Have you ever wondered how everyday metal objects with complex shapes are created? Metal spinning is the fascinating process behind items like lampshades and aerospace components. This technique involves rotating a metal disc at high speed and shaping it with a tool against a mold. In this article, you’ll explore the step-by-step operations of metal spinning, learn about the materials used, and understand the design considerations crucial for producing high-quality parts. Dive in to uncover the secrets of this intricate and essential metalworking method!

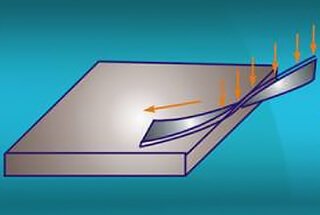
Metal spinning is a versatile, symmetrical rotational forming process for sheet metal that finds widespread application across diverse industries. This technique involves plastically deforming a rotating metal blank over a mandrel using specialized tools, resulting in axisymmetric components with high precision and structural integrity.
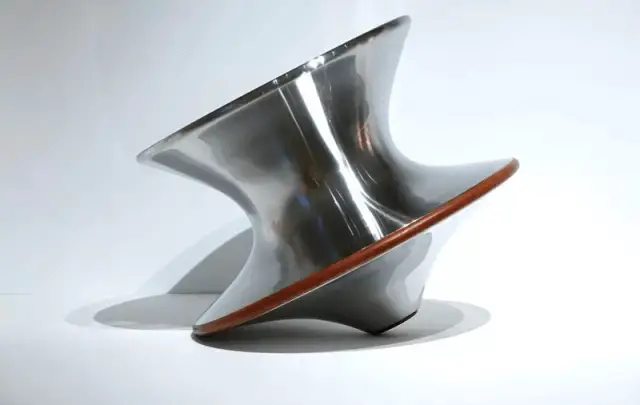

Cost: The initial tooling costs for metal spinning are relatively low compared to other forming processes, as it primarily requires a mandrel and simple forming tools. However, the unit cost is moderate due to the skilled labor involved and the semi-automated nature of the process. For complex geometries or high-volume production, CNC metal spinning can offer improved cost-efficiency.
Typical Products: Metal spinning’s versatility allows for the production of a wide range of components, including:
Suitable Batch Size: Metal spinning is particularly well-suited for small to medium production runs, typically ranging from prototypes to several thousand units. Its flexibility and low tooling costs make it ideal for customized or specialized components where traditional stamping or deep drawing processes may be cost-prohibitive.
Quality: The surface quality and dimensional accuracy of metal-spun products are highly dependent on several factors:
Skilled operators can achieve excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances, often eliminating the need for secondary finishing operations. However, maintaining consistent quality across large production runs can be challenging without advanced CNC spinning systems.
Speed: Production speed in metal spinning is moderate and varies based on several factors:
While not as fast as high-volume stamping processes, metal spinning offers quicker turnaround times for small to medium batches and complex geometries. Recent advancements in CNC metal spinning technology have significantly improved production speeds and consistency, making it increasingly competitive for larger production runs.

Suitable for mild metal plates, such as stainless steel, brass, copper, aluminum, titanium, etc.

Limitations: Metal spinning is only suitable for producing rotationally symmetrical parts, with hemispherical thin shell metal parts being the most ideal shape.
Size Constraints: The internal diameter of parts formed through metal spinning should be kept within 2.5m.
