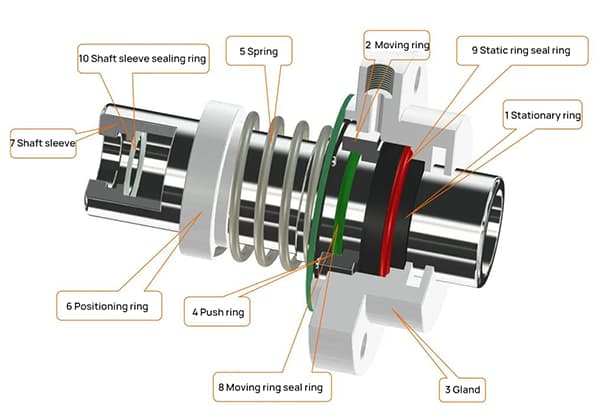
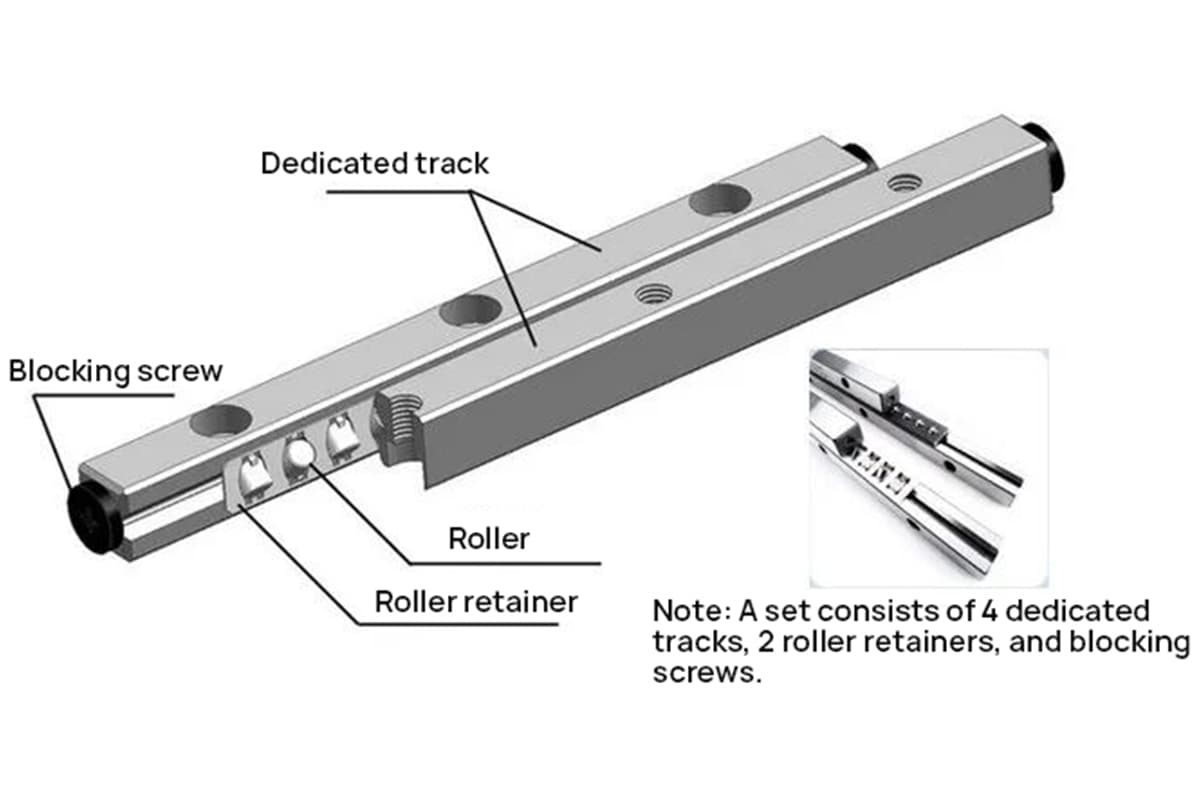
How can improving the efficiency of mechanical transmissions transform your machinery’s performance? This article delves into the empirical values of various mechanical transmission systems, from gear drives to belt and chain drives. You’ll learn how to identify and apply these efficiency standards to enhance your machines’ output and longevity. Dive into the specifics and optimize your mechanical systems with proven data and insights.
Want to optimize your mechanical transmission efficiency?
Discover the typical empirical values used in the industry and improve your machine’s performance. Read on to learn more.

