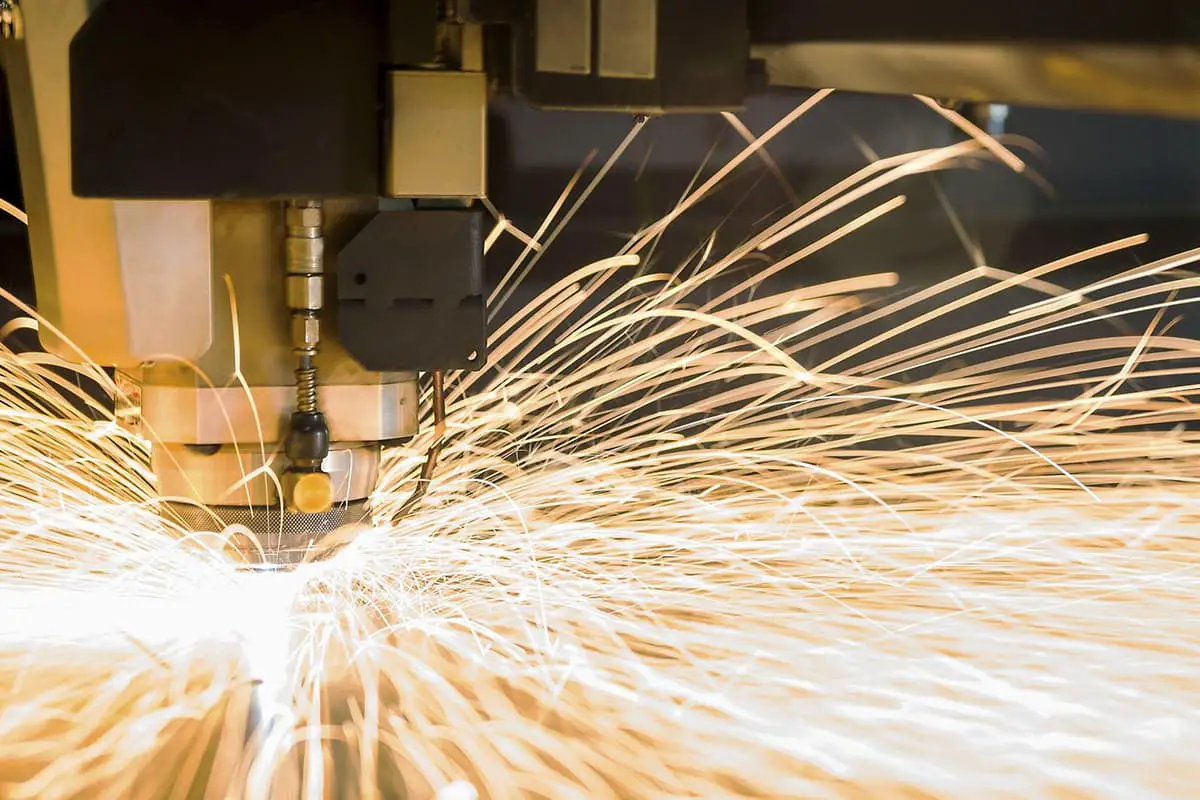
Imagine effortlessly etching intricate designs onto metal surfaces with pinpoint accuracy. This is the magic of metal laser engravers, a technology transforming metalworking. In this article, you’ll explore the principles, types, and applications of these machines, and learn how they bring precision, efficiency, and environmental benefits to industries ranging from automotive to jewelry. Prepare to delve into the world of laser engraving and discover how this innovation is reshaping the metalworking landscape.

The laser metal engraving machine refers to a laser device used for engraving metal, including stainless steel, copper, aluminum, carbon steel, iron, aluminum alloys, and various metal alloys.
Laser metal engraving machines are mainly divided into two types based on the power used: high-power and medium-to-low power laser engraving machines.
High-power metal laser engraving machines are mainly suitable for cutting and engraving thick steel materials and steel plates in construction and heavy industries. Medium-to-low power laser engraving machines are mainly used for engraving relatively thin metal materials, with thicknesses ranging mainly from 1mm to 8mm.

These devices generally use imported semiconductor pump sources and high-speed marking mirrors from Germany. They have high photoelectric conversion efficiency, good beam quality, and high laser power.
They are particularly suitable for deep marking and high-precision cutting of precious metals and non-ferrous metals. They can also be equipped with rotating devices for precision processing of ring-shaped materials.
