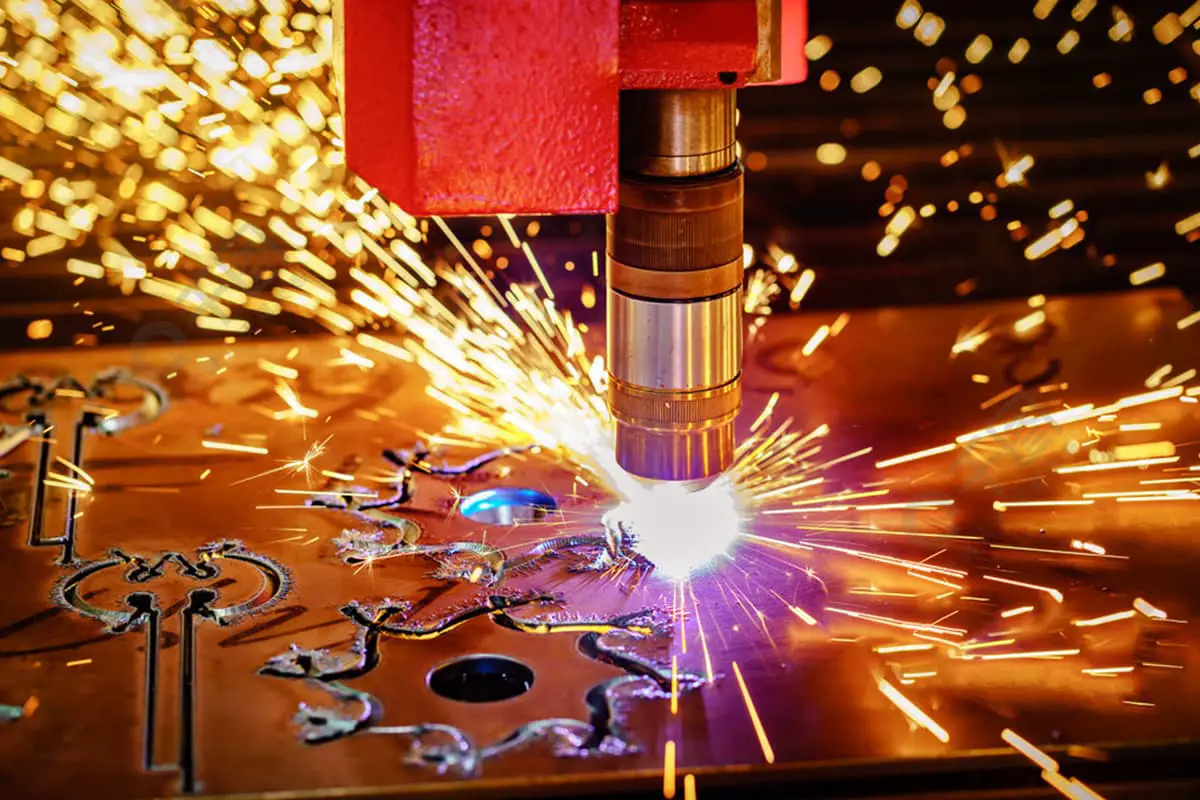
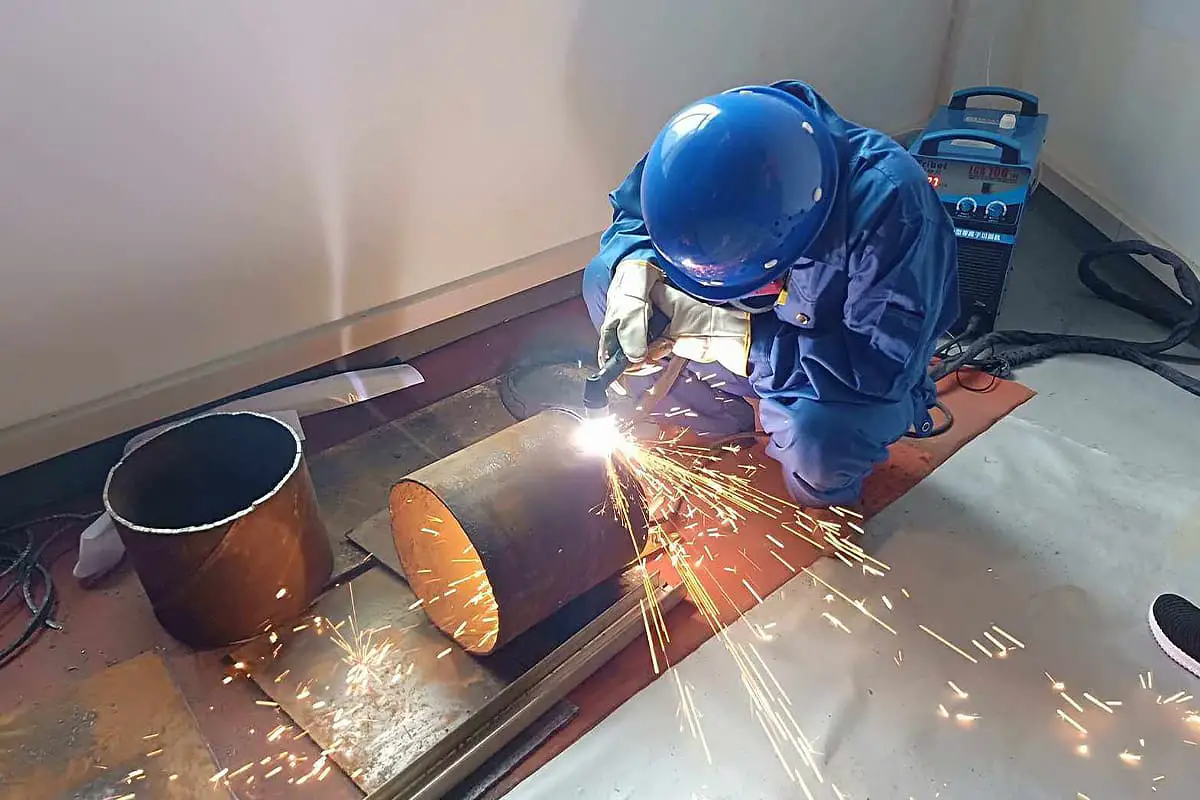
Imagine being surrounded by a cloud of invisible, harmful particles every time you work. Plasma cutting, though efficient, produces hazardous dust and gases that can severely affect health and the environment. This article explores the dangers of plasma cutting smoke and offers effective solutions to purify the air. Discover how to protect yourself and