevent overheating.
Cost is another significant factor, including not just the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership, which encompasses maintenance, replacement parts, and operational expenses.
Finally, check for warranty and support services provided by the manufacturer, ensuring you have access to technical support and replacement parts if needed. By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your cutting needs and budget.
To troubleshoot issues with the motion control system of a laser cutting machine, start by ensuring the power supply to the motion system is normal. Check for any electrical supply issues, such as a burned-out power fuse or a damaged main power switch. Verify that the motion system is powered on and that the DSP motion control card is functioning correctly, replacing it if damaged.
Next, inspect the mechanical components, including the drive system, cutting head, and guide rails. Look for loose belts or transmission gears and adjust or tighten them as necessary. Examine parts such as bearings, idler pulleys, and drive gears for wear or damage, and clean, replace, or adjust them according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure the guide rails and sliders are clean and properly lubricated to facilitate smooth movement.
Check the alignment and calibration of the X, Y, and Z axes. Make sure the X arm is square and adjust it if necessary by loosening couplings and aligning the arm with the hard stops on the Y rails before retightening them. Verify that the Z axis sensors are functioning correctly and adjust or replace them if needed.
Ensure the software and control parameters are correctly set for the material being cut. This includes updating any outdated software and ensuring there are no conflicts with other software. Verify that control parameters like speed, power, and focal point are accurately set for the material being processed.
Inspect the home sensors and limit switches to ensure they are functioning correctly. Adjust or replace any faulty sensors or circuit boards if the X or Y axis is not registering properly. Confirm that the origin switch is working correctly to avoid issues with the machine returning to the origin.
Check all signal wires for secure connections and any signs of damage. Replace any damaged signal lines as necessary.
If there are errors in the movement of the laser head, inspect and tighten any loose motor or light axis synchronous wheels. Address any loss of step phenomena by adjusting processing speed, acceleration settings, or the drive current, and consider replacing the motor if it is faulty.
Regular preventive maintenance is crucial. Clean and inspect the machine’s components regularly, lubricate moving parts to prevent wear, update software and firmware, and periodically calibrate the machine to maintain accurate and consistent cutting performance.
By systematically addressing these areas, most issues related to the motion control system of a laser cutting machine can be identified and resolved effectively.
The cooling unit in a laser cutting machine is essential for managing the heat generated during the cutting process. High-power lasers, such as CO2 and fiber lasers, produce significant heat, which must be dissipated to maintain optimal performance and prevent damage to the machine’s components.
Effective cooling helps protect critical parts like the laser tube and optical components from overheating, which can lead to reduced cut quality and potential damage. By keeping these components within their proper temperature ranges, the cooling unit ensures their longevity and reliability.
Additionally, maintaining a stable temperature is crucial for precision. Thermal distortion can negatively impact the accuracy of cuts and engravings, especially in high-tolerance applications. A well-regulated cooling system keeps the laser beam stable, resulting in consistent and high-quality output.
Safety is another critical aspect, as proper cooling reduces the risk of accidents related to overheating, creating a safer working environment for operators.
There are various types of cooling systems used in laser cutting machines, including water cooling systems, laser chillers, and freon-cooled chillers. Each system uses different methods to absorb and dissipate heat but ultimately serves the same purpose of maintaining the machine’s optimal operating temperature.
Key elements of these systems include steady water flow, thermal sensors and alarm systems, display panels for real-time monitoring, and mobility features for flexible usage. Maintaining the cooling unit involves regular water quality checks, periodic water changes, and ensuring proper ventilation.
In summary, the cooling unit is vital for heat management, protecting laser components, maintaining precision and quality, ensuring safety, and contributing to the overall performance and durability of the laser cutting machine.
Laser cutting machines primarily employ two types of cooling systems: the water circulation cooling system and the refrigerant circulation cooling system.
Water Circulation Cooling System:
The working principle of this system involves the refrigerant liquid throttling and depressurizing through a capillary tube, flowing into the evaporator. Here, it vaporizes, absorbing the heat of the cooled water from the external water circulation cooling system, turning into high-temperature refrigerant vapor that gets sucked into the compressor. Once inside the compressor, it gets compressed into high-temperature and high-pressure vapor for discharge. However, it may have drawbacks such as needing regular maintenance to prevent pipe blockages or leaks, and in some cases, water quality issues may affect the long-term operation of the equipment.
Refrigerant Circulation Cooling System:
This system, similar to the water circulation cooling system, achieves cooling effects through the circulation of the refrigerant. Its advantage lies in providing more precise and stable cooling effects, especially when dealing with high-power density laser systems. However, this system typically comes at a higher cost and may require professional technical support for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Choosing the right cooling system is crucial to ensure the normal operation of the laser cutting machine and extend its lifespan. The water circulation cooling system, due to its lower cost and ease of maintenance, is widely used, while the refrigerant circulation cooling system, with its efficient and precise cooling ability, is suitable for applications with higher cooling requirements. Users should choose the most appropriate cooling system type based on their specific needs and budget.
To optimize the gas supply system of a laser cutting machine for enhanced cutting efficiency and quality, consider the following aspects:
Choose the appropriate auxiliary gas: Select the most suitable auxiliary gas based on different materials and cutting requirements. For instance, nitrogen is primarily used as a significant auxiliary gas in the laser cutting industry. The carbon dioxide laser is one of the most commonly used gas lasers for laser cutting.
Maintain consistency of the auxiliary gas: The laser machine requires consistent auxiliary gas pressure and flow to maintain cutting quality. Gas supply failures may lead to unnecessary pressure drops, affecting production quality.
Optimize the gas supply pipeline: The length and diameter of the gas supply pipeline determine the flow of the auxiliary gas. Ideally, the supply pipeline should have the least amount of bending to reduce gas flow resistance, ensuring the stability and sufficiency of the gas supply.
Adjust the distance between the nozzle and the material: By adjusting the distance between the nozzle and the material, you can effectively improve the cutting efficiency of the equipment.
Increase power: Properly increasing laser power can improve cutting speed and quality while ensuring safety.
Establish a good working environment: A favorable working environment temperature is equally important for the efficiency and cutting quality of the laser cutting machine.
Use a professional nitrogen generator: By optimizing a professional PSA laser cutting nitrogen generator, you can provide high-quality nitrogen for the laser cutting process, thereby improving cutting efficiency and quality.
The microcomputer numerical control cabinet plays a pivotal role in laser cutting machines. It forms the core of the laser cutting system in conjunction with the laser generator, beam transmission components, workbench (machine tool), cooler, and computer.
The primary function of the microcomputer numerical control cabinet is to control the precise movement and cutting process of the laser through computer programming, ensuring the laser accurately operates on the workpiece along a predetermined path.
The microcomputer numerical control cabinet greatly influences machining accuracy.
Firstly, it ensures high precision and quality during the laser cutting process by precisely controlling the output power and movement speed of the laser.
Secondly, the microcomputer numerical control cabinet adjusts cutting parameters such as focal point location and gas pressure according to different material types and thicknesses to cater to various cutting needs, further enhancing machining accuracy.
Moreover, it supports complex cutting path planning, enabling the laser cutting machine to carry out efficient and accurate cutting on complex workpiece shapes, significantly improving processing efficiency and yield rate.
The microcomputer numerical control cabinet is not only a key component in laser cutting machines but also plays a decisive role in ensuring machining accuracy, enhancing production efficiency, and improving product quality.