Metal is one of the most common materials we encounter in our daily lives. But how can we leave a permanent mark on metal? This requires the use of laser technology. Laser can leave etched marks on metal surfaces through high-temperature laser beams, which has many advantages over traditional printing methods:
Long-lasting marking:
Laser engraving is often used for traceability marking on various metal components, such as automobile parts, saw blades, hardware, etc. This engraved mark is enduring and will not fade over time.
Environmentally friendly marking:
Laser engraving is a non-polluting and odorless process that uses laser beams to engrave, eliminating the need for chemicals or pigments. With zero waste disposal, it is an environmentally friendly process.
Cost-effective marking:
Laser engraving is a zero-consumable process that requires no additional materials. When combined with a production line, it can achieve fully automated processes. Additionally, laser machines can operate for 100,000 hours without maintenance costs, resulting in better cost control for businesses.
Flexible marking:
Laser engraving is a non-contact process that allows for precise and rapid marking as long as the laser beam is directed towards the surface of the object to be marked.

A laser engraving machine is a mechanical device that uses lasers to engrave materials. The principle behind it is that the laser is directed onto the object being processed through a focusing lens, which causes the point to quickly melt or vaporize due to the high temperature, achieving the purpose of engraving.
Principle of Laser Engraving Machine:
Laser is a type of light that, like other naturally occurring light sources, is generated by the transition of atoms (molecules or ions) and is caused by spontaneous radiation. Although laser is light, it is fundamentally different from ordinary light in that laser depends only on spontaneous radiation for an extremely short period of time, after which the process is entirely determined by stimulated radiation.
As a result, laser has very pure colors, almost no divergence in direction, and extremely high brightness.
Laser also has high coherence, high intensity, and high directionality. After being generated by a laser, it is transmitted through a reflection mirror and directed onto the surface of the material being processed through a focusing lens, which rapidly increases the temperature of the surface due to the strong thermal energy.
This causes the point to quickly melt or vaporize, achieving the purpose of processing as directed by the movement of the laser head.
The speed at which the laser head moves is usually expressed in IPS (inches per second), which affects production efficiency. Speed is also used to control cutting depth. For a specific laser intensity, the slower the speed, the greater the cutting or engraving depth. The speed can be adjusted using the engraving machine panel or through the computer’s print driver program.

Laser engraving machines can be divided into three types: CO2 type, galvanometer type, and YAG type.
If classified by size, power, and speed, there are many types of laser engraving machines, but only CO2 and YAG types are suitable for the gift industry. The main difference between CO2 and YAG laser engraving machines is the material used to generate the laser.
CO2 type generates laser by exciting a mixture of ions and carbon dioxide molecules, while YAG type generates laser by exciting yttrium aluminum garnet crystals or crystal rods. Different light sources emit lasers of different wavelengths, so each type of engraving machine is suitable for engraving different materials.
Flying light type, also known as flatbed type laser engraving machine, is the most common type used in the gift industry, and it uses CO2 laser tube. Flatbed laser engraving machines that use YAG laser tubes are rare. For flatbed laser engraving machines, the laser beam moves on the flatbed through a small car that moves back and forth.
There is another type of engraving machine that uses CO2 laser tube, which is galvanometer type, also known as mirror type. It controls the movement of the laser beam on the workbench by quickly rotating a reflecting mirror. This allows the laser beam to move at high speed without moving the entire car.
However, the galvanometer type also has its drawbacks. Its processing size is smaller (usually 12×12 inches or 14×14 inches), and if used for cutting, it does not cut straight down, but has a certain curvature.
When it is upgraded to 100 watts, the galvanometer type can have the same power as the flatbed laser engraving machine, with a maximum of 100 watts, but at the same power, the galvanometer type has a great advantage in speed.
The galvanometer type is mainly used for marking, not cutting. Their company sells both galvanometer and flatbed CO2 laser engraving machines.
In addition, the speed of flatbed laser engraving machines has been increasing, and the speed difference with galvanometer type is getting smaller and smaller.
The reason why CO2 laser tubes are widely used is simple: their applications are extremely extensive. CO2 laser engraving machines can engrave or mark plastics, acrylics, painted metals, glass, leather, paper, fabrics, wood, marble, etc., and can also be used to cut many of these materials. The only thing they cannot engrave is uncoated metal.
YAG lasers are divided into two main types, mainly distinguished by whether the YAG crystal is excited by a flash lamp or a diode. The main difference between the two is how the light is generated to excite the crystal to form a laser beam. Compared to flash lamp lasers, diode lasers produce a finer and purer beam of light and do not require high-power sources.
“The key is for both to produce lasers of the same wavelength.” Diode YAG laser engravers are more efficient than flash lamp laser engravers, while the latter are cheaper. Both are more expensive than CO2 laser engravers.