maintain a safe workspace while ensuring compliance with environmental standards.

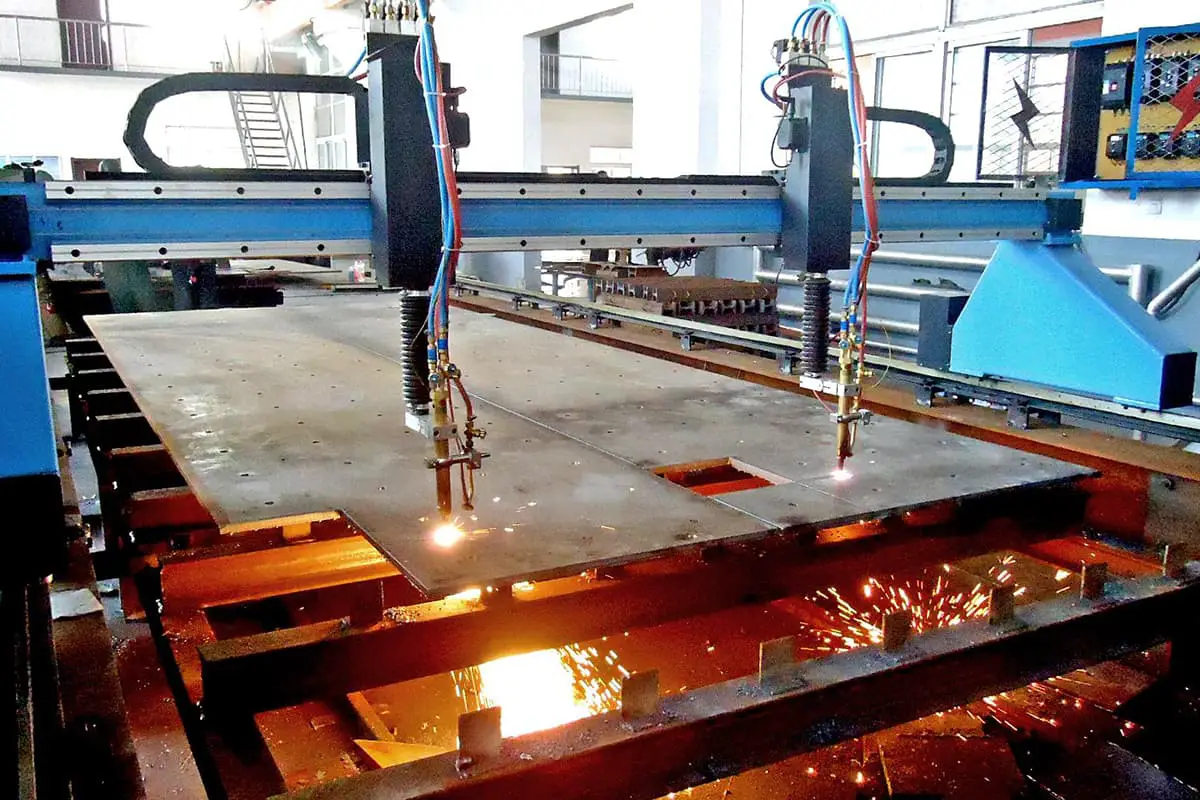
Plasma laser cutting machines have become ubiquitous in modern manufacturing facilities, prized for their exceptional cutting efficiency and superior edge quality. This technology has gained widespread adoption across industries, earning accolades from both manufacturers and end-users for its precision and versatility.
