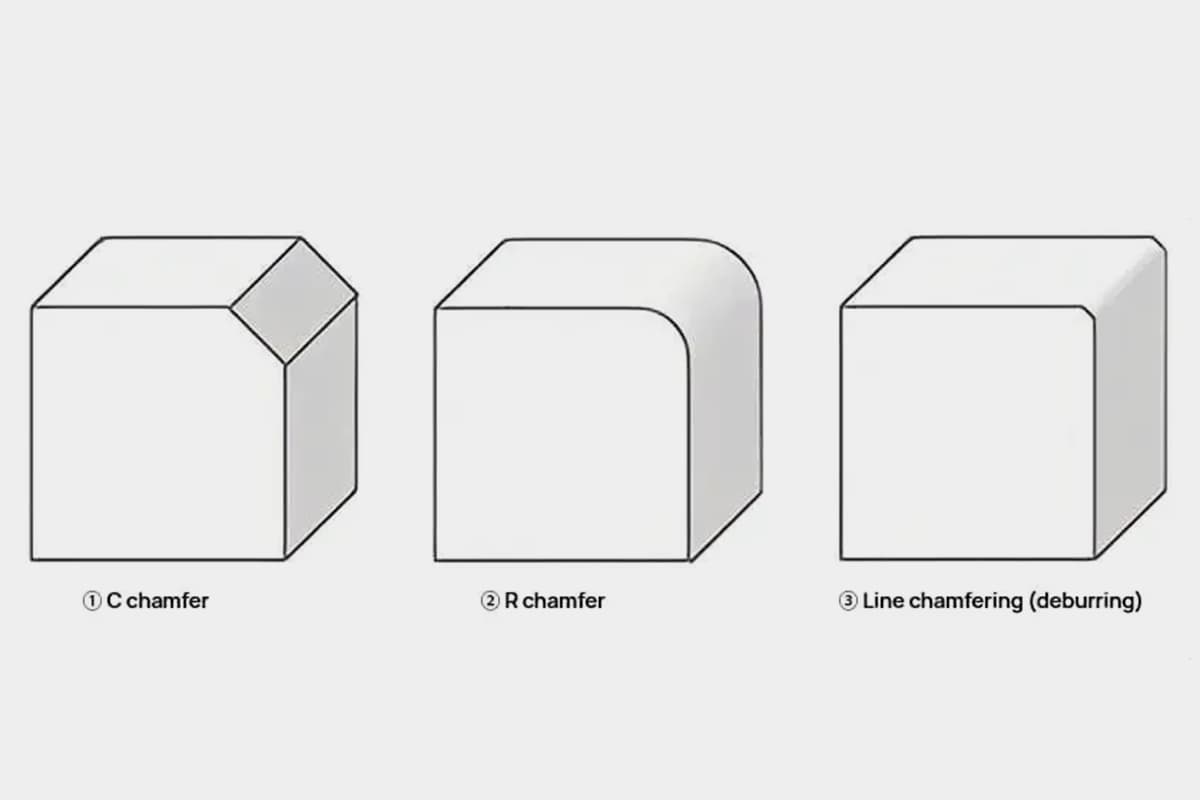
In this blog post, our seasoned mechanical engineering expert shares insider tips on selecting the perfect linear guide system for your application. Discover how to optimize performance, minimize wear, and avoid common pitfalls. Whether you’re a novice or a pro, you’ll gain valuable insights to take your designs to the next level.
Linear guides, also known as slide rails, linear rails, or linear sliders, support and guide moving components in reciprocating linear motion along a predetermined direction.
Given the same size of moving components, they have a higher rated load and motion accuracy than linear bearings, while also able to withstand a certain amount of torque load.