The advantage of YAG laser engravers is that their wavelength can be well absorbed by metals, making them perform well in device marking and other industrial applications. However, many materials cannot be engraved with YAG laser engravers, while CO2 laser engravers can engrave materials such as wood, paper, fabric, glass, and some gypsum.
Speaking of laser engravers, it is necessary to mention computerized mechanical engravers that have been used in the gift industry for a long time. Mechanical engravers are still widely used in the gift industry today because the tactile feeling of the engravings and patterns they produce cannot be replaced. Although YAG laser engravers can mark on metals, only mechanical engravers can engrave them deeper.
Because people always appreciate traditional and classic things, there is a natural inclination towards mechanical engraving, which is why it still exists. When you see an engraved item, you always want to touch it.
Without a laser engraver, there will be many limitations to your business, and some businesses can only be done with mechanical engravers. Therefore, it is a good idea to have both mechanical and laser engravers, as they complement each other.

1. Wood:
Wood is easily engraved and cut by laser engraving machines. Light-colored woods such as birch, cherry, or maple are more suitable for engraving because they can be vaporized by laser.
Tulipwood is easy to carve and similar to European Bodhi trees.
When processing thick boards, there is a large amount of smoke, so a smoke purifier can be installed.
2. Organic glass:
Organic glass is widely used in the advertising industry, and the cost of using laser engraving machines for carving or cutting is relatively low.
Usually, organic glass is engraved on the back, meaning the front is engraved and the back is viewed to make the finished product more three-dimensional. When engraving, please mirror the image first, and the engraving speed should be fast while the power should be low.
Organic glass is easy to cut, and an air blowing device should be used to improve the quality of the cut. When cutting organic glass, the operator should not leave, as there may be flames during the cutting process.
3. Painted copper plate:
Under normal circumstances, copper cannot be engraved by laser, but now there is a material with a special paint film on the surface. The laser can completely evaporate the paint film on the surface, revealing the copper plate underneath.
Usually, the copper plate is polished or specially treated before painting, so that the exposed area after engraving has sufficient smoothness and can be preserved for a long time. If the copper surface has not been treated, a protective film should be made after using the laser engraving machine to avoid oxidation and surface contamination over time.
4. Double-color board:
The double-color board is an engineering plastic made up of two or more layers of colors, specifically designed for engraving. Its specification is generally 600×1200mm, with a few brands having a specification of 600×900mm.
The effect of engraving with a laser engraving machine is very good, with clear contrast and sharp edges.
5. Medium-density fiberboard:
This material is a high-density board with fine wood grain on the surface. Laser engraving machines can be used to engrave on this sharp material, but the resulting pattern is uneven and black, so it is usually colored.
Usually, appropriate designs can be learned, and 0.5mm double-color boards can be used for splicing to achieve better results. After engraving, clean the surface of the medium-density fiberboard with a wet cloth.
The main industries that use metal engraving machines include: the arts and crafts industry, the decoration industry, the packaging and printing industry, the modeling industry, advertising lettering, large-format cutting, metal sheet cutting for kitchen utensils, the furniture industry, the footwear industry, the leather industry, and clothing sample making.

Laser can create marks on metals through various techniques. However, laser engraving has some distinct advantages. Taking aluminum as an example, below are some benefits of laser engraving aluminum.
Permanent Marking:
Laser engraving on aluminum provides a mark that can withstand mechanical stress, repeated wear and tear, UV exposure, and temperature stress. This is a crucial feature if you are creating marks for quality control and traceability, such as for aircraft and automotive parts. It also applies if you want to create promotional items that stand the test of time.
Eco-Friendly:
Laser engraving does not use chemicals and inks, meaning zero processing and waste disposal issues.
Cost-Effective:
Due to zero consumables, laser engraving aluminum is an economically efficient marking option. Additionally, lasers require less maintenance and part replacement, meaning more savings.
Flexibility:
Laser engraving is essentially a non-contact technology, making its process extremely flexible. You can use it to create countless shapes and sizes. Since you don’t need to clamp the parts before engraving, you can save a lot of time using lasers.
Maintain Aluminum’s Original Properties:
Laser engraving does not strip the protective anodized layer of the substrate. This means its corrosion resistance remains intact, unlike other techniques such as coating removal for salt spray testing.
High-Resolution Images:
Using lasers, you can engrave images and designs up to 1200 dpi.
First, you need to know which industry you are in. Currently, there are two main categories of engraving machines on the market: one is for non-metal engraving, and the other is for metal engraving. Non-metal engraving mainly uses CO2 laser tubes, while metal engraving mainly uses YAG laser engraving machines.
