How do you keep bolts from rusting in harsh marine environments? Traditional methods often fall short, leading to costly maintenance and safety risks. This article explores a groundbreaking anti-corrosion technique combining zinc penetration and sealing paint. Discover how this new method significantly enhances durability and reduces long-term maintenance, ensuring safer and more reliable offshore structures.

Abstract: This article introduces several common methods of bolt anti-corrosion in offshore projects, analyzes the problems encountered in the actual construction, and puts forward a new method of bolt anti-corrosion.
Introduction
Bolted connection is a common connection method for offshore projects.
It is simple in structure, reliable in connection, and convenient in construction and disassembly, so it is widely used.
However, due to the factors such as installation location, installation method and degree of attention, the anti-corrosion of bolts is often ignored.
The anti-corrosion coating of bolts is easy to be damaged and difficult to repair during installation.
In the project maintenance stage, bolts also need to be checked and replaced regularly.
After repeated disassembly and assembly of bolts, the original anti-corrosion layer is easily damaged.
In marine environments, bolts are often surrounded by water vapor trapped in bolt holes.
In this way, the bolts and the surrounding metal structures will form corrosive galvanic cells, resulting in extreme corrosion of large cathode and small anode.
As a small anode, the corrosion rate of bolts is very fast.
The corrosion occurring in the bolt hole can hardly be seen from the bolt surface in the early and middle stages, and only in the later stages can there be obvious corrosion products on the surface.
Therefore, the corrosion of bolts has a strong concealment, which will cause great potential safety hazards.

Common anti-corrosion forms of bolts include electroplating, hot dip plating, chemical surface treatment, paint, ceramic protective film, etc.
Electroplating is to use electrolysis principle to attach a layer of uniform and good adhesion coating on the surface of the bolt.
The coatings are mostly zinc, chromium and other materials that can be used as sacrificial anodes.
When the coating is in good condition, the coating can isolate the bolt from the corrosive environment and inhibit corrosion;
When the coating is damaged, the coating can be used as a sacrificial anode to protect the bolts.
Hot dip plating is a process to immerse the bolt into the molten plating metal liquid and then take it out for cooling to form a metal coating on its surface.
The anti-corrosion principle of hot dip plating is similar to electroplating, but compared with electroplating, the coating thickness is thicker, the adhesion between layers is better, and the corrosion resistance is stronger.
The common form of hot dip galvanizing is hot dip galvanizing.
Chemical surface treatment is placing the bolt in some specific chemical solutions to change the surface of the bolt and modify the surface of the bolt to form a protective coating.
It can be roughly divided into phosphate passivation, chromate treatment and oxidation treatment.
Chemical surface treatment is mostly used for stainless steel bolts.
Chemical surface treatment is irreversible, and once damaged, it is difficult to repair.
Paint is the most common and widely used anti-corrosion method.
It can be applied on the surface of bolts with different construction methods to form a solid film with firm adhesion, certain strength and continuity.
The film can isolate the bolt from the surrounding environment, and it can also play a role in cathodic protection if the coating contains zinc and other elements.
The principle of the ceramic protective film is to use the characteristics of high melting point, high hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and good insulation of ceramics to spray ceramic material particles in molten state on the surface of bolts by spraying, forming a layer of ceramic film.
However, compared with other anti-corrosion methods, the construction of the ceramic protective film is more difficult and costly, which makes it difficult to popularize in a large number of projects.

