What is octagonal bar? Octagonal bar, also known as octagonal steel, is a specialized type of section steel characterized by its regular eight-sided cross-sectional profile. This unique geometry offers a blend of structural and aesthetic advantages, making it a versatile choice in various industrial and architectural applications. Key features of octagonal bars include: Octagonal bars […]
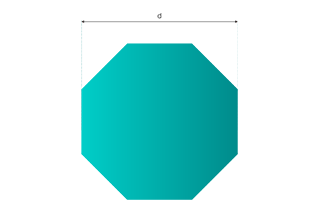
Octagonal bar, also known as octagonal steel, is a specialized type of section steel characterized by its regular eight-sided cross-sectional profile. This unique geometry offers a blend of structural and aesthetic advantages, making it a versatile choice in various industrial and architectural applications.
Key features of octagonal bars include:
Octagonal bars offer several advantages over traditional round or square profiles:
Hot-rolled octagonal steel bars, as specified in GB/T702-2008, are manufactured with a distance between opposite edges ranging from 16mm to 40mm. This standard outlines critical specifications for dimension, shape, weight, and allowable deviations, ensuring consistency and quality in industrial applications.
In the metal fabrication market, hot-rolled octagonal steel is typically supplied based on either its actual weight or its theoretical weight. The choice between these two methods can impact pricing and material planning in manufacturing processes.
To accurately determine the weight of octagonal steel for your specific requirements, you can utilize the octagonal steel weight calculator provided below. This tool incorporates the latest industry standards and material properties to deliver precise calculations, essential for project planning, cost estimation, and inventory management.
Understanding the weight of octagonal steel bars is crucial for various manufacturing processes, including:
By using this calculator, you can optimize material usage, improve cost efficiency, and ensure adherence to industry standards in your metal fabrication projects.
Related Tool: Steel Weight Calculator
| Grade (mm) | Weight (kg/m) |
|---|---|
| 16 | 1.66 |
| 18 | 2.11 |
| 20 | 2.6 |
| 22 | 3.15 |
| 25 | 4.06 |
| 28 | 5.1 |
| 30 | 5.85 |
| 32 | 6.66 |
| 34 | 7.51 |
| 36 | 8.42 |
| 38 | 9.39 |
| 40 | 10.4 |
Calculating the weight of an octagonal pole requires precise input parameters to ensure accuracy and reliability. These parameters include material type, outer diameter, wall thickness, and length. Each parameter plays a critical role in determining the overall weight of the pole, essential for applications in construction, engineering, and logistics.
The material from which the pole is made significantly impacts its weight due to varying densities. Common materials include:
The outer diameter of the octagonal pole is essential for calculating the cross-sectional area. This measurement, typically in inches or millimeters, determines the size of the pole and influences the overall volume calculation. The outer diameter is the distance across the pole, measured from one flat side to the opposite flat side.
Wall thickness impacts both the structural integrity and weight of the pole. Thicker walls provide greater strength but also increase the weight. This measurement should be taken in inches or millimeters and is critical for determining the pole’s cross-sectional area and volume.
The length of the pole is another vital parameter, measured in units such as feet, inches, meters, or centimeters. The length, combined with the cross-sectional area, helps calculate the total volume of the pole.
To find the weight of the octagonal pole, it is necessary to determine its cross-sectional area. For a regular octagonal pole, the formula for the cross-sectional area is:
where the side length can be derived from the outer diameter. This area calculation is pivotal for determining the volume of the pole.
The volume of the pole is obtained by multiplying the cross-sectional area by the length:
Volume= Cross-sectional Area x Length
This volume calculation is essential for determining the total weight when combined with the material’s density.
The density of the material is used to calculate the final weight of the pole. The formula for weight calculation is:
Weight=Density x Volume
By using the correct density values for the chosen material, the weight of the octagonal pole can be accurately determined.
For a steel pole with an outer diameter of 4 inches and a length of 20 feet (240 inches):
Calculate the Cross-Sectional Area:
Determine the Volume:
Calculate the Weight:
In a real-world application, suppose this steel pole is used in a construction project to support a heavy structure. The accurate weight calculation ensures that the pole meets the necessary strength requirements and helps in planning for transportation and installation logistics. By inputting accurate parameters into the calculation, the weight of the octagonal pole can be precisely determined, ensuring safety, stability, and structural integrity in various applications.
