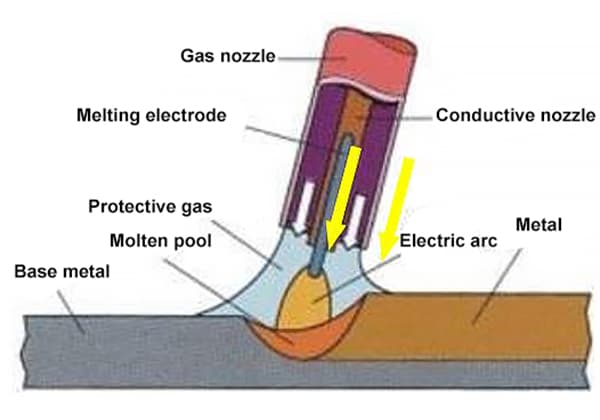
What if you could prevent welding cracks and ensure stronger joints by simply adjusting your process? Preheating before welding is crucial for reducing rapid heating and cooling, which can lead to cracks. This article covers the techniques and parameters necessary for effective preheating, ensuring optimal welding results. You’ll learn how to select the right preheating temperatures based on material and ambient conditions, leading to more robust and reliable welds.

Before the start of the formal welding work, the weld joint area of the thick steel plate should be preheated.
During welding, cracks may occur in the welding area due to local rapid heating and cooling.
Preheating is a process to slow down the rapid heating and cooling process in the welding area.
Joints with high restraint force can reduce shrinkage stress after preheating, and preheating can also eliminate moisture and humidity in the welding area, eliminating the source of hydrogen gas.

When welding, the appropriate preheating temperature should be selected according to the ambient temperature of the work site, the material and thickness of the steel, and preheat the weldment.
When there are no special requirements, the preheating temperature can be selected according to Table 1.
Table 1 Commonly used preheating temperature.
| Steel classification | ambient temperature | Plate thickness (mm) | Preheating and interlayer temperature control (℃) |
| Ordinary carbon structural steel | Above 0 ℃ | ≥50 | 70~100 |
| Low alloy structural steel | Above 0 ℃ | ≥36 | 70~100 |
For components that require preheating, preheating should be carried out evenly within a 100mm range on both sides of the weld line before welding. The measurement of the preheating temperature should be taken 50mm away from the weld line.
Table 2 Conditions for preheating required for different thickness of steel materials.
| Low carbon steel components | Low carbon steel pipe components | Q345,16Mnq 15MnV, 15MnVg components | |||
| Steel thickness (mm) | Temperature below (℃) | Steel pipe wall thickness (mm) | Temperature below (℃) | Steel thickness (mm) | Temperature below (℃) |
| ≤30 | -30 | ≤16 | -30 | ≤10 | -26 |
| 31~50 | -10 | 17~30 | -20 | 10~16 | 10 |
| 0 | 16~24 | -5 | |||
| 51~70 | 0 | 31~40 | -10 | 25~40 | 0 |
| 41~50 | 0 | Above 40 | Any temperature | ||
When the ambient temperature at the work site is below 0℃, the preheating temperature of the welding component should be determined by trial.
Table 3 Preheating temperature required for different material steel materials.
| Carbon content in carbon steel (%) | Preheating temperature (℃) | low alloy steel | Preheating temperature (℃) |
| <0.20 | Not preheating | ||
| 0.20~0.30 | <100 | ||
| Carbon content in carbon steel (%) | Preheating temperature (℃) | low alloy steel | Preheating temperature (℃) |
| 0.30~0.45 | 100~200 | 100~150 | |
| 0.45~0.80 | 200~400 |
When welding in an environment where the temperature is below 0℃, low carbon steel should also be preheated.
Table 2 is the condition for preheating thick steel plate. Table 3 is the temperature that needs to be preheated.