However, the plasma cutting process is not without its drawbacks. During operation, it generates a complex mixture of harmful byproducts, including metal fumes, particulate matter, and noxious gases. These emissions pose significant environmental and occupational health risks, contributing to both air pollution and noise pollution in the workplace.
To mitigate these hazards and comply with stringent environmental regulations, it is imperative that the dust and fumes produced during plasma cutting operations be effectively captured and treated. This necessitates the implementation of advanced air purification systems designed specifically for metalworking applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the multifaceted risks associated with plasma cutting dust and explore state-of-the-art purification solutions. By understanding the composition of these emissions, their potential health impacts, and the latest filtration technologies available, manufacturers can make informed decisions to protect their workforce and minimize their environmental footprint.
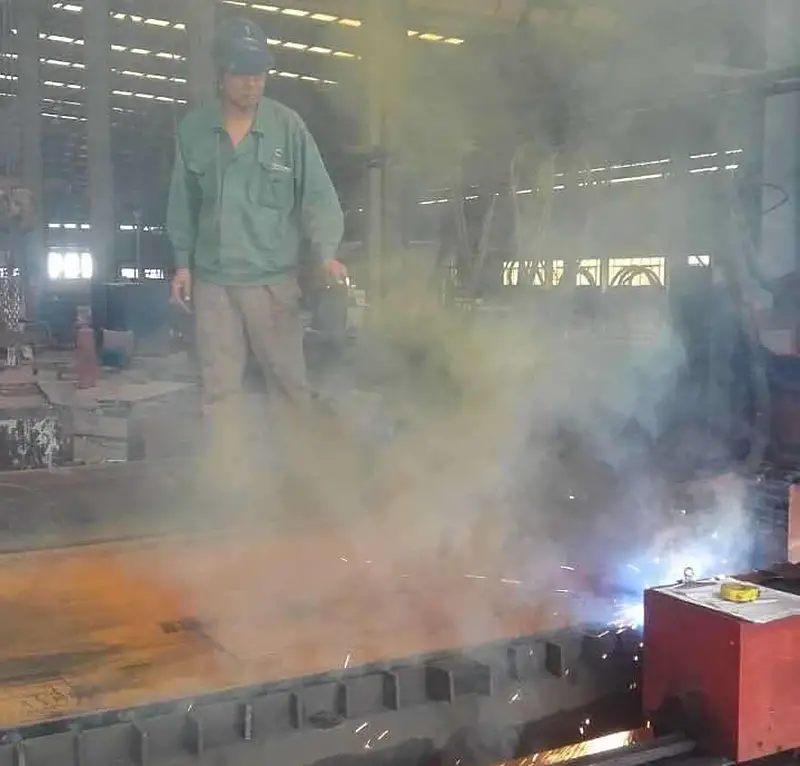

Plasma cutting machines, renowned for their high cutting efficiency and versatility across a wide range of materials, do have a notable drawback – they generate significant amounts of dust and fumes during operation.
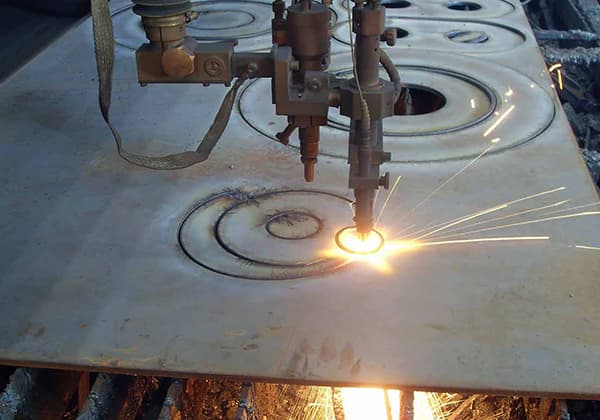
This byproduct, often referred to as plasma cutting dust or fume, is a complex mixture primarily composed of vaporized metal particles, oxides, and various gases. The composition can vary depending on the material being cut, the plasma gas used, and the cutting parameters. Typically, it includes:
The size of these particles can range from submicron to several microns in diameter, with the majority falling into the respirable range (< 10 μm). This makes them particularly hazardous if inhaled, as they can penetrate deep into the lungs.
