Shearing: The process of obtaining rectangular workpieces from materials using plate shears. Cutting: The process of cutting workpieces using a laser or NC punch. Blanking: The process of shaping a product using a die on a punch or other equipment. Punching: The process of forming a workpiece using a punch and die. Bending: The process […]


Shearing: The process of obtaining rectangular workpieces from materials using plate shears.
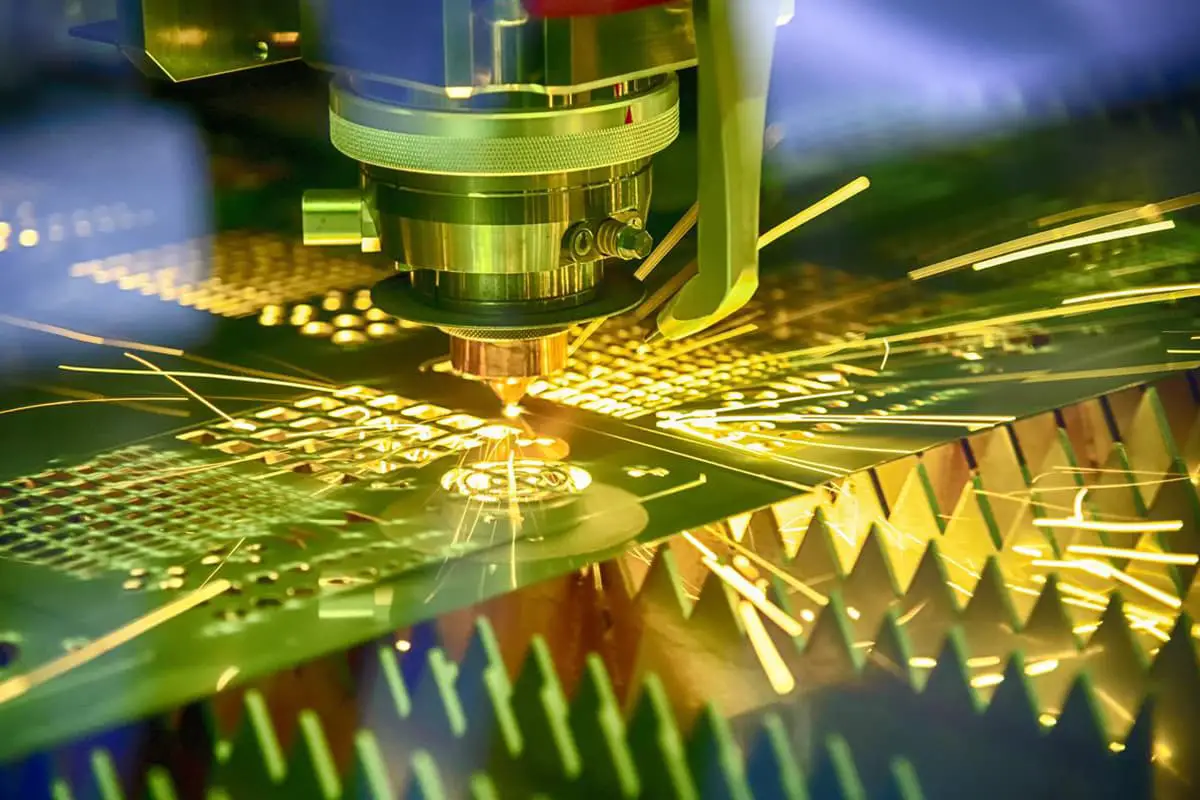
Cutting: The process of cutting workpieces using a laser or NC punch.
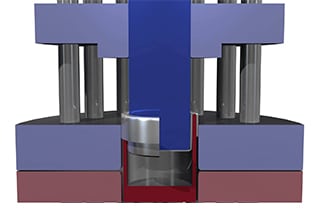
Blanking: The process of shaping a product using a die on a punch or other equipment.
Punching: The process of forming a workpiece using a punch and die.
Bending: The process of forming a workpiece using a bending machine.
Forming: The process of deforming a workpiece using a die on a punch or other equipment.
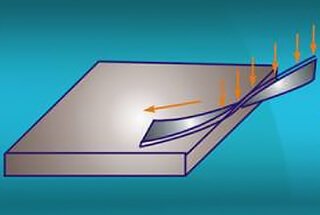
Hole Drawing: Also known as flanging, it is the process of turning up the edge of a round hole formed by a die on a punch or other equipment.
Tapping: The process of machining internal threads on a workpiece.