In addition, there are many different types of engraving machines, such as laser welding machines, laser marking machines, laser inner engraving machines, laser demo machines, and laser punching machines.
Therefore, it is necessary to choose the laser engraving machine correctly based on the specific content of your industry and the products you engrave.
Second, know the size of the products you want to process. Choose a suitable laser engraving machine based on the actual size of the products you want to engrave, which is the choice of the machine’s working area.
For example, if the size of the product you want to engrave is 130cm * 90cm, you can choose a model with a working area of 130cm * 250cm.
However, note that a larger working area does not necessarily mean a better machine, as larger machines are not only more expensive, but also some machines with poor quality have unstable laser output at various points on the large working area, resulting in uneven engraving depth on the same surface.
Therefore, it is necessary to choose the most suitable machine for the processing area.
Third, the engraving precision of the laser machine. Laser machines with high precision are naturally favored by people.
Therefore, the biggest difference between laser engraving and traditional engraving equipment and manual engraving is high precision.
Therefore, when choosing, pay attention to the parameter of engraving precision of the laser engraving machine. The higher the engraving precision, the better the effect, and the more satisfying the products to consumers and customers.
Fourth, the power of the laser tube. As the name suggests, the laser engraving machine has a lot to do with the laser tube. Therefore, the power of the laser tube largely determines the final effect of the engraving.
This is not to say that the higher the power of the laser tube, the better. On the contrary, some materials may produce poor effects if a laser tube with a higher power is used.
Therefore, choose a suitable laser tube based on the material, such as acrylic and double-color board engraving do not require a laser tube with too much power, but wood and stone engraving, and cutting of any material may require a laser tube with a larger power to achieve better results.
Fifth, reputation and good after-sales service. This depends on whether the customer has enough knowledge of the market and the industry. The quality of after-sales service directly affects production efficiency.
If the machine purchased has an unsolvable problem, it directly causes production to stop working. Therefore, after-sales service and maintenance are very important.
Therefore, when customers choose laser engraving machine products, they need to actively understand the market, analyze which manufacturers produce better machines with guaranteed reputation and good quality, and which manufacturers have better engraving effects. It is necessary to master this information as soon as possible so that you can make an informed choice when purchasing.

Trumpf from Germany
Trumpf, a laser cutting machine manufacturer from Germany, is a well-known name in the laser cutting industry and a role model for other laser equipment manufacturers. As a brand from the industrial powerhouse of Europe, Trumpf’s laser cutting machines are not only fast and precise, but also at the forefront of developing new equipment.
Germany’s reputation for quality has always been reliable, so choosing their products means you can trust the quality. However, as a well-known brand, the price of Trumpf’s laser equipment is also very expensive, and due to import issues, it can be even more expensive.
Bystronic from Switzerland
Bystronic, a laser equipment manufacturer from Switzerland, is second only to Trumpf in terms of popularity. Their laser cutting machines are more focused on developing for CNC punching machines and shears, but their brand recognition is slightly lower than that of Trumpf from Germany.
TANAKA from Japan
Although Japan’s territory is small, they are a powerhouse in the industrial field worldwide. As a star pupil of Germany, Japan has learned from them the best. Not only are they on par with Germany in automobile manufacturing, but they are also very skilled in manufacturing laser equipment.
KOIKE from Japan
KOIKE is one of Japan’s two major laser equipment companies, and their laser equipment has been imported to China for a long time and is very popular. However, they still lag behind Bystronic from Germany. Also, due to insufficient promotion in the Chinese market, the attention received by KOIKE’s laser equipment is decreasing.
1. Accuracy and Performance
In terms of accuracy, there are domestically produced glass tube laser engraving machines and imported metal radio frequency (RF) tube laser engraving machines.
The glass tube machines have poor accuracy and overall performance, and are mostly used for large-area machines to do rough processing and customization with lower accuracy requirements. The imported metal RF tube laser engraving machines have high accuracy, stable operating power and output energy, and excellent performance.
2. Budget
In terms of budget, the glass tube laser engraving machines are currently inexpensive in China, with prices ranging from around 20,000 to 30,000 yuan, making them relatively affordable. The imported metal RF tube laser engraving machines, on the other hand, are relatively expensive, with prices starting at 100,000 yuan or higher.
3. Service Life
In terms of service life, the glass tube laser engraving machines have a high failure rate and unstable machine stability, and require frequent maintenance. The overall stability of CO2 metal RF tube laser engraving machines is very high, and the failure rate is very low, with a lifespan of more than ten years, and only requires occasional refilling of the laser tube’s gas.