It’s important to note that the composition and toxicity of plasma cutting dust can be significantly influenced by any coatings or contaminants present on the workpiece, such as paint, galvanization, or oils. These can introduce additional harmful substances like hexavalent chromium, zinc oxide, or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the fume.
To mitigate the health and environmental risks associated with plasma cutting dust, proper ventilation, fume extraction systems, and personal protective equipment are essential in any plasma cutting operation.
Here is a detailed description of the specific hazards posed by the metal dust produced during cutting:
Workers involved in cutting have noted that when using plasma cutting machines to cut 3-6mm carbon steel plates, a lot of yellow smoke is generated. This yellow smoke poses a significant threat to human health and can easily cause pneumoconiosis if inhaled over long periods.
Given these hazards associated with plasma cutting dust, it’s crucial to implement effective dust purification when performing plasma cutting work to reduce the incidence of occupational diseases.
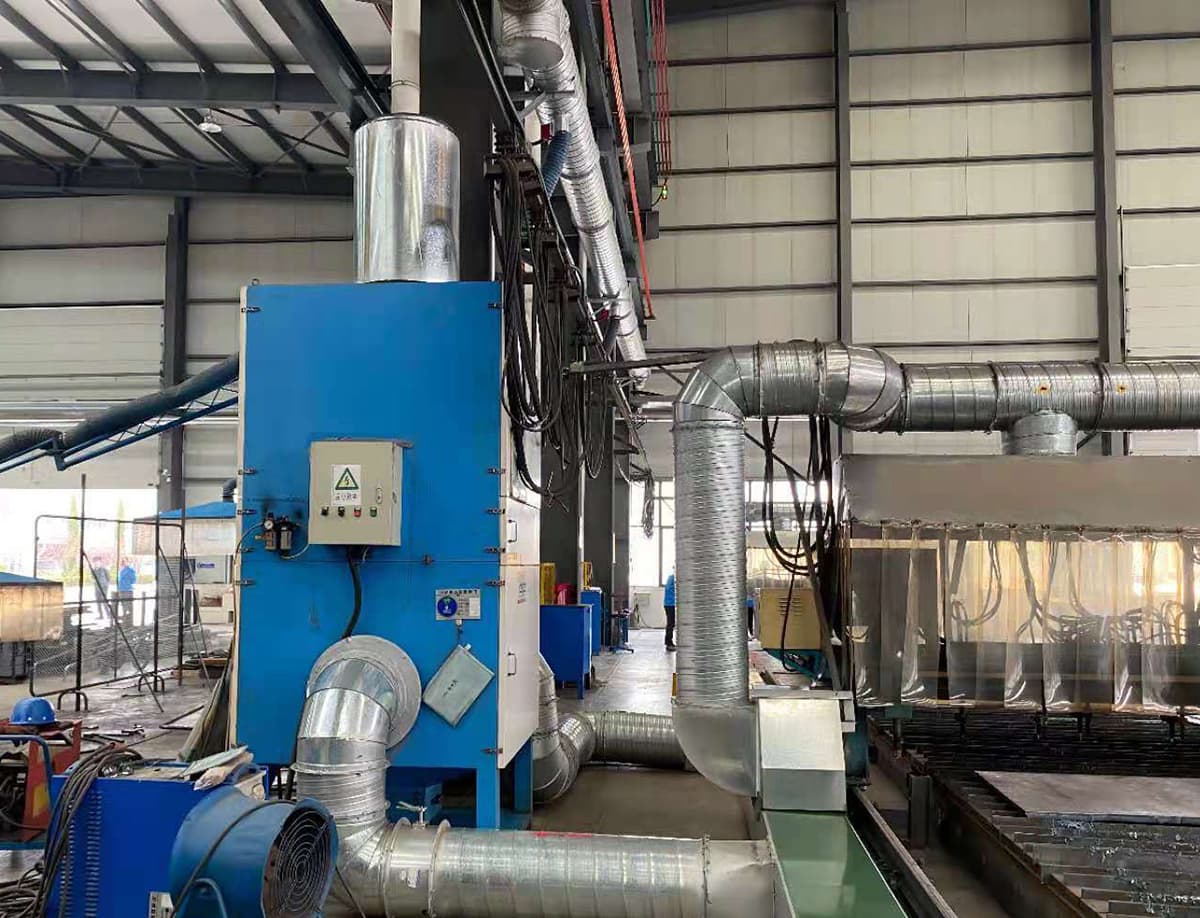

Harms Operator’s Health
The dust produced by plasma cutting machines contains many inhalable substances (such as manganese oxide and oxides of potassium and sodium). Once these substances enter the human body, they can cause significant harm.