In the field of offshore engineering, bolts, as a common connection method, are widely used.
Therefore, when selecting the anti-corrosion form of bolts, it is necessary to consider not only the anti-corrosion performance, but also the cost and maintenance costs.
At present, in China’s offshore engineering field, the most widely used anti-corrosion form of carbon steel bolts is generally zinc penetration.
Zinc penetration is prepared by embedding the bolt in zinc alloy powder and holding it for a period of time after rising to a certain temperature, which will produce a metallurgical diffusion effect between zinc and iron.
Due to the special porosity of the zinc coating surface, it is necessary to seal the zinc coating surface within 2 hours after the zinc coating is completed.
Compared with zinc plating, zinc atoms diffuse into the bolt surface, changing the composition and structure of the surface layer, making the zinc coating very uniform and dense, with strong adhesion, and not easy to peel off under impact.
However, in the process of transportation, storage and installation, the bolts will inevitably cause irreversible damage to the zinc coating on the surface.
The damaged zinc coating is usually repaired with zinc rich primer before installation.
However, the anti-corrosion performance of the repaired part is much worse than that of the original zinc penetration layer, so it is easy to form a corrosion galvanic cell with a large cathode and a small anode after the bolt is installed, and corrosion often occurs here.
These repairs are only applicable before installation. During installation, the bolts need to meet a certain tightening torque.
Therefore, the zinc coating is easy to be damaged during installation, and these damages cannot be repaired.
This has buried hidden danger for the corrosion of bolts in later stage.
In combination with the special service environment of offshore engineering, the anti-corrosion method of zinc penetration coating and sealing paint is adopted, which has strong anti-corrosion performance and good mechanical impact resistance.
However, sealing paint is used to seal the gaps of zinc penetration coating, which does not play a role in anti-corrosion.
The zinc penetration coating itself is a sacrificial and consumable anti-corrosion coating, which will gradually dissolve in the marine environment and is prone to corrosion in the later period.
Therefore, a new recommended practice is put forward, that is, coating paint on the basis of the original zinc penetration plus sealing paint in the same anti-corrosion form.
Before the installation of bolts, the screws shall be coated and reserved at both ends.
Paint both ends of the screw and the nut after the bolt is installed.
Before leaving the factory, the bolts shall be galvanized and sealed with paint according to the standard requirements;
After arriving at the site, the installation and painting shall be completed.
Before the primer is applied on the sealing paint coating, all oil, grease, lubricant and other surface contaminants on the bolt surface shall be removed by solvent wiping.
It can be sprayed or brushed. Considering the particularity of bolt coating, it is recommended to adopt the brushing method to reduce unnecessary loss of paint.
The painting system of bolts and nuts shall refer to the surrounding service environment.
If it is a high-temperature environment, the high-temperature paint painting system shall be selected.
For the coating of bolts, it is recommended to follow the following steps, as shown in Figure 1 and Fig. 2.
3.5.1 Single head nut bolt
(1) Cover the 2 nut thickness locations.
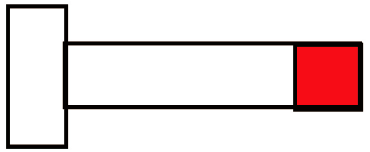
(2) Other parts shall be painted with primer.

(3) The contact parts shall be coated with intermediate paint and finish paint.
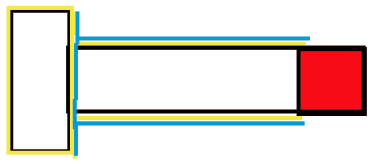
(4) Remove the cover.
After installing the nut, remove the grease on the surface, and make the rest as the specified coating system (bottom, middle and surface).

Fig. 1 Single-head nut bolt
3.5.2 Stud nut bolt
(1) Cover the 2 nut thickness locations.

(2) Paint primer on other parts

(3) The contact parts shall be coated with intermediate paint and finish paint.

(4) Remove the cover.
After installing the nut, remove the grease on the surface, and make the rest as the designated coating system (bottom, middle and surface).
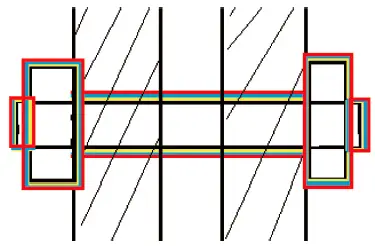
Fig. 2 Single head nut bolt
With this anti-corrosion method, a layer of anti-corrosion coating can be formed on the surface of the sealing paint to resist some corrosion before the zinc coating starts to be consumed, which greatly reduces the consumption rate of the zinc coating.
At the same time, as the nuts of the exposed parts are coated after installation, it can play a certain role in plugging the bolt holes and reducing the entry of water vapor.
The double-layer protection of coating and zinc penetration can effectively slow down corrosion and reduce later maintenance.
To sum up, this new recommended method of bolt anti-corrosion has increased the cost of labor and materials in the project construction stage, although compared with other anti-corrosion forms, it has increased the process of coating construction on site.
However, compared with the huge investment, super long service time, high reliability and high safety of the entire offshore engineering project, it is completely feasible and recommendable from the perspective of the overall project.