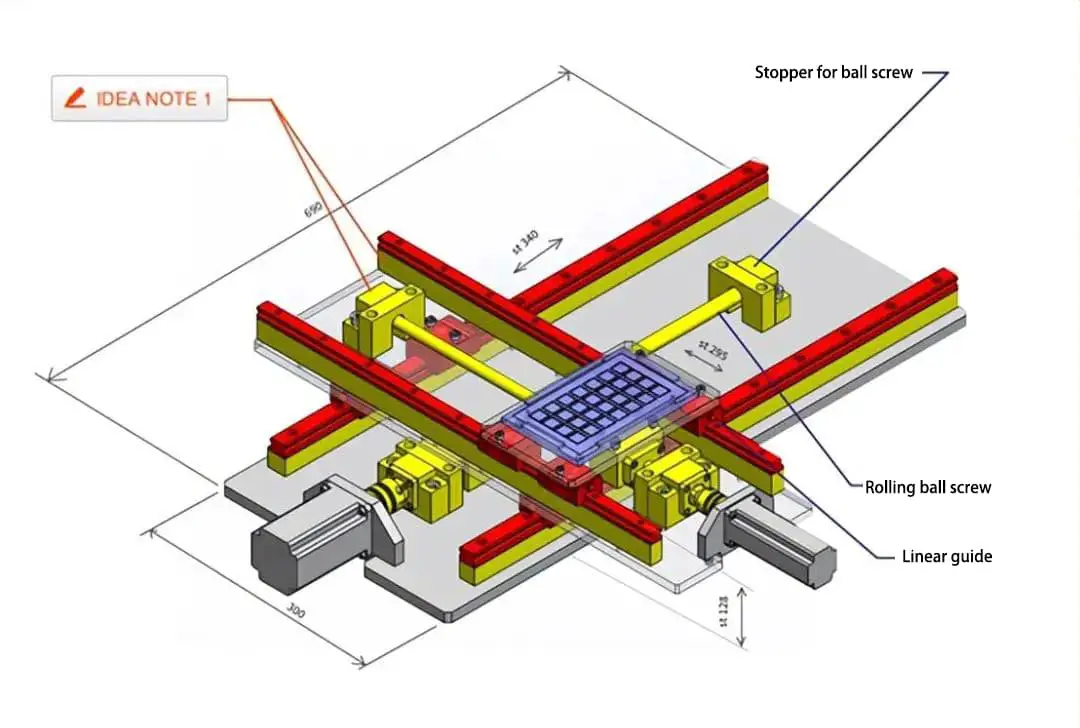
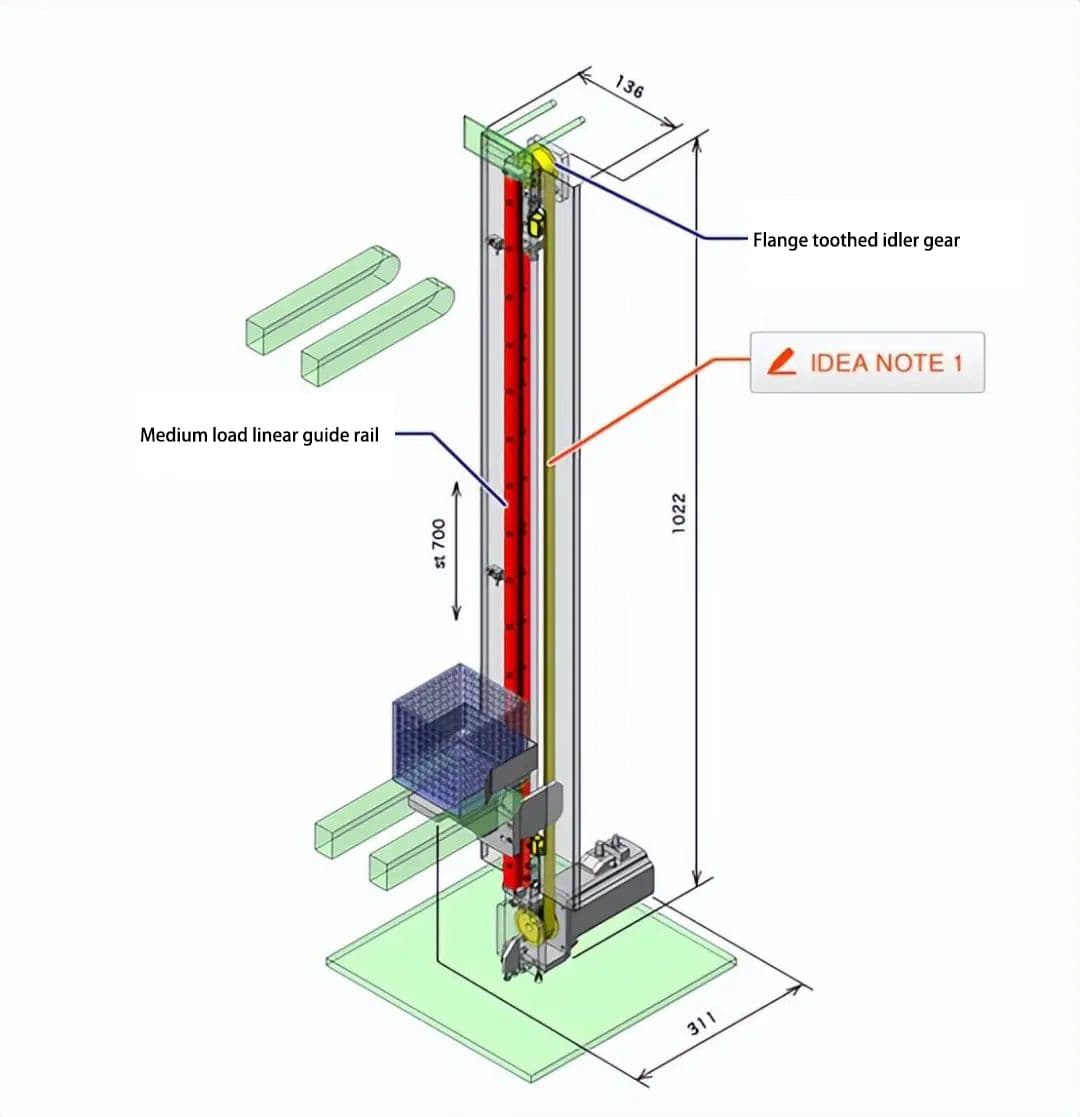
As shown in Figure 1 and 2, linear guides can be used for heavy load transportation in horizontal spaces, precise positioning movement, and accurate guidance movement in vertical spaces. They ensure reliable movement in small spaces and have broad applications in machine tools, electronics, medical, and robotics industries.