Workers who spend a long time working in conditions with dust from CNC plasma cutting machines have a significantly higher proportion of respiratory diseases like chronic bronchitis than others.
Moreover, these inhalable substances can accumulate in the body’s bones and blood, leading to a decrease in their function, and may even cause cancer.
Impacts Enterprise Benefits
Environmental protection has become an international and national trend. Pollution caused by dust could potentially result in fines for companies.
Additionally, not promptly managing dust pollution can affect the precision of production machines, thereby impacting production efficiency.
Given these two major reasons, the dust hazards of plasma cutting machines are significant and need timely purification treatment. So, how should the dust from plasma cutting machines be managed?
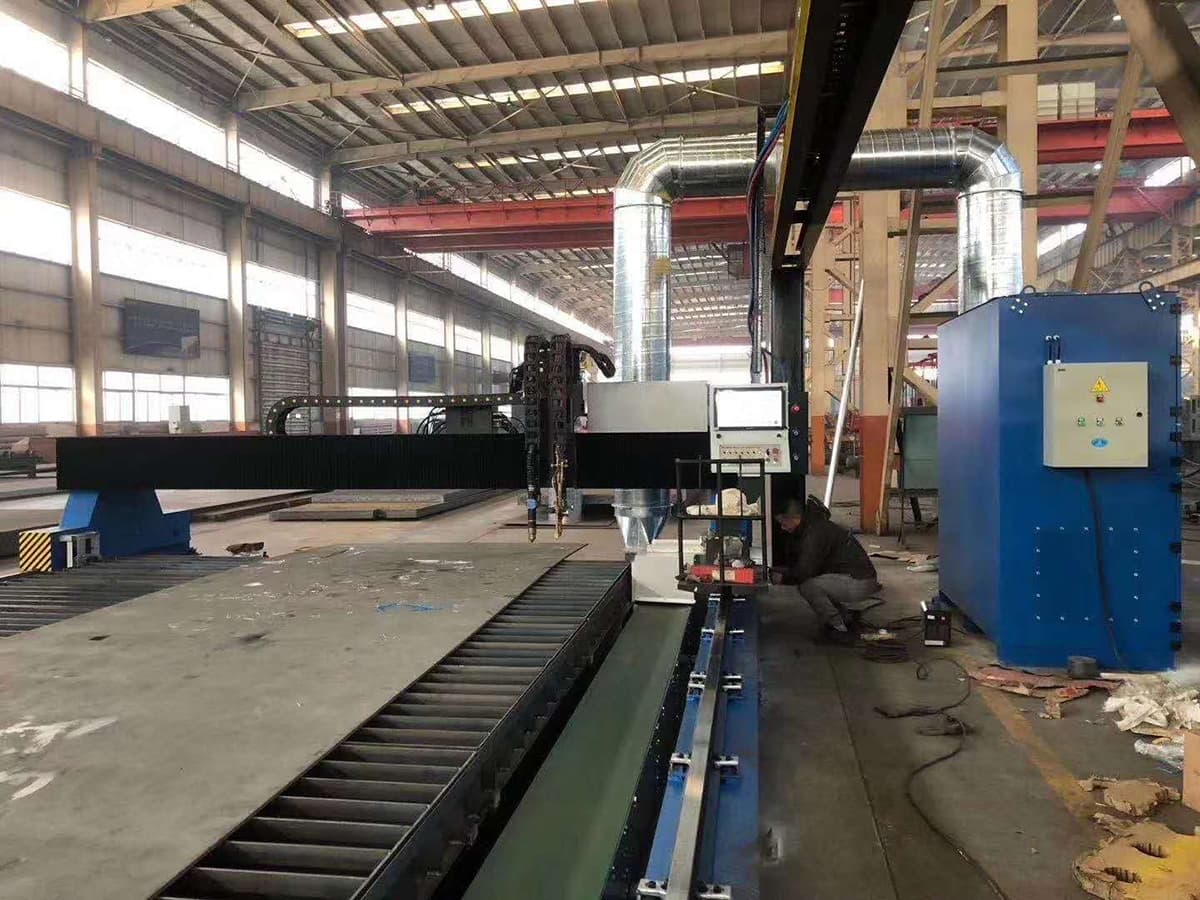

Currently, there are two primary methods for managing dust from plasma cutting:
This method involves setting up a water bed under the cutting platform, allowing the workpiece to be submerged in water. Cutting is performed underwater, so the oxides produced during cutting are collected by the water, thereby purifying the working environment. This method only requires a water-holding container as a one-time investment.
However, it can lead to secondary pollution (water pollution), and metal oxides are likely to agglomerate underwater, making cleanup challenging. For users in colder regions, the water in the cutting platform may freeze during winter, causing inconvenience.