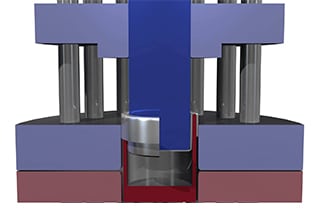
Step 1: Fix the cut circular metal plate on the machine mandrel
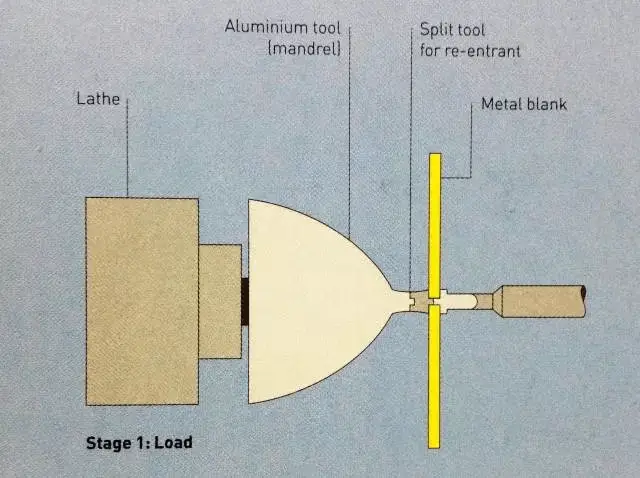
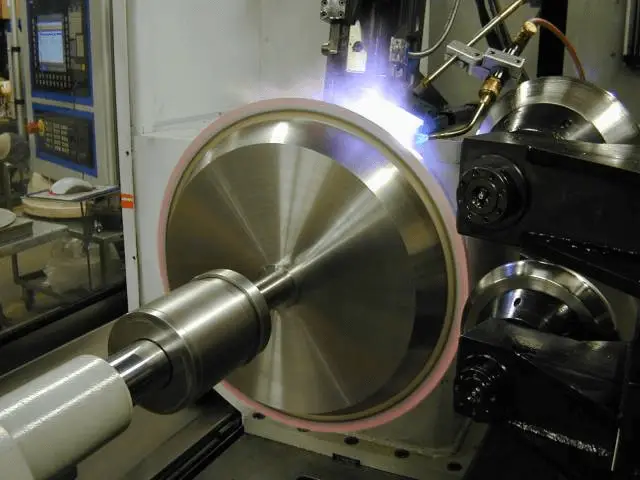
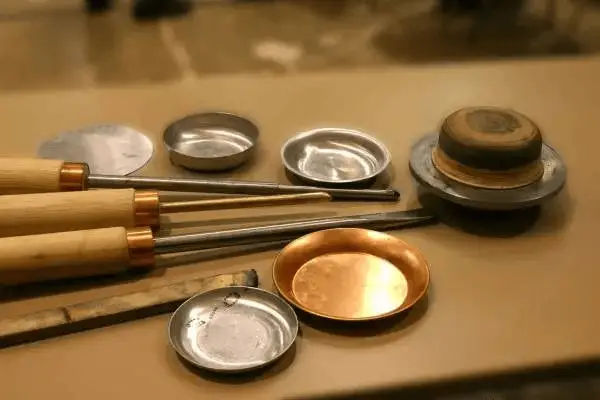
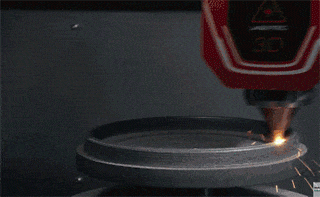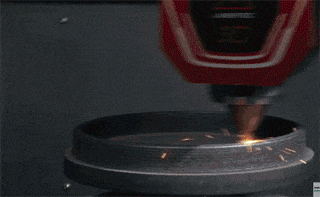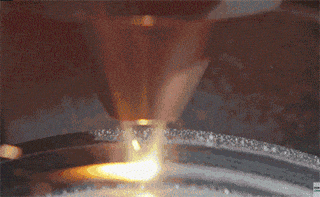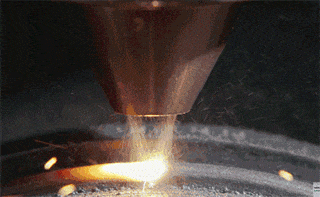
Step 2: The mandrel rotates the circular metal plate at high speed, while the tool with the wheel begins pressing against the metal surface until the metal plate conforms to the inner wall of the mold.
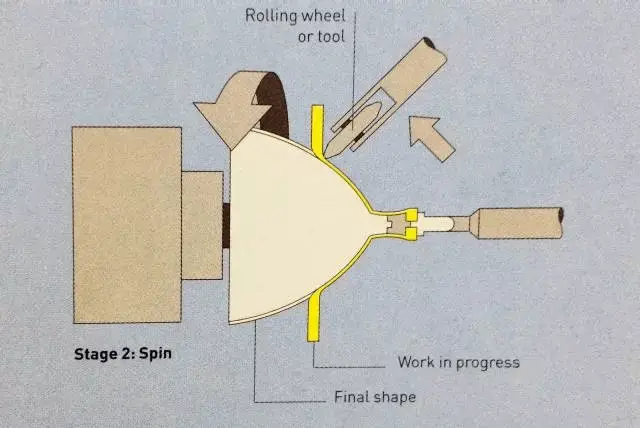
Step 3: Once the molding process is complete, the mandrel is removed and the top and bottom of the part are trimmed for demolding.
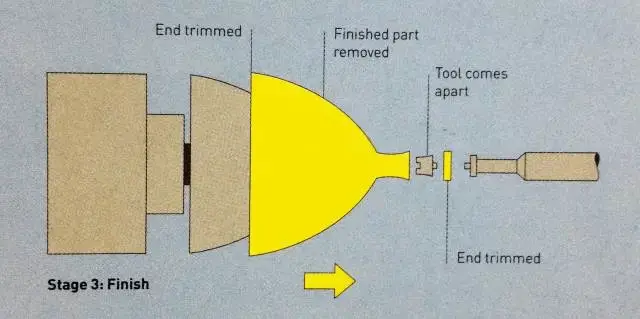
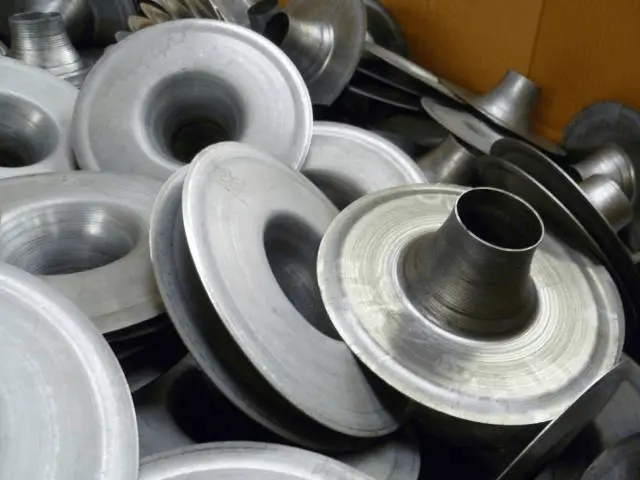
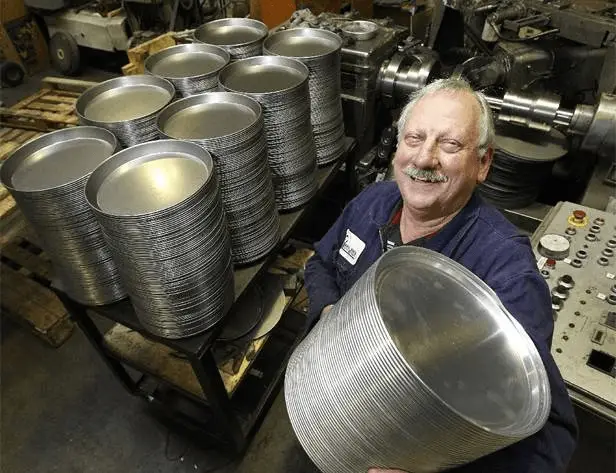
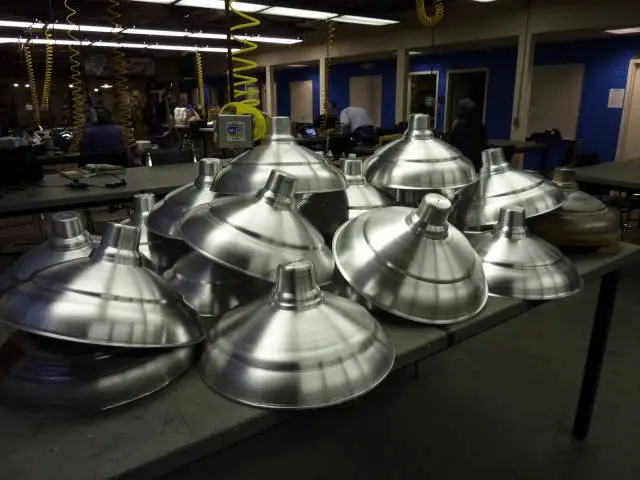
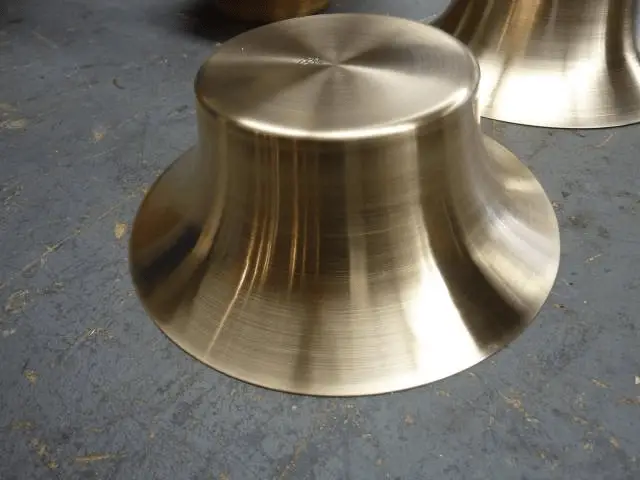
Example 1: Metal spinning of lampshade (picture)
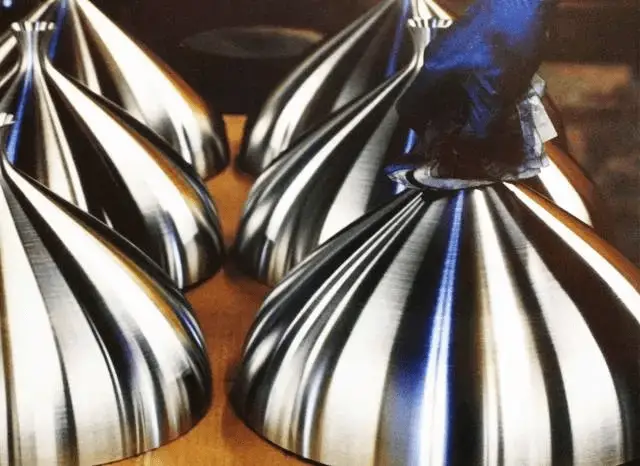

Procedure:
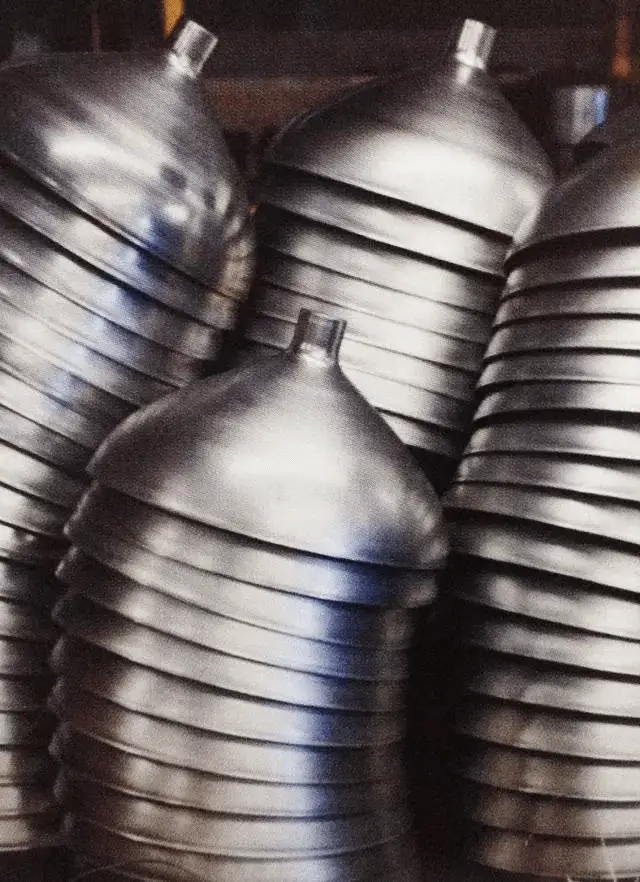
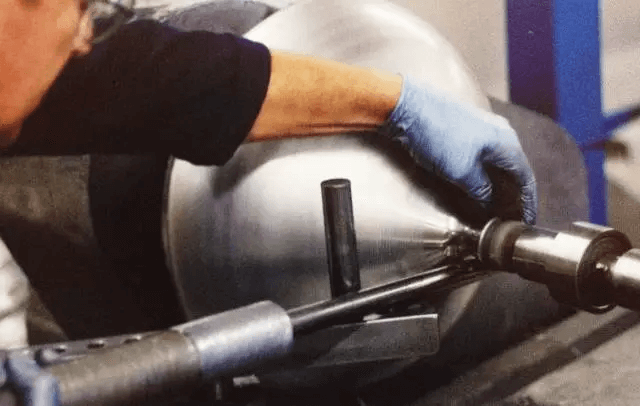