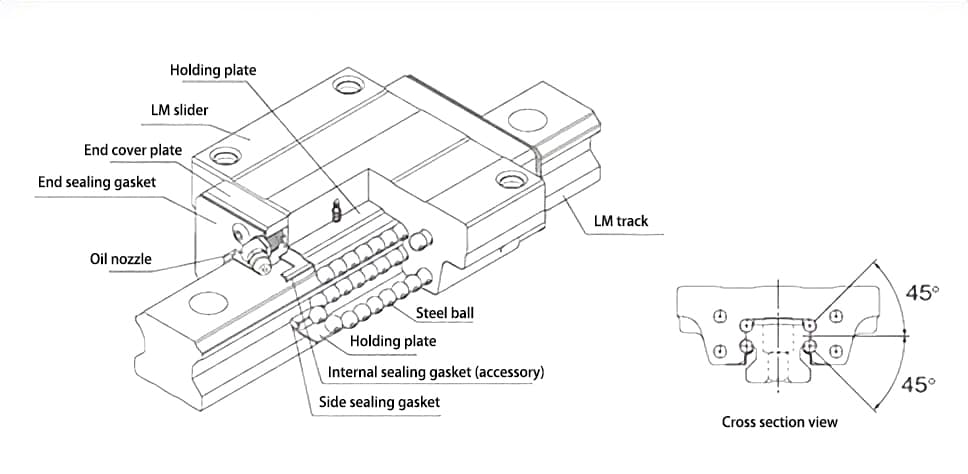
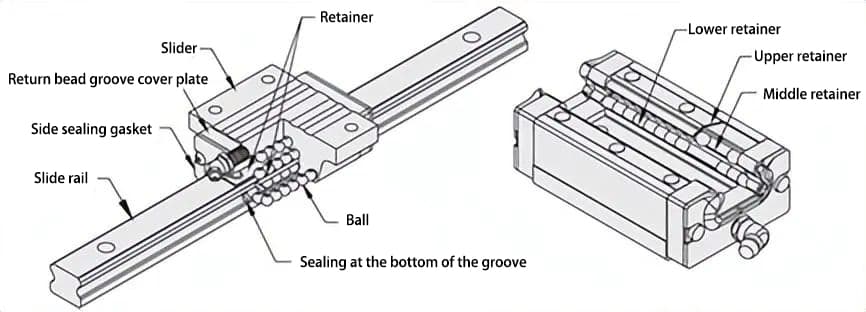
As shown in Figure 3, the linear guide is composed of slide rails, sliders, ball bearings, ball retainers, and recirculation grooves. The main principle is to make the steel balls circulate through the structure of recirculation grooves and ball retainers, thereby achieving low-friction linear motion of the slider on the slide rail.
