What makes one valve type better than another? This article dives into the pros and cons of five major valve types—gate, butterfly, ball, globe, and plug valves. Each type has unique advantages and drawbacks, affecting flow control, maintenance, and application suitability. By reading, you’ll gain insights into which valve might best suit your specific needs, whether for low-resistance flow, quick operation, or high-pressure applications.
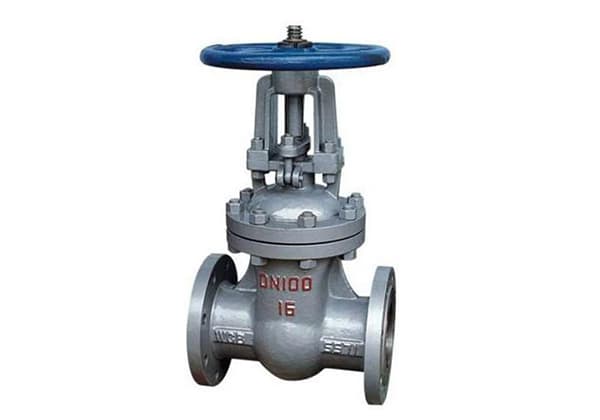

There are many types of valves, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Below, we will list the advantages and disadvantages of the top five valves, including the gate valve, butterfly valve, ball valve, globe valve, and plug valve. We hope this will be helpful to you.

A gate valve is a type of valve in which the closing member (gate) moves perpendicular to the axis of the passage. It is mainly used in pipelines to cut off the medium, that is, it is used in fully open or fully closed states. Generally, gate valves cannot be used to regulate flow.
They can be used for low-temperature and high-temperature and high-pressure applications, and can be made of different materials. However, gate valves are generally not used in pipelines that transport slurry and other media.
Advantages:
① Low fluid resistance;
② Requires less torque to open and close;
③ Can be used in ring networks where the medium flows in two directions, which means that the flow of the medium is not restricted;
④ When fully open, the sealing surface is less eroded by the working medium than the globe valve;
⑤ Has a relatively simple body structure and better manufacturing processability;
⑥ Has a relatively short structure length.
Disadvantages:
① The dimensions and opening height are relatively large, and the required installation space is also large;
② Relative friction of the sealing surface during opening and closing can cause significant wear, and can cause scratches during high-temperature operation;
③ Generally, gate valves have two sealing surfaces, which makes processing, grinding, and maintenance more difficult;
④ Long opening and closing time.

A butterfly valve is a type of valve that uses a circular disc-shaped closing member to open, close, and regulate fluid channels by rotating back and forth by about 90 degrees.
Advantages:
① Has a simple structure, small size, light weight, low consumption of materials, and is suitable for use in large-diameter valves;
② Opens and closes quickly and has low flow resistance;
③ Can be used for media containing suspended solid particles, and depending on the strength of the sealing surface, can also be used for powdery and granular media. It can be used for bi-directional opening and closing and regulation of ventilation and dust removal pipelines, and is widely used in gas pipelines and waterways of metallurgy, light industry, electric power, and petrochemical systems.
Disadvantages:
① The flow adjustment range is not large. When the opening reaches 30%, the flow rate will be above 95%;
② Due to the limitations of the valve structure and sealing material, it is not suitable for use in high-temperature and high-pressure pipeline systems. Generally, the working temperature is below 300°C and the PN40 or less;
③ The sealing performance is relatively poor compared to ball valves and globe valves, so it is suitable for use in places where sealing requirements are not very high.

A ball valve evolved from a plug valve. Its closing member is a sphere, which rotates 90 degrees around the axis of the valve stem to achieve opening and closing.
Ball valves are mainly used in pipelines to cut off, distribute, and change the direction of the medium flow. Ball valves with V-shaped openings also have good flow adjustment functions.
Advantages:
① Has the lowest flow resistance (actually 0);
② When working, it does not jam (without lubricant), so it can be reliably used in corrosive media and low-boiling liquids;
③ Can achieve complete sealing within a large range of pressure and temperature;
④ Can achieve quick opening and closing, and the opening and closing time of certain structures is only 0.05-0.1s to ensure that it can be used in automation systems of test benches. There is no impact when operating fast-opening and closing valves;
⑤ The ball-shaped closing member can automatically position itself at the boundary position;
⑥ The working medium is reliably sealed on both sides;
⑦ When fully open and fully closed, the sealing surface of the ball and the valve seat is isolated from the medium, so high-speed medium passing through the valve will not cause erosion of the sealing surface;
⑧ Has a compact structure and lightweight, and can be considered the most reasonable valve structure for low-temperature medium systems;
⑨ The valve body is symmetrical, especially the welded valve body structure, which can withstand the stress from the pipeline well;
⑩ The closing member can withstand high pressure difference when closing.
⑪ Fully welded ball valves can be directly buried underground, which makes the internal components of the valve not affected by immersion corrosion. The highest service life can reach 30 years, making it the most ideal valve for petroleum and natural gas pipelines.
Disadvantages:
① Because the main sealing ring material of the ball valve is polytetrafluoroethylene, it is inert to almost all chemicals, and has comprehensive characteristics such as low friction coefficient, stable performance, not easy to age, wide temperature range, and excellent sealing performance.
However, the physical properties of polytetrafluoroethylene, including a higher expansion coefficient, sensitivity to low-flow rates, and poor thermal conductivity, require the design of the seat sealing to be based on these characteristics.
Therefore, when the sealing material becomes hard, the sealing reliability is compromised.
In addition, the temperature resistance level of polytetrafluoroethylene is relatively low, and it can only be used below 180°C. If it exceeds this temperature, the sealing material will age. Considering long-term use, it is generally only used at temperatures lower than 120°C.
② Its regulation performance is relatively worse than that of the globe valve, especially for pneumatic valves (or electric valves).

Shutoff valve: refers to a valve that closes by moving the closure element (valve disc) along the centerline of the valve seat.
According to the movement form of the valve disc, the change of the valve seat opening is proportional to the stroke of the valve disc.
Because the opening or closing stroke of this type of valve stem is relatively short, and it has a very reliable cutting function, and because the change in the valve seat opening is proportional to the stroke of the valve disc, it is very suitable for flow regulation.
Therefore, this type of valve is very suitable for use as a cut-off, regulating, and throttling valve.
Advantages:
① During the opening and closing process, the friction force between the valve disc and the sealing surface of the valve body is smaller than that of the gate valve, so it is wear-resistant.
② The opening height is generally only 1/4 of the valve seat channel, so it is much smaller than that of the gate valve.
③ There is usually only one sealing surface on the valve body and valve disc, so its manufacturing process is better and easier to maintain.
④ Since the packing is usually a mixture of asbestos and graphite, its temperature resistance level is higher. Globe valves are generally used in steam valves.
Disadvantages:
① Due to the change in the flow direction of the medium through the valve, the minimum flow resistance of the globe valve is higher than that of most other types of valves.
② Due to the long stroke, the opening speed is slower than that of the ball valve.

The Plug Valve is a type of valve in which the closure member is in the shape of a cylinder which rotates. It is a valve that opens and closes by rotating 90° to connect or disconnect the channels on the plug with those in the valve body.
The plug can be in the shape of a cylinder or cone. Its principle is similar to that of a ball valve, developed on the basis of the plug valve, and is mainly used in oil field development and petroleum refining.
Advantages:
Disadvantages: