Why does one CNC machine tool outperform another? The answer often lies in the clamps used. This article explores the selection of appropriate clamps to enhance CNC machine tool efficiency. Readers will discover various clamp types, including combination clamps, precision flat pliers, and magnetic-holding clamps, and learn how proper selection and usage can drastically reduce downtime and improve production output.

Why does the same machine tool show significant differences in production efficiency?
The reason is that the clamps used for CNC machine tools are often not appropriate, leading to a significant reduction in the production efficiency of these tools.
In this article, we will discuss the proper selection and use of clamps for CNC machine tools.
How can we improve the efficiency of CNC machine tools?
Technical analysis has revealed that the choice of clamps plays a crucial role in this regard.
Statistics indicate that a large proportion of clamps used in domestic CNC machine tools are selected inappropriately, with an estimated 50% of cases. By the end of 2018, there were nearly one million CNC machine tools in China, meaning that over 500,000 of these tools experienced “downtime” as a result of poor clamp selection or usage.
From an economic perspective, there is a significant opportunity to improve the selection and use of clamps for CNC machine tools, which could lead to substantial benefits.
Small batch production cycle = production (preparation / waiting) time + workpiece processing time.
In small batch production, the “workpiece processing time” is relatively short, making the length of “production preparation/waiting time” a critical factor in determining the overall processing cycle.
To enhance production efficiency, it is essential to find ways to reduce the duration of production preparation/waiting time.
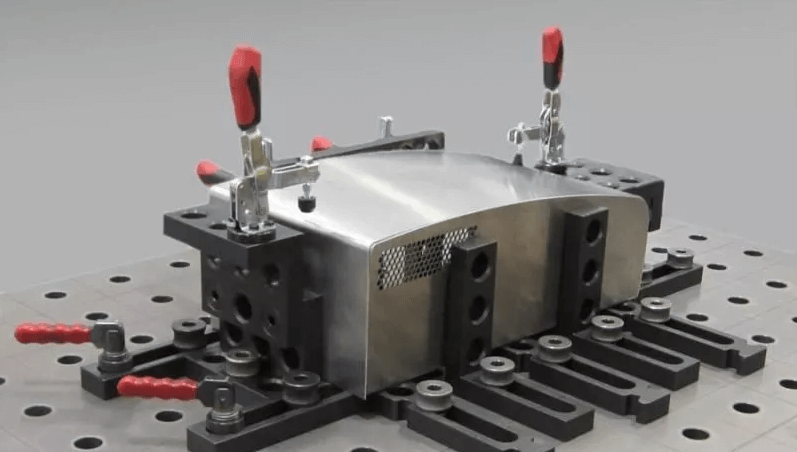
The combination clamp, also known as the “building block clamp,” is made up of a series of standardized components with varying functions, specifications, and sizes. Customers can easily assemble different types of machine tool clamps as needed, much like building blocks.
Using a combination clamp can save time on design and manufacturing, significantly reduce production preparation time, and therefore, effectively shorten the processing cycle in small batch production, leading to improved efficiency.
Additionally, combination clamps offer several advantages, including high positioning accuracy, large clamping versatility, the ability to be used repeatedly, energy and material savings, and low cost of use.
Therefore, when processing small batches, especially when the product shape is complex, the use of combination clamps is highly recommended.
The combined precision flat pliers are a component of the combination clamp.
Compared to other components of the combination clamp, they have more versatility, higher levels of standardization, easier usage, and more reliable clamping, making them widely used across the world.
The combined precision flat pliers have the advantage of quick installation and removal, as well as fast clamping, which helps reduce production preparation time and improves the efficiency of small batch production.
Currently, the commonly used combined precision flat pliers have a clamping range of usually within 1000mm, with a clamping force of up to 5000Kgf.
Smooth clamp bases are not widely used in China, but they are commonly used in industrialized countries such as Europe and the United States.
These clamp bases are made from finely finished machining and have a finished positioning connection part for components, as well as a finished positioning surface on the clamp. This allows for the creation of custom clamps based on specific needs.
It is important to note that the combined precision flat pliers mentioned are not the traditional machine vices. Traditional machine vices have limited functions, low manufacturing accuracy, short lifespan, and cannot be used in conjunction with other vices.
They are not suitable for use on CNC machine tools or machining centers.
The combined precision flat pliers mentioned are a new type of flat pliers originating from industrialized countries such as Europe and the United States, specifically designed for use on CNC machine tools and machining centers.
These pliers offer large clamping versatility, high positioning accuracy, and fast clamping, and can be used in groups, making them ideal for use on CNC machine tools and machining centers.
The Electromagnetic Permanent Magnetic-holding Clamp is a new type of clamp designed using advanced permanent magnet materials such as neodymium iron boron and modern magnetic circuit principles.