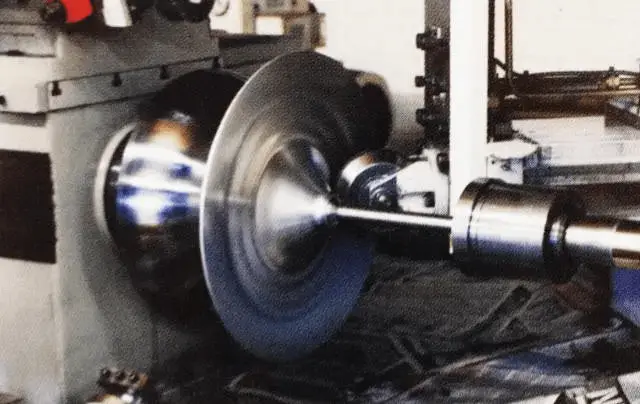
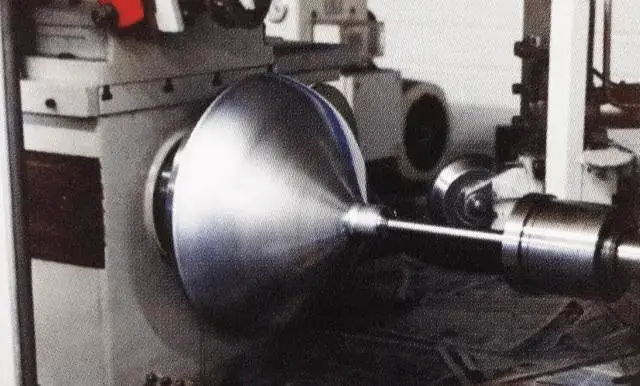




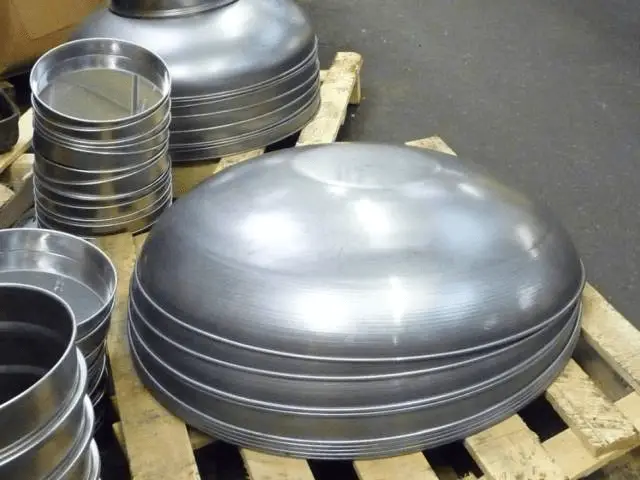
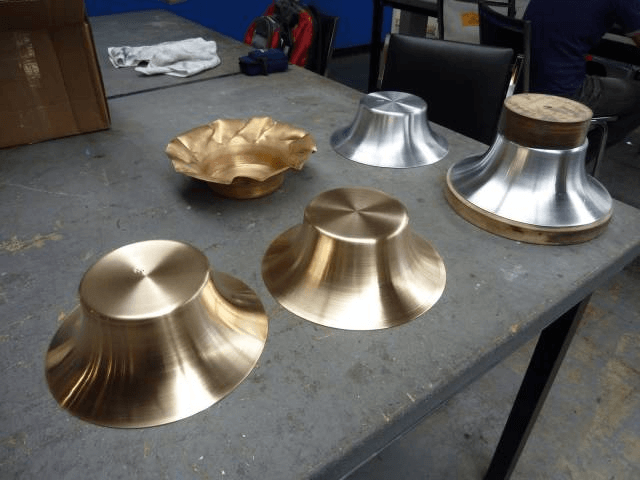
Example 2: Spinning process of other metal products