Ever struggled with setting the correct press brake stroke length? Many operators do, often resorting to trial and error. This article demystifies the process, providing a clear formula to calculate the stroke accurately. By understanding factors like daylight, punch height, and die base height, you can avoid inefficiencies and mistakes. Dive in to learn how to master press brake stroke calculations and enhance your metalworking precision!
Press brake operators often face challenges when adjusting stroke data (Y-axis data) on the controller, particularly with older machine models. The uncertainty in setting the correct press brake stroke can lead to inefficient trial-and-error approaches. This article presents a precise method for calculating the optimal press brake stroke length using a specific formula.
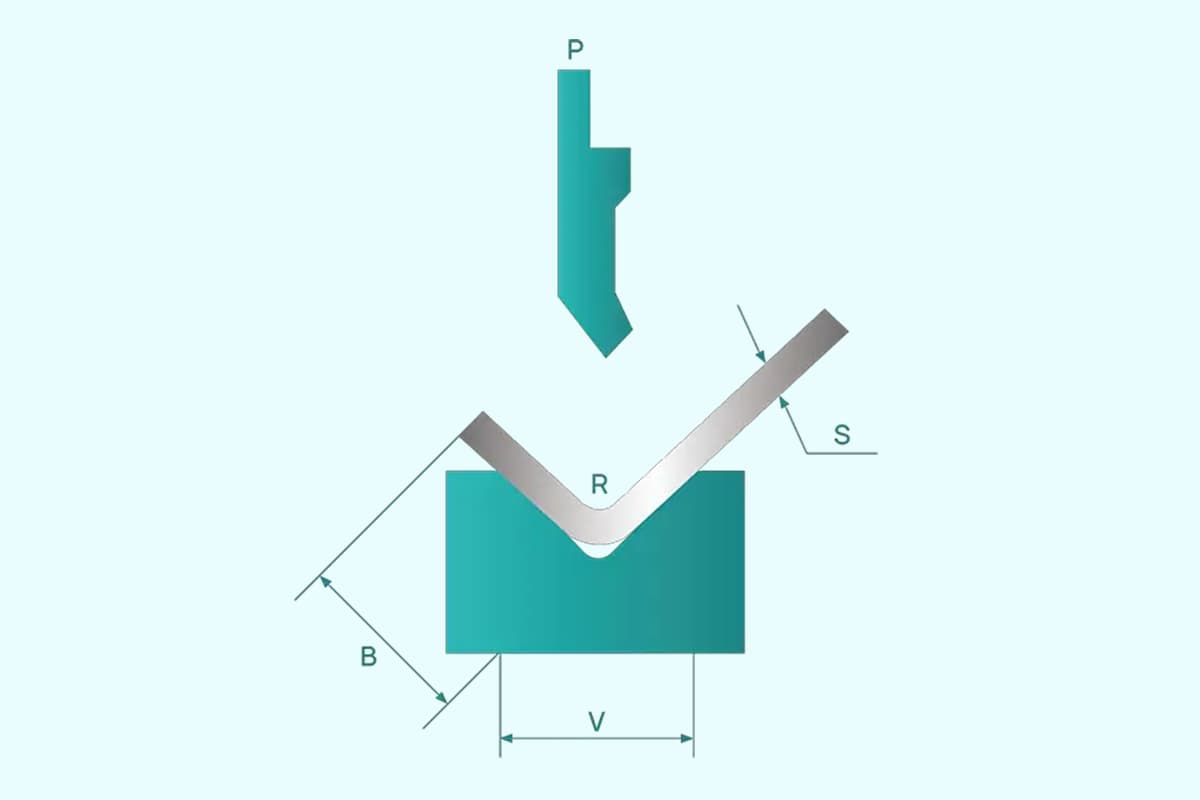
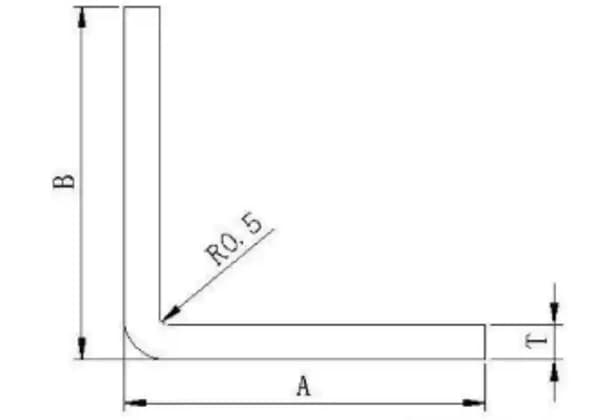
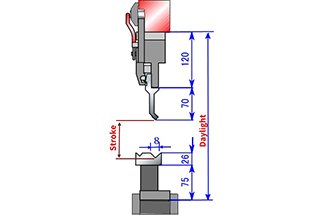
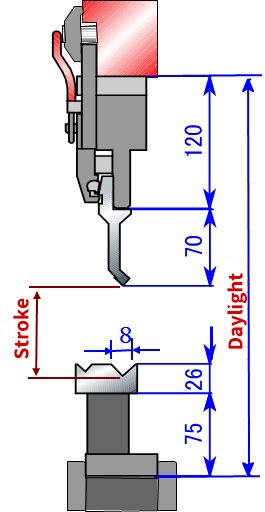
Refer to the schematic diagram below for visual reference. We’ll use the data provided as an example to demonstrate the calculation process.
The formula for calculating press brake stroke is:
Stroke = Daylight – Middle Plate Height – Punch Height – Die Base Height – (Die Height – 0.5V + t)
Where:
Example calculation:
Given:
Daylight: 370mm
Max Stroke: 100mm
Stroke = 370 – 120 – 70 – 75 – (26 – 0.5 * 8 + t)
= (83 – t) mm
It’s crucial to note that when selecting the die height, the following condition must be met:
0.5V < Stroke < Max Stroke
This ensures that the stroke is sufficient for the bending operation while remaining within the machine’s capabilities.
Implementing this formula allows for precise stroke calculations, eliminating guesswork and improving efficiency in press brake operations. Operators can now confidently set the correct stroke for various bending tasks, optimizing both productivity and accuracy.
For determining the required ram depth (tool stroke) for bending specific angles, an online calculator is available for quick and accurate results. This tool can further streamline the setup process and enhance overall bending precision.
Related reading: Press Brake Ram Depth Calculator
By mastering this calculation method and utilizing available tools, press brake operators can significantly improve their setup times, reduce material waste, and achieve consistently high-quality bends across various applications.