Basic features of the linear guide:
Such a structure determines the following basic features of the linear guide:
Depending on the different load applications, they can be primarily divided into miniature, medium, and heavy-duty types.
As linear guides mainly transfer loads through ball bearings, the difference between the miniature, medium, and heavy-duty types mainly lies in the number of ball rows.
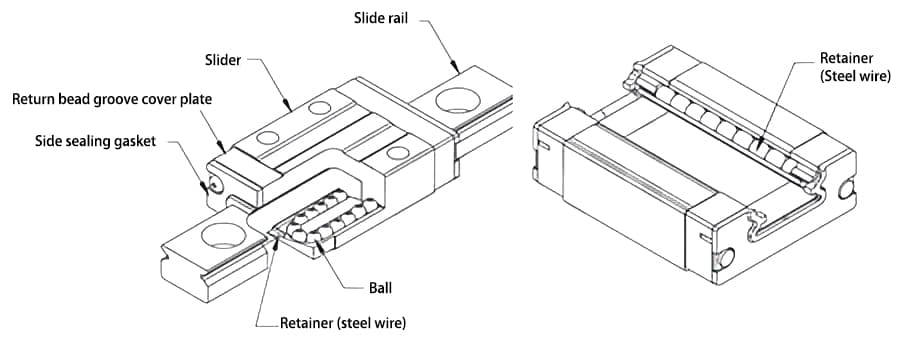
As shown in Figures 4 and 5, miniature linear guides generally have 2 rows of steel balls, with 4 points of contact with the rail surface, making for a compact structure.
Medium and heavy-duty linear guides usually have 4 rows of steel balls, enhancing their load-bearing capacity. The basic dynamic rated load of miniature linear guides is generally less than 10KN, whereas that of medium and heavy-duty guides can reach up to 80KN.
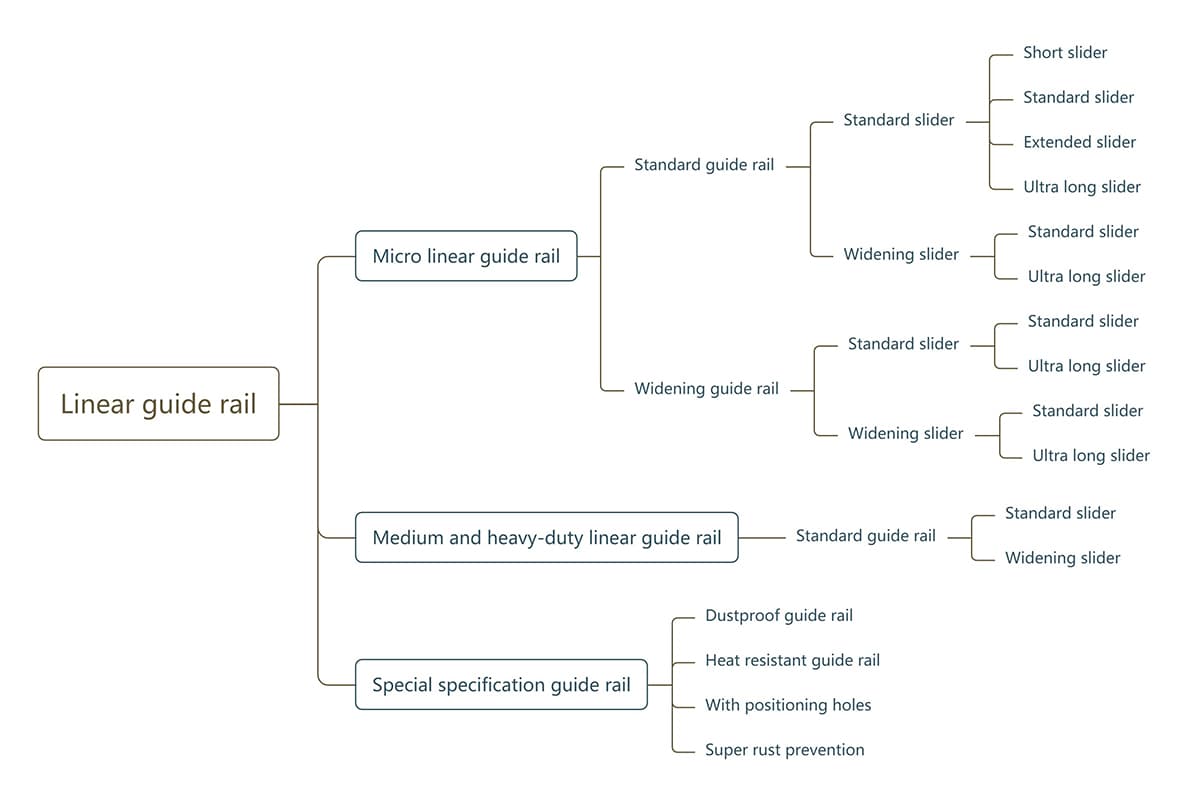
Linear guides are classified according to different track widths and slider widths and lengths, as follows:
Linear guide rails are classified as follows based on the width of the rail and the width and length of the slider:
The total height and track width ratio of standard guides is about 1.1, while that of wide guides is about 0.65. The total height of the wide track is 40% lower than that of the standard track. Therefore, in situations where height is limited, wide tracks are most suitable; conversely, use standard tracks where width is restricted.
On the other hand, with a lower height-to-width ratio, the static permissible torque of wide tracks is more than twice as much as that of standard tracks. Their stiffness is significantly increased, making them ideal for structures with offset centers of gravity.
Usage scenarios for wide sliders:
Wide sliders and standard sliders have similar basic rated loads and static permissible torque. However, the fixing bolts on the wide slider are larger than those on the standard slider, increasing the fixing strength.
Usage scenarios for sliders of various lengths:
After selecting the track, the decision to use sliders of what length is mainly based on the fact that the longer the slider, the greater the basic rated load and static permissible torque.
| Category | Types of sliders | Features | Product number | Rail length (mm) | Rated dynamic load (KN) | Slider width W (mm) | Slider length L (L1) (mm) | Slider height K (mm) | Price |
| Micro type | Standard type | The most basic type in the industry-standard specifications, with a wide variety of sizes and a high cost-performance ratio. | Misumi micro linear guide standard slider type (recommended) | 25~700 | 0.3~5.2 | 12~40 | 17.4~50 | 4.5~15 | ¥176+ |