Reaming: The process of enlarging small holes on workpieces into larger holes using a drill or milling cutter.
Countersunk Hole: The process of machining tapered holes on a workpiece for cooperation with connectors such as countersunk screws.
Press Riveting: The process of securely crimping riveted nuts, screws, or nut columns onto a workpiece using a punch or hydraulic press.
Expanding Riveting: The process of first sinking the workpiece and then securely crimping an expanding riveting nut onto the workpiece using a punch or hydraulic press.
Pull Nut: A process similar to riveting that involves securely connecting riveting nuts (POP) and other connectors to a workpiece using a pull gun.
Pull Riveting: The process of closely connecting two or more workpieces using pull riveters.
Riveting: The process of connecting two or more workpieces face to face using rivets. In the case of countersunk riveting, the workpieces are countersunk first.
Punching Convex Hull: Refers to the process of forming a convex shape on a workpiece using a die in a punch press or hydraulic press.
Punching and Tearing (also known as “Punching Bridge”): Refers to the process of forming a bridge shape on a workpiece using a die in a punch press or hydraulic press.
Stamping: Refers to the process of punching words, symbols, or other marks onto a workpiece using a die.
Notching: Refers to the process of cutting off a corner of a workpiece using a die in a punch press or hydraulic press.
Punching Mesh Hole: Refers to the process of punching holes in a mesh pattern on a workpiece using a die in an ordinary punch press or CNC punch press.
Flattening: Refers to the process of transforming a workpiece into a flat shape.
Drilling: Refers to the process of creating a hole in a workpiece using a drill on a drilling machine or milling machine.
Chamfering: Refers to the process of machining sharp corners of a workpiece using tools such as molds, files, and grinders.
Leveling: Refers to the process of making a workpiece level before and after machining, using equipment specifically designed for this purpose.
Tooth Return: Refers to the process of repairing a missing tooth on a workpiece by adding teeth in advance.
Sticking: Refers to the process of protecting the surface of a workpiece by covering it with a film.
Tearing: Refers to the process of removing the protective film from the surface of a workpiece.
Shape Correction: Refers to the process of adjusting the shape of a formed workpiece.
Heat Shrinkage: Refers to the process of compressing the plastic covering a workpiece using heating equipment such as a hot air gun or oven.
Labeling: Refers to the process of applying labels to a designated position on a workpiece.
Wire Drawing: Refers to the process of treating the surface of a workpiece using a wire drawing machine and abrasive belt.
Polishing: Refers to the process of smoothing the surface of a workpiece using polishing equipment.
Heat Treatment: Refers to the process of special treatment to improve the hardness of a workpiece.
Deburring: Refers to the process of removing rough edges from a workpiece using tools such as grinders and files to make the machined surface smooth and flat.
Argon Arc Welding: Refers to the process of connecting two workpieces and welding them at the edge or joint using an argon arc welding machine. It is divided into two types, intermittent welding and full welding, which should be clearly indicated on the drawings.
Touch Welding (also known as “Spot Welding”): Refers to the process of welding two workpieces face-to-face using a touch welding machine.
Planting Welding: Refers to the process of securely welding a planting screw onto a workpiece using a planting welding gun.
Welding and Grinding: Refers to the process of smoothing out the welding scar on a workpiece using tools such as a grinding machine or file.
Pretreatment: Refers to the process of cleaning a workpiece of oil and rust using an electrolytic solution and adding a film coating, such as a phosphating film, before painting or powder spraying.
Dust Scraping: Refers to the process of using atomic ash to fill in defects on a workpiece surface, such as welding gaps or pits.
Dust Scraping and Polishing: Refers to the process of polishing a workpiece surface after dust scraping using a flat grinder or abrasive cloth.
Oil Spraying: Refers to the process of evenly spraying paint onto a workpiece surface using a special spray gun.
Powder Spraying: Refers to the process of evenly spraying powder onto a workpiece surface using a spray gun.
Silk Screen Printing: Refers to the process of creating words or patterns on a workpiece surface using special ink that penetrates through a special grid.
Electroplating: Refers to the process of adding a layer of metal onto a workpiece surface to protect or enhance its appearance.
Oxidation: Refers to the process of forming an oxide film on a workpiece surface to protect or enhance its appearance.
Sand Blasting: Refers to the process of treating a workpiece surface using a sand blasting machine.
Assembly: Refers to the process of putting together two or more workpieces.
Packaging: Refers to the process of protecting a workpiece for transportation.
Others: Offset, drawing (punching die), back pressure, tooth drawing (tapping after hole drawing), salad (counterbore), through hole.