Choosing between riveting and welding for your project can be tricky. Riveting involves mechanically joining parts with rivets, ideal for minimal deformation and harsh environments. Welding, on the other hand, fuses materials together, offering stronger, lighter joints but requires careful handling due to potential hazards. This article breaks down the pros and cons of each method, guiding you to the best choice for your specific needs. Discover which technique suits your application and what to expect from each process.


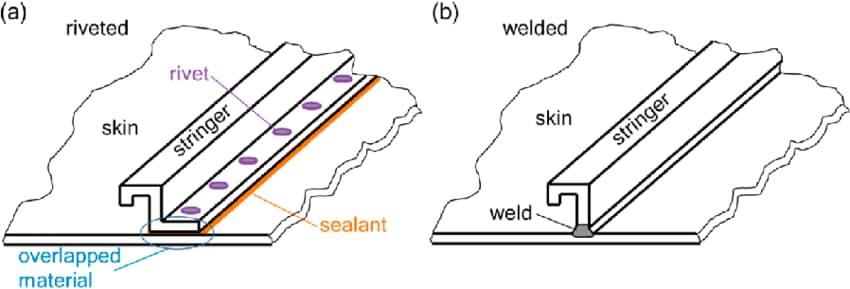
Riveting is a mechanical process that involves connecting multiple parts by applying axial force to a nail rod in a rivet hole of a part, thereby forming a nail head. It is a method of establishing a mechanical connection between components.
Riveting is divided into:
1. Movable Riveting: The joint parts can rotate with each other, creating a non-rigid connection. Examples include scissors and pliers.
2. Fixed Riveting: The joints are fixed and do not move with each other, resulting in a rigid connection. Examples include an angle ruler, a nameplate on a three-ring lock, and bridge construction.
3. Sealing Riveting: The riveted joint is tightly sealed to prevent the leakage of gas and liquid, resulting in a rigid connection.
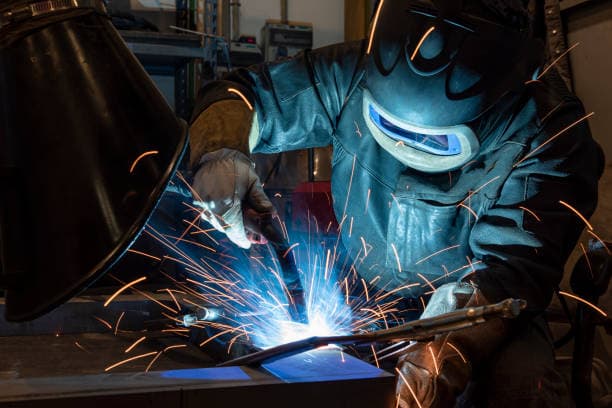

Welding, also referred to as fusion welding, is a manufacturing process and technology for joining metals or thermoplastic materials such as plastics. This process is accomplished through heating, high temperature, or high pressure.
There are several energy sources utilized in modern welding, including gas flame, arc, laser, electron beam, friction, and ultrasonic waves.
Welding can be performed in a variety of settings, including factories, fields, underwater, and even in space.
However, it is important to note that welding can pose a risk to the operator, regardless of the environment. Therefore, proper protective measures must be taken to minimize the potential for harm.
Possible injuries associated with welding include burns, electrical shock, damage to vision, inhalation of toxic gases, and exposure to excessive ultraviolet radiation.
Advantages of welding over riveting
Compared to riveting, welding has the following advantages:
1. High Connection Strength and Good Sealing Properties: Welding creates a metallurgical bond that results in an ideal strength.
2. Lightweight Joints: Welding typically involves a simple butt joint, reducing the weight of the joint. In contrast, riveting requires base metal lapping and a large number of rivets.
3. Low Connection Costs: Welding is generally cost-effective and saves time and effort.
4. Ease of Use and Versatility: Welding is easy to use and can be applied to various connection forms.
Disadvantages of welding compared with riveting
One disadvantage of welding is that it often results in relatively large deformation, making it less suitable for connecting thin parts.
Advantages of riveting
One advantage of riveting is that it results in minimal connection deformation and has low environmental requirements. Riveting can be performed in various conditions, including wind, water, and oil, making it particularly suitable for connecting thin pieces.
Disadvantages of riveting
The connection joint has low strength, poor sealing, low efficiency and heavy joint.
Riveting is a process of connecting multiple parts by applying axial force to a nail rod, causing it to expand and form a head within the rivet hole of the part.
Typically, riveting involves punching holes in the parts to be connected, inserting a rivet, and then using a rivet gun to expand the rivet and secure the connection. This method is commonly used to connect two plates or objects of small thickness.
The difference between riveting and welding is:
1. Lighter Weight: Welded products are lighter in weight compared to riveted parts, which reduces overall weight and saves energy in transportation vehicles.
2. Different Categories: Welding can be divided into three categories: fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing. Riveting can be divided into three types: movable riveting, fixed riveting, and sealing riveting.
3. Distinct Processes: The welding process can result in various manifestations in metal, such as welding cracks, air holes, undercuts, incomplete penetration, incomplete fusion, slag inclusions, weld beads, collapses, pits, burn through, and inclusions. The riveting process involves drilling, dimpling, deburring, inserting rivets, jacking the rivets with a top mold, and riveting with a rotary riveting machine or manually.