| THK micro, SRS type slider variant M | 50~630 | 2.69~6.66 | 20~32 | 30.8~43 | 8.5~13.3 | ¥289+ | |||
Short type | Compared to the standard type of slider, it can be reduced in volume by 20%. | Misumi micro linear guide short slider type | 35~670 | 0.79~3.08 | 17~32 | 19.6~32.7 | 65~12 | ¥1788+ | |
Widened type | Compared to standard products, the bolt size increases and the fixing strength improves. | Misumi micro linear guide slider, widened standard type | 35~700 | 0.9~5.2 | 24~54 | 23.6~50 | 6.5~15 | ¥203+ | |
Extended type | Compared to the standard slider type, it has higher rated load and permissible torque. | Misumi micro linear guide slider, extended type | 40~700 | 0.6~7.2 | 12~40 | 21~67.7 | 4.5~15 | ¥172+ | |
Widened and extended type | The bolt size increases, improving the fixing strength. It also has a higher rated load and permissible torque compared to the standard slider type. | Misumi micro linear guide slider, widened and extended type | 40~700 | 1.6~7.2 | 24~54 | 32~67.7 | 6.5~15 | ¥265+ | |
With locating hole type | It effectively reduces equipment assembly time and enables easier repetitive positioning. | Misumi micro linear guide with locating hole, short slider type | 35~670 | 0.79~3.08 | 17~32 | 19.6~32.7 | 6.5~12 | ¥234+ | |
| Misumi micro linear guide with locating hole, standard slider type | 35~700 | 0.9~5.2 | 17~40 | 23.6~50 | 6.5~15 | ¥244+ | |||
Rail widened type | Compared to standard products, the bolt size increases, resulting in improved fixing strength. | Misumi micro linear guide rail, widened type, slider widened type | 50~670 | 1.4~5.8 | 36~74 | 31.1~55 | 7~13 | ¥246+ | |
| THK micro, SRS type slider variant WM | 50~630 | 3.29~9.12 | 30~60 | 39~55.5 | 9.1~13.3 | ¥327+ | |||
High-temperature resistant | It can be used in environments with a maximum temperature of 150℃. | Misumi micro linear guide, heat-resistant type | 35~670 | 0.79~5.8 | 17~32 | 19.6~58.3 | 6.5~12 | ¥268+ | |
| Heavy-duty type | Standard type | Used for high-precision positioning, high load, and high-frequency driving. | Misumi ultra-heavy-duty linear guide with resin retainer | 220~1960 | 16.3~35.5 | 44~90 | 69.8~98.6 | 25~33 | ¥1021+ |
| This THK product is a world-standard size and has automatic self-aligning capability, providing excellent durability. | THK, HSR type slider variant R | 64~1960 | 8.33~50.2 | 34~70 | 56.6~134.8 | 23.3~47.5 | ¥370+ | ||