The material used for an octagonal pole significantly influences its weight due to differences in densities. Common materials for constructing octagonal poles include steel, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel. Understanding the properties of these materials is crucial when using an octagonal pole weight calculator.
Steel is a versatile material, with common types including mild steel, carbon steel, and stainless steel. These materials are known for their strength and durability. The density of steel is typically around 7.9 g/cm³ (0.2835 lb/in³). Different grades, such as EN-19 and EN-24, offer varying mechanical properties but have similar densities. EN-19 steel is known for its high tensile strength and toughness, while EN-24 is valued for its resistance to wear and fatigue. Stainless steel, such as SS 304 and SS 316, also falls within this density range but offers added corrosion resistance.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³ (0.0975 lb/in³). This makes it ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial. Common aluminum alloys used in structural applications include Aluminum 6061 and 6063. Aluminum 6061 is known for its good mechanical properties and weldability, while 6063 offers excellent extrudability and surface finish.
Copper has a density of about 8.96 g/cm³ (0.324 lb/in³), making it denser than both steel and aluminum. It is often used in applications requiring high electrical conductivity. The substantial weight of copper makes it important to consider in designs where weight is a critical factor.
Stainless steel shares a similar density with other steel types, around 7.9 g/cm³, but stands out due to its resistance to corrosion. Grades like SS 304 and SS 316 are commonly used, with SS 316 offering higher resistance to corrosion and pitting in chloride environments.
Brass, with a density around 8.5-8.7 g/cm³, and other alloys like bronze, titanium, and nickel, each have unique properties that influence their use in octagonal poles. Brass is often chosen for its machinability and corrosion resistance, while titanium is valued for its high strength-to-weight ratio.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Density (lb/in³) | Example Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | 7.9 | 0.2835 | EN-19, EN-24 |
| Stainless Steel | 7.9 | 0.2835 | SS 304, SS 316 |
| Aluminum | 2.7 | 0.0975 | 6061, 6063 |
| Copper | 8.96 | 0.324 | Pure Copper |
| Brass | 8.5-8.7 | 0.307-0.314 | Various Alloys |
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
An octagonal pole weight calculator can be used with a variety of materials, each having unique properties and densities that affect the weight calculation. Common materials include metals such as aluminum (various alloys like 6061, 7075), steel (carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel), stainless steel (grades like SS 304, SS 316), copper and its alloys, brass, cast iron, nickel and its alloys (such as Nickel 200, Nickel 625), titanium, zinc, and zirconium. Additionally, other metals like beryllium, columbium, molybdenum, silver, gold, tantalum, and tungsten can also be used. While metals are most common, some calculators may also handle non-metals like EPDM rubber, natural rubber, and SBR rubber. Users need to input the material type and dimensions of the pole to obtain an accurate weight calculation.
Calculating the weight of an octagonal pole accurately is important for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the structural integrity and safety of the pole. Knowing the precise weight allows engineers to determine how much load the pole can safely support, including the weight of any attached equipment and external forces like wind and snow. This is crucial for preventing pole failure, which can lead to accidents and service disruptions.
Secondly, the weight of the pole influences its stability and deflection under various loads. Accurate weight calculations help engineers predict how the pole will behave under different conditions, ensuring it remains stable and does not deflect excessively. This is vital for maintaining the pole’s long-term performance and preventing potential failures.
Thirdly, precise weight calculations are necessary for optimizing the pole’s design. Engineers use this information to select the appropriate materials and dimensions that balance strength, durability, and cost, ensuring the pole meets the required specifications while minimizing material usage and costs.
Additionally, knowing the exact weight of the pole is essential for planning its transportation and installation. Accurate weight information helps in selecting the right equipment and ensuring the pole can be safely moved and erected, avoiding logistical issues, increased costs, and potential safety hazards.
Lastly, accurate weight calculations are needed to comply with industry standards and regulations, such as those outlined in the National Electric Safety Code (NESC). These standards often require specific strength and load capacity ratings, which are directly tied to the pole’s weight and material properties.
In summary, accurately calculating the weight of an octagonal pole is crucial for ensuring safety, structural integrity, stability, optimal design, efficient transportation and installation, and compliance with industry standards.