4. Safety
From currently available data, China is the only country still using glass tube laser engraving machines, and has the largest number of users and machines.
Other countries are already using metal RF tube laser engraving machines, as glass tube machines have lower safety and haven’t undergone many safety tests, with uncertain connections and operation between various components, and often experience glass tube explosions. Metal RF tube laser engraving machines have high safety and stability, making them suitable for businesses and universities.
Ultimately, it depends on your budget. Although imported machines are more expensive, their overall performance and productivity are better than domestically produced glass tube laser engraving machines.
We know all this because our company has purchased both types of machines. Initially, due to budget constraints, we purchased a glass tube laser engraving machine, but it broke three times in the first month and required frequent maintenance, which was expensive.
Later, we purchased a metal RF tube laser engraving machine from Laser Master, and it has been in use for nine years with minimal issues and high accuracy. We suggest you invest in an imported machine if your budget allows, as it can help you target the high-end market, which can potentially generate higher profits. The low-end market in modern society is already saturated, so it may not be a sustainable option.

Safety Precautions for Laser Engraving Machines:
Users must strictly comply with the above regulations, otherwise, if there is personal injury or damage to the machine, the manufacturer will not be held responsible.
As a precision instrument, maintenance and upkeep are crucial for the longevity of the laser engraving machine and ensuring processing accuracy.
(1) Ensure the reliability of the device’s ground wire and proper grounding.
(2) It is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of the cooling circulating water, which should be changed frequently, twice a week.
If the equipment is not used for an extended period, drain the water and maintain the water temperature to prevent overheating. (If possible, use pure water.)
(3) Avoid cooling water from freezing in low-temperature environments to prevent the laser from cracking due to freezing.
(4) The machine must be kept clean, especially the optical and motion systems. The guide rails and crossbeams should be wiped regularly and coated with a thin layer of lubricating oil to prevent rust. (Use degreased cotton to wipe and apply sewing machine oil.)
(5) Maintenance of optical equipment
After prolonged use, especially with organic material, smoke and dust may accumulate on the optical lenses (reflective mirrors and focusing mirrors), which can affect laser power, lens lifespan, and engraving results. Wipe the lenses with lens paper or degreased cotton and medical alcohol in a gentle manner. Do not use rough materials or touch the lenses.
Cleaning method for the focusing mirror: First, unscrew the mirror barrel from the laser tube carefully to prevent dropping and damage. Then blow away the surface dust and gently wipe with degreased cotton dipped in alcohol.
Note: Do not wipe back and forth, and do not use rough materials to wipe the lenses. The lens surface is coated with a special metal film, and damage to the film will lead to a significant decrease in laser energy.
Use degreased cotton only once for wiping. After wiping, check for any remaining cotton or other residue, and wait for the alcohol to evaporate completely before turning on the machine.
1. The laser head does not emit light.
1. To troubleshoot, press the test button on the operation panel and observe the status of the ammeter: (high-speed and low-speed machines are equipped with ammeters, while other models are not equipped but can be installed by the user)
① If there is no current: check whether the laser power supply is connected, whether the high-voltage wire is loose or disconnected, and whether the signal line is loose or disconnected.
② If there is current: check whether the lens is broken and whether the optical path is severely misaligned.
③ The laser tube or laser power supply has a problem.
④ The mainboard or wiring board may have a problem.
2. Check if the water circulation system is working properly:
① If the water is not flowing: check whether the water pump is damaged or not connected to power.
② If the water is flowing: check whether the inlet and outlet are connected correctly or whether the water pipe is broken.
③ Check whether the water protection is damaged and whether the water protection line is disconnected.
The laser head can fire and perform self-check, but does not emit light when sending data (check if the computer settings are correct).
2. Uneven or shallow carving
3. Abnormal Reset
4. Leaks
5. Cleaning the hooking edge, misalignment, and non-closure:
6. The computer cannot output:
7. Cannot calculate the path:
8. Common computer problems:
The metal laser engraving machine has brought about a revolutionary change in the field of metal processing, ushering in a new era of high precision, high efficiency, and versatility. This innovative technology has been widely applied in multiple industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical equipment, and jewelry, injecting new vitality into these fields.
With its unparalleled precision, waste reduction, and increased production efficiency, the metal laser engraving machine has become an essential asset for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
As the field of metal processing continues to rapidly develop, the metal laser engraving machine will further consolidate its position as a key technology that disrupts tradition.
This technology has the potential to redefine “possibility,” bringing new innovative and creative opportunities to the metal manufacturing industry. As we embrace the future of metal processing, the metal laser engraving machine undoubtedly will play a crucial role in driving the industry’s growth over the next several years.