| This THK product is a world-standard size and has automatic self-aligning capability. It features a low center of gravity and high rigidity. | THK, SHS type slider variant V | 71~1960 | 14.2~72.9 | 34~70 | 64.4~152 | 21~40.5 | ¥373+ | ||
| It features a steel ball contact structure with strong load-bearing capacity in the radial direction, making it suitable for horizontal installation. | THK, SSR type slider variant XW | 64~1960 | 14.7~31.5 | 34~48 | 56.9~83 | 19.5~26.2 | ¥379+ | ||
| It has a built-in lubrication-free system, offering high precision, low friction coefficient, and low maintenance costs. | ABBA, BR series slider variant R0 | 80~2200 | 8.5~48 | 34~70 | 66~134.8 | 28~55 | ¥167+ | ||
| ABBA, BR series (with flange threaded type) | 80~2200 | 8.5~48 | 47~100 | 66~134.8 | 24~48 | ¥172+ | |||
| ABBA, BR series (without flange threaded type) | 80~2200 | 8.5~48 | 34~70 | 66~134.8 | 28~55 | ¥167+ | |||
Short type | Compared to the standard slider type, it can be reduced in volume by 20%. | THK, SSR type slider variant XV | 47~1960 | 9.1~21.7 | 34~48 | 40.3~60 | 19.5~26.2 | ¥328+ | |
| ABBA, BR series slider variant SU (short type without flange threaded type) | 80~2200 | 5.2~12.5 | 34~48 | 47.6~62.5 | 24~33 | ¥151+ | |||
Widened type | The bolt size increases, resulting in improved fixing strength. It also has a higher rated load and permissible torque compared to the standard slider type. | THK, HSR type slider variant A | 64~1960 | 8.33~50.2 | 47~100 | 56.6~134.8 | 19.3~40.5 | ¥334+ | |
| THK, HSR type slider variant B | 64~1960 | 8.33~50.2 | 47~100 | 56.6~134.8 | 19.3~40.5 | ¥335+ | |||
| This THK product is a world-standard size and has automatic self-aligning capability. It features a low center of gravity and high rigidity. | THK, SHS type slider variant C | 71~1960 | 14.2~72.9 | 47~100 | 64.4~152 | 21~40.5 | ¥155+ | ||
Extended type | Compared to the standard slider type, it has a higher rated load and permissible torque. | ABBA, BR series slider variant LR (without flange threaded type) | 80~2200 | 8.5~48 | 34~70 | 66~134.8 | 28~55 | ¥235+ | |
Widened and extended type | The bolt size increases, improving the fixing strength. It also has a higher rated load and permissible torque compared to the standard slider type. | THK, HSR type slider variant LB | 64~1960 | 8.33~50.2 | 47~100 | 56.6~134.8 | 19.3~40.5 | ¥421+ | |
With locating hole type | It effectively reduces equipment assembly time and enables easier repetitive positioning. | Misumi medium-duty linear guide | 100~1960 | 5~11.7 | 34~48 | 41~92.6 | 20~26.5 | ¥484+ |