Furthermore, this method is not suitable for purifying dust from metals like aluminum and magnesium, which produce explosive dust during cutting.
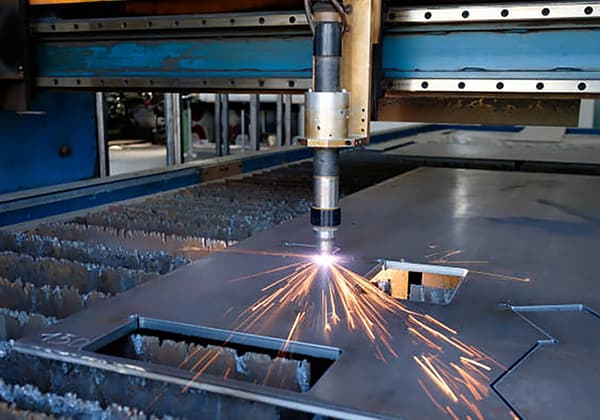
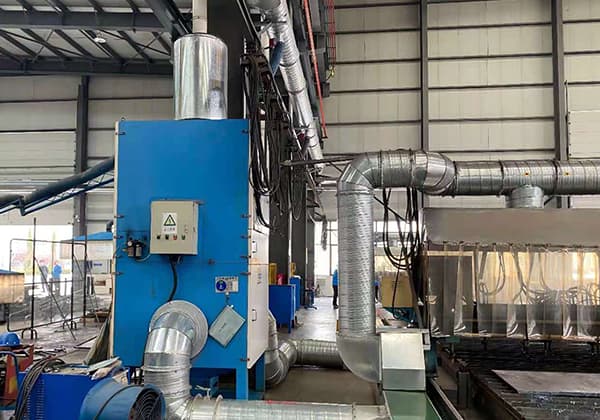
Dry dust removal involves adding a dust capture device to the CNC cutting platform. The captured dust is directly transported to a dust filter and purification device. After treatment, the purified air is then discharged.
Dust produced during plasma cutting is mainly formed below the workpiece’s cut, making exhaust-type negative pressure cutting platforms the most common dust capture device. Because of its simple structure, reliable operation, and effective dust removal, the dry dust removal method is widely used.
The dust collector for a plasma cutting machine is designed and manufactured based on the machine’s specifications, with a focus on economic efficiency, easy maintenance, economical operation, and minimal subsequent costs while ensuring effective dust removal.
Depending on the width of the cutting work platform, it can be divided into a single-side down-draft air door style workbench and a double-side down-draft air door style workbench.
Plasma Cutting Machine Dust Collector Workflow
The goal is to collect the dust produced during plasma cutting. The collection method can be side suction, bottom suction, or top suction, with the dust directly drawn into the pipeline by the fan. A dust removal device is added to the pipeline’s end, and the collected dust is directly purified by the dust removal equipment before being discharged inside or outside the workshop. Within the designed air volume, the purified dust can meet environmental emission requirements.