| Mechanical transmission efficiency table | ||
| category | drive system | efficiency |
| Cylindrical gear transmission | Gear transmission with good running-in accuracy of Level 6 and Level 7 (thin oil lubrication) | 0.98~0.99 |
| General gear transmission with 8-level accuracy (thin oil lubrication) | 0.97 | |
| Gear transmission with class 9 accuracy (thin oil lubrication) | 0.96 | |
| Open gear transmission for machining teeth (dry oil lubrication) | 0.94~0.96 | |
| Open gear transmission with cast teeth | 0.90~0.93 | |
| bevel gear drive | Good running-in precision gear transmission with grades 6 and 7 (thin oil lubrication) | 0.97~0.98 |
| General gear transmission with 8-level accuracy (thin oil lubrication) | 0.94~0.97 | |
| Open gear transmission for machining teeth (dry oil lubrication) | 0.92~0.95 | |
| Cast tooth open gear transmission | 0.88~0.92 | |
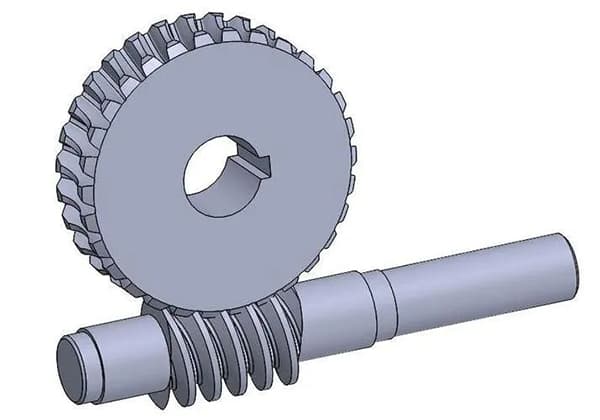
| worm drive | Self-locking worm | 0.40~0.45 |
| Single head worm | 0.7~0.75 | |
| Double headed worm | 0.75~0.82 | |
| Three-head and four-head worm | 0.8~0.92 | |
| Circular arc surface worm drive | 0.85~0.95 | |
| Belt drive | Open drive with flat belt without compression wheel | 0.98 |
| Open drive with flat compression wheel | 0.97 | |
| Flat belt cross drive | 0.90 | |
| V-belt drive | 0.96 | |
| Synchronous toothed belt drive | 0.96~0.98 | |
| Chain drive | Welded chain | 0.93 |
| Piece joint chain | 0.95 | |
| Roller chain | 0.96 | |
| Silent chain | 0.97 | |
| sliding bearing | Poor lubrication | 0.94 |
| Normal lubrication | 0.97 | |
| Lubrication characteristic d (pressure lubrication) | 0.98 | |
| Liquid friction | 0.99 | |
| Rolling bearing | Ball bearing (thin oil lubrication) | 0.99 |
| Roller bearing (thin oil lubricated d) | 0.98 | |
| Friction drive | Flat friction drive | 0.85~0.92 |
| Slot friction drive | 0.88~0.90 | |
| Rope reel | 0.95 | |
| coupling | Floating coupling | 0.97~0.99 |
| Toothed coupling | 0.99 | |
| Elastic coupling | 0.99~0.995 | |
| Universal coupling( α≤ 3°) | 0.97~0.98 | |
| Universal coupling( α> 3°) | 0.95~0.97 | |
| Quincunx shaft | 0.97~0.98 | |
| Hydraulic coupling (at design point) | 0.95~0.98 | |
| Complex pulley block | Sliding bearing (i=2~6) | 0.98~0.90 |
| Rolling bearing (i=2~6) | 0.99~0.95 | |
| Winch drum | 0.94~0.97 | |
| Decelerator | Single stage cylindrical gear reducer | 0.97~0.98 |
| Double stage cylindrical gear reducer | 0.95~0.96 | |
| Single stage planetary cylindrical gear reducer | 0.95~0.96 | |
| Single stage planetary cycloid pin wheel reducer | 0.90~0.97 | |
| Single stage bevel gear reducer | 0.95~0.96 | |
| Double stage conical cylindrical gear reducer | 0.94~0.95 | |
| Continuously variable transmission | 0.92~0.95 | |
| Rolling mill herringbone gear seat (sliding bearing) | 0.93~0.95 | |
| Rolling mill herringbone gear seat (rolling bearing) | 0.94~0.96 | |
| Rolling mill main reducer (including main coupling and motor coupling) | 0.93~0.96 | |
| Lead screw drive | Sliding lead screw | 0.3~0.6 |
| Rolling lead screw | 0.85~0.95 | |