Numerous machining practices have shown that this type of clamp can greatly improve the overall machining efficiency of CNC machine tools and machining centers.
Its clamping and releasing process takes only about 1 second, significantly reducing the clamping time.
Traditional machine tool clamps have positioning and clamping components that occupy a lot of space, while Electromagnetic Permanent Magnetic-holding Clamps do not have these space-consuming components. This allows for a larger clamping range compared to traditional clamps, making full use of the table and machining stroke of the CNC machine tool and improving its overall machining efficiency.
The suction force of Electromagnetic Permanent Magnetic-holding Clamps is typically between 15 to 18Kgf/cm2, so it is crucial to ensure that the suction force (clamping force) is strong enough to resist the cutting force.
In general, the adsorption area should not be less than 30cm2, meaning the clamping force should not be less than 450Kgf.
The processing cycle for large batch production is composed of processing waiting time, workpiece processing time, and production preparation time.
The “processing waiting time” primarily includes the time for workpiece clamping and tool changing.
The “workpiece clamping time” for traditional manual machine tool clamps can reach 10-30% of the total processing cycle in large batch production.
As a result, workpiece clamping has become a crucial factor affecting production efficiency and is a key area for improvement in machine tool clamps.
For large scale processing, it is recommended to use clamps with fast positioning and clamping/releasing capabilities. The following three types of machine tool clamps are highly recommended:
Hydraulic/Pneumatic Clamps are special clamps that utilize hydraulic or pneumatic components as the power source to position, support, and compress the workpiece.
These clamps accurately and quickly determine the position between the workpiece, machine tools, and cutting tools. The clamp ensures the position accuracy of the workpiece and, with its high machining accuracy and fast positioning and clamping process, it greatly reduces the time spent on clamping and releasing the workpiece.
Hydraulic/Pneumatic Clamps also offer several advantages, including a compact structure, multi-station clamping, high-speed heavy cutting, and automatic control.
These benefits make Hydraulic/Pneumatic Clamps suitable for use on CNC machine tools, machining centers, and flexible production lines, and are particularly well-suited for large-scale processing.
The Electric Permanent Magnetic-holding Clamp has several advantages, including fast clamping, easy multi-station clamping, multi-face processing in one clamping, reliable and stable clamping, energy efficiency and environmental protection, as well as automatic control.
Compared to traditional machine tool clamps, Electric Permanent Magnetic-holding Clamps can significantly reduce the clamping time and increase clamping efficiency by reducing the number of clamping cycles.
Therefore, these clamps are not only suitable for small batch production, but also for large batch production.
The smooth clamp base can effectively shorten the manufacturing cycle of special clamps and reduce production preparation time, resulting in a shorter overall mass production cycle and improved production efficiency.
Additionally, it can lower the cost of manufacturing special clamps.
Therefore, the smooth clamp base is particularly suitable for mass production with tight schedules.
Use clamps properly and tap the potential of the equipment.
Experience has shown that to improve the machining efficiency of CNC machine tools, it is not enough to simply “select” the right clamps. We must also make an effort to “use” the clamps effectively.
Three effective methods for utilizing CNC machine tool clamps are:
Multi-station Method
Basic principle:
To optimize machining efficiency, multi-station clamping allows for simultaneous fixturing of multiple workpieces, reducing unit clamping time and maximizing tool cutting time.
Multi-station clamps feature multiple positioning and clamping positions on a single fixture. As CNC machining technology advances and production efficiency demands increase, multi-station clamps are becoming increasingly prevalent. This design concept is being widely adopted in hydraulic/pneumatic clamps, combination fixtures, electro-permanent magnetic chucks, and precision vise arrays.
Group Usage
Arranging identical clamps on the same worktable enables multi-station clamping capabilities.
For optimal performance, the clamps should be standardized in design and manufactured to high precision tolerances to meet CNC machining process requirements.
Utilizing clamps in groups maximizes the CNC machine’s axis travel, promoting even wear distribution across machine components. This approach offers flexibility, allowing for independent multi-piece clamping or combined fixturing for larger workpieces.
Local Quick-Change Method
The local quick-change method involves rapidly swapping specific components of a CNC machine tool clamp, such as locating elements, clamping mechanisms, tool-setting devices, and guide features. This approach enables swift functional changes or clamp reconfiguration.
For example, quick-change combination vise jaws allow rapid adaptation from clamping square stock to round bar materials by simply exchanging jaw plates. Similarly, clamping modes can be quickly altered from manual to hydraulic actuation by replacing the clamping elements.
This method significantly reduces setup and adjustment times, making it particularly advantageous for small-batch production scenarios where flexibility is crucial.