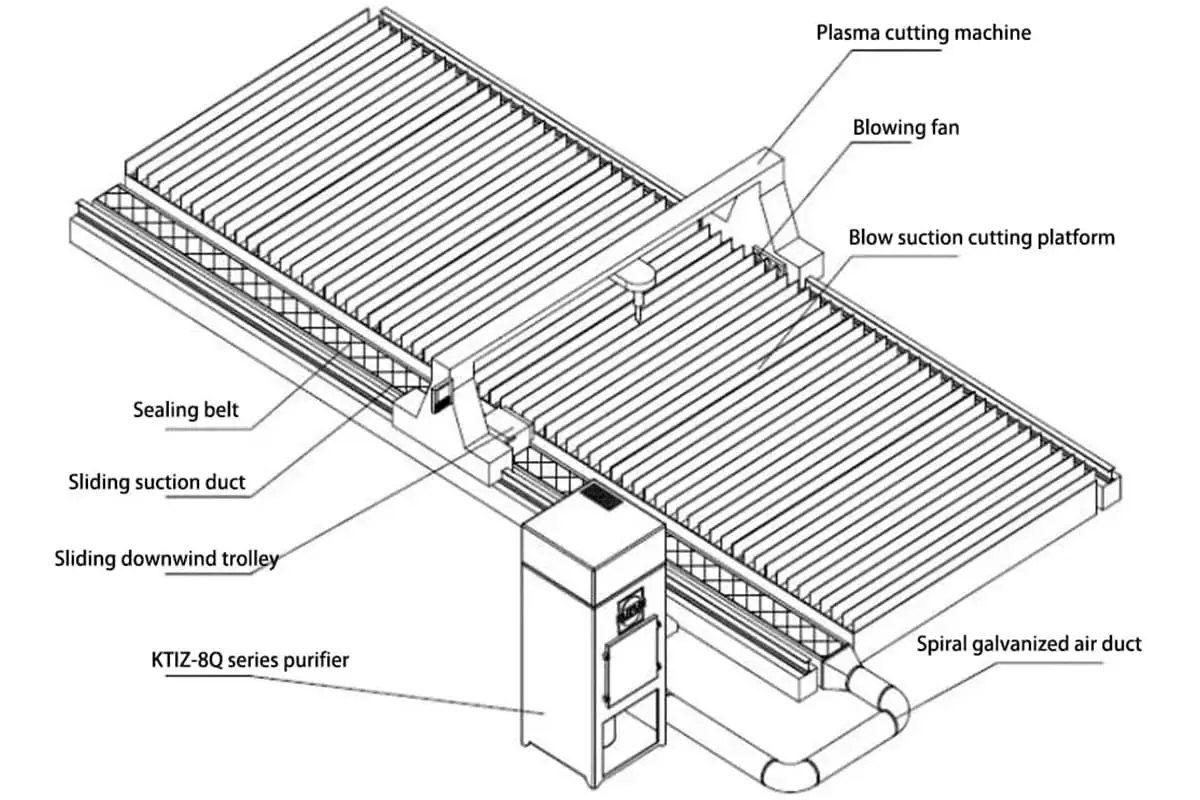
The Blow-Suction Type Plasma Cutting Machine Dust Removal System
The blow-suction type plasma cutting machine dust removal system involves placing a square suction duct on one side of the cutting platform, which has a suction port that can move with the cutting machine.
Related reading: CNC Plasma Cutting Dust Removal: Explained
On the other side of the cutting platform is a blower port with a small axial flow fan. The suction port and the blower port are both fixed on the cutting machine and kept consistent with the cutting head.
The lower part of the cutting platform is equipped with an exhaust duct with vertical plates, which ensures that suction occurs at the position where dust is generated within a limited width during cutting. When the plasma cutting machine dust removal system operates, the sealing strip can closely adhere to the top of the square suction duct under the effect of the pipeline negative pressure to play a sealing role.
The suction port has two rollers where the sealing strip is lifted, allowing the smoke to enter through the suction duct of the suction port, and then be sucked into the dust removal equipment for filtration and purification.
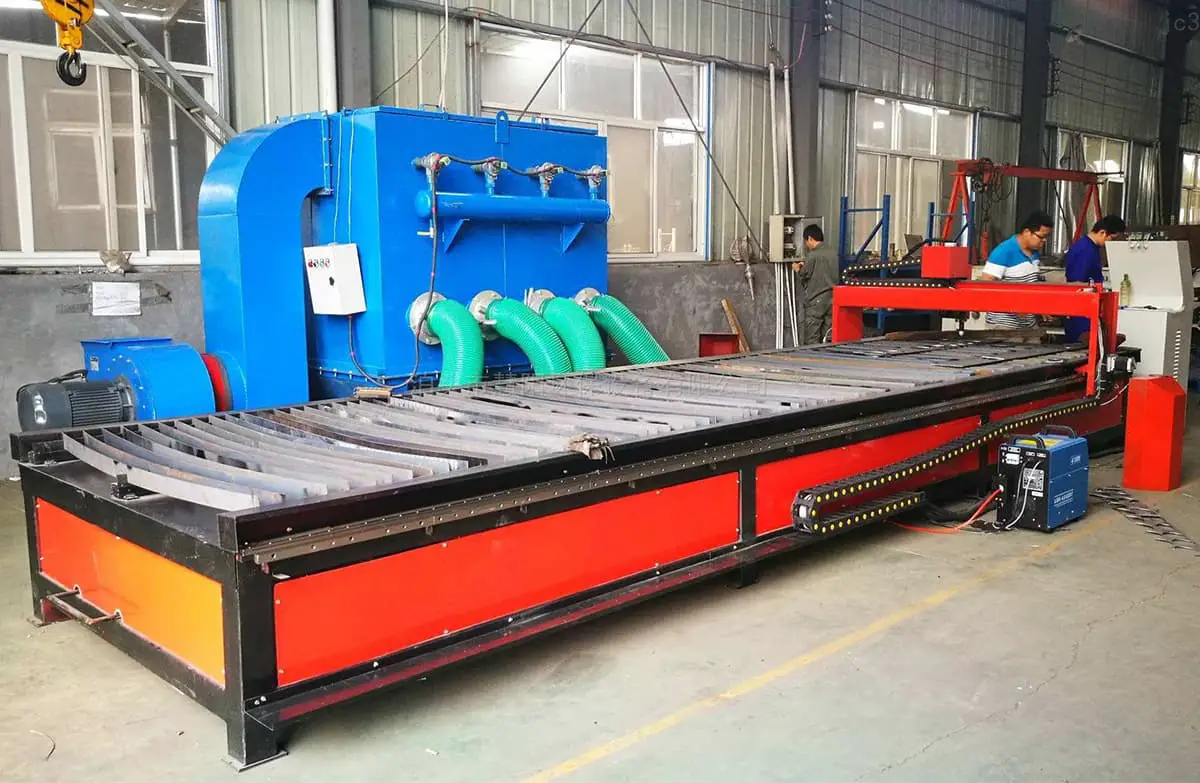

Plasma cutting can pose several hazards:
The harm caused by plasma cutting can be divided into two categories:
The harmful factors in plasma arc cutting mainly include harmful gases, metal dust, noise, arc light (infrared) radiation, and high-frequency electromagnetic fields. The main risk is electric shock.
