Ever wondered how ordinary lathes create rectangular threads? This article unveils the process, highlighting the unique challenges and techniques involved. Rectangular threads, known for their efficiency in transmitting power, require precise movements and specialized tools for accurate machining. You’ll learn the essential steps and tools necessary to achieve these intricate threads, making complex mechanical tasks manageable. Dive in to enhance your understanding and skill in machining rectangular threads.

Type of thread:
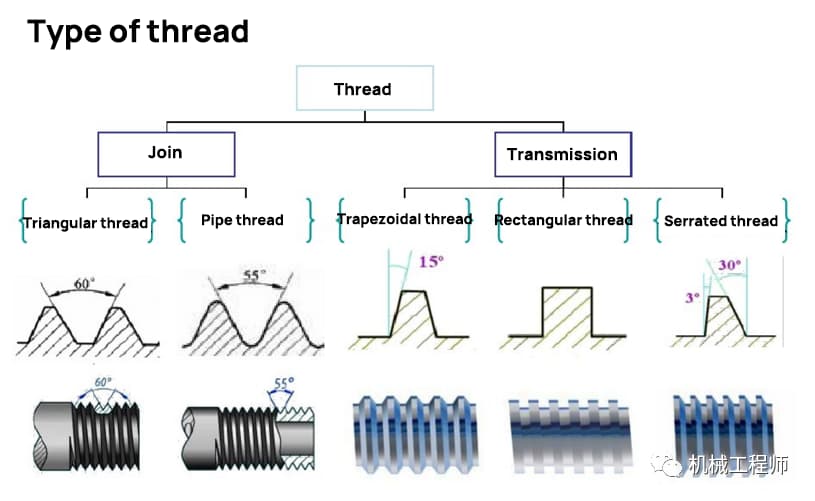
The rectangular thread features a square profile, and the thread thickness is half of the pitch, making it highly efficient in transmitting power. However, it has some limitations, including low centering accuracy and weak root strength.
Manufacturing rectangular threads with precision is challenging, and compensating or repairing the clearance of worn screw pairs is difficult. The thread of a bench vice is a recent example of a rectangular thread, which requires frequent tightening and loosening, requiring significant force.
Rectangular threads are commonly used in valves, water pipes (including small ones like water faucets), jacks, and screw presses, with slight variations in size.
In summary, rectangular threads are ideal for handling heavy loads where thread strength is essential, and thread accuracy is not a primary concern.
The lathe spindle and tool must maintain a precise movement relationship. Specifically, the tool should move a consistent lead distance with every rotation of the spindle, which holds the workpiece.
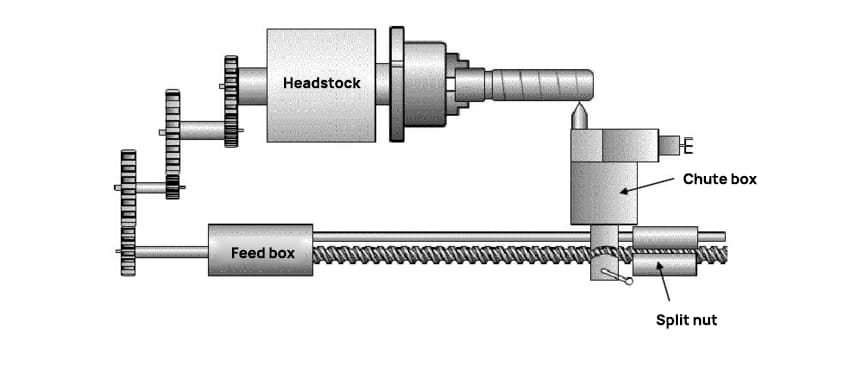
By default, if the tooth size is not specified, the thread’s cross-section is typically square-shaped.
To produce rectangular threads, the turning tool should be fed in a straight line, and the threads can be processed based on the depth of the groove (i.e., the height of the tooth).
Rectangular thread turning tool:

When it comes to machining short threads, a grooving turning tool is suitable due to the shape of thread teeth. The blade width of the tool should only be half of the pitch.
However, for threads with a wide pitch, high-speed steel elastic turning tools are often used.
One of the biggest challenges in machining rectangular threads is the grinding method of the turning tool. When the pitch and lead increase, the thread rise angle (lead angle) becomes larger, and the rear angle of the turning tool can touch the side of the thread.
It is important to note that the thread rise angle at the top and bottom of the thread will differ for threads with a large lead.
To avoid these issues, a trapezoidal turning tool with a small front edge width is used for the concave part. This ensures that the width of the cutting edge on the outer circumference (thread crown) is the same as that of the groove, and the lower part of the thread on the groove at the bottom of the tooth will be recessed.

When turning rectangular threads, the machining allowance should be allocated reasonably.
For details, please refer to the following figure:
Reasonably allocate thread machining allowance
(generally rough turning ap:0.10~0.50; fine turning ap: 0.01~0.10.)
| Feed times | Back cutting depth | Processing steps | Machining allowance |
| First feed | a=0.50mm | Rough machining | 0.75mm |
| Second feed | a=0.15mm | ||
| Third feed | a=0.10mm | ||
| Fourth feed | a=0.03mm | finish machining | 0.06mm |
| Fifth feed | a=0.02mm | ||
| Sixth feed | a=0.01mm |
Rectangular threads are distinct from triangular and trapezoidal threads.
Unlike the other thread types, rectangular threads do not experience issues with single or double-sided cutting, nor do they encounter problems with pitch diameter due to their lower accuracy requirement.
In fact, thread machining for rectangular threads is relatively straightforward.