Hence, it’s critical to prioritize safety and protection during plasma arc cutting.
1. Electric Shock Prevention
The no-load voltage of the power supply for plasma arc cutting is relatively high, especially during manual operation, posing a risk of electric shock. Therefore, the power supply must be properly grounded during use, and the cutting torch and areas touched by hands must be reliably insulated.
A lower voltage can be used to ignite the non-transferred arc before connecting the higher voltage transferred arc circuit. If the switch is placed on the handle, an insulating rubber sleeve should be applied to cover the exposed switch, to avoid direct hand contact with the switch. Whenever possible, automated operation is encouraged.
2. Arc Light Radiation Prevention
The intensity of arc light radiation is high, mainly consisting of infrared radiation and visible light radiation. The light radiation from plasma arcs is stronger than other arcs, especially ultraviolet light, which can severely damage the skin. During manual cutting, operators must wear proper masks, gloves, and also protect their necks.
Apart from having dark glasses on the mask, it is better to include lenses that absorb ultraviolet light. During automatic operation, a protective screen can be set up between the operator and the operating area. Plasma arc cutting can be performed underwater, utilizing water to absorb the light radiation.
3. Dust and Smoke Prevention
The plasma arc cutting process accompanies large amounts of vaporized metal steam, ozone, nitrogen compounds, etc. Combined with the large airflow during cutting, dust on the working site can be massively stirred up, causing serious impacts on the operator’s respiratory tract and lungs.
Therefore, the workspace must be equipped with good ventilation equipment and dust prevention measures. When cutting, an exhaust device can be installed below the grid worktable, or underwater cutting can be used to reduce dust.
4. Noise Prevention
High-intensity, high-frequency noise is generated during plasma arc cutting, especially when using high-power plasma arc cutting, the noise is even louder. This could significantly affect the operator’s auditory and nervous system. The noise level mainly depends on the cutting current; the larger the current, the stronger the noise.
When noise energy is concentrated within the 2000-8000Hz range, operators are required to wear earplugs. If possible, try to use automatic cutting, with the operator working in a soundproof room.
Underwater cutting can also be utilized, using water to absorb noise. Placing the workpiece underwater for cutting can significantly reduce noise. Test results show that when cutting is performed underwater, the noise is reduced by 22-24dB compared to dry cutting.
Moreover, using a water curtain cutting torch (with a water flow rate of 70-80L/min) can reduce noise by about 20dB. When the cutting current is below 100A, the noise is relatively low, and the impact on the surrounding environment is not significant.
5. High-Frequency Electromagnetic Field Protection
Plasma arc cutting requires a high-frequency oscillator to ignite the arc. However, high-frequency can cause certain harm to the human body.
Preventive measures mainly include:
Plasma Arc Cutting Protection Tips
The following safety precautions should be observed when using a plasma cutting machine:
Grounding is required: The plasma cutting machine must be grounded to ensure safety.
Prevention of electric shock: Measures should be taken to prevent electric shocks from all components and gas pipes of the cutter to protect users.
Oxygen safety: Care must be taken when using oxygen to prevent leakage and accidents.
Avoiding gas poisoning: Improper use of gas indoors can lead to poisoning. Choose a well-ventilated space and change the air regularly when using gases.
Maintain safe distance: Keep a safe distance during operation to prevent accidents during cutting.
Wear protective equipment: When operating a plasma cutter, wear safety equipment such as a protective mask, insulating gloves, fire and explosion-resistant work clothes, and shoes to ensure personal safety.
Avoid cutting dust: Plasma cutting machines generate a lot of dust, so protective glasses and masks should be used to protect the eyes and respiratory system.
Follow standard procedures: Adhere to the standard operating procedures of the plasma cutter, strictly follow the instruction manual to avoid operational errors and accidents.