Have you ever wondered how sheet metal parts are joined together to create complex structures? In this blog post, we’ll explore the fascinating world of sheet metal joining techniques. As an experienced mechanical engineer, I will guide you through the various methods used in the industry, from welding and riveting to adhesive bonding. Discover the pros and cons of each technique and learn how to choose the best one for your project. Get ready to dive into the art and science of sheet metal joining!
Sheet metal joining refers to the process of connecting different sheet metal parts through specific techniques during sheet metal fabrication, aiming to achieve the functionality and performance of the overall structure.
Sheet metal joining technology is widely used in industries like mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, automotive, aerospace, and electrical appliances. The main methods of sheet metal joining include welding, riveting, threaded connections, and adhesion.
Welding is one of the most common and crucial methods in sheet metal joining. It achieves a durable connection by heating the workpieces as a whole or partially, or by inducing plastic deformation in the workpieces.
Welding methods include TIG welding, spot welding, and CO2 gas shielded welding. Among them, TIG welding requires no flux, demands high precision, but can produce robust and high-quality weld joints. Different welding methods generate different temperature fields and thermal deformations, making the choice of an appropriate welding method critical for controlling workpiece deformation.
In addition to welding, sheet metal can be joined using riveting and threaded connections. Riveting is an irreversible method of connection, typically used for lightweight or temporary connections. Threaded connections utilize mechanical elements like screws and bolts to achieve connection, suitable for situations requiring frequent disassembly.
When choosing a sheet metal joining method, one must consider factors such as the properties of the material, the structural design of the connection area, and the anticipated usage conditions.
Moreover, with technological advancements, new methods of connection like pressure joining are being researched and applied, aimed at improving connection efficiency and quality while reducing cost and time.

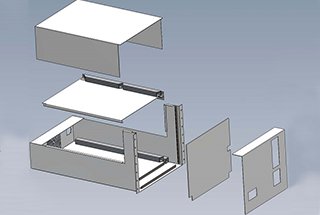
Sheet metal joining is an essential process in the fabrication of various products and structures using sheet material. It involves connecting or attaching multiple sheets of metal together to create a desired shape or form. This process is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and appliance manufacturing.
There are several methods and techniques for joining sheet metal, each with its unique advantages and limitations. Some common methods include mechanical fastening, welding, adhesive bonding, and soldering. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the type of materials, the application, and the required joint strength.
Mechanical fastening is a popular method for joining sheet metal because it is quick and straightforward. It involves using hardware like screws, rivets, and bolts to connect the sheets, and can be easily disassembled if necessary. This method is suitable for a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
Welding involves heating the surfaces of the sheet metals to join them and forming a fusion bond. This method provides a robust and durable connection and is commonly used for applications that require high joint strength. Some common welding techniques for sheet metal include resistance spot welding, gas metal arc welding, and laser welding.
Adhesive bonding is a technique that employs special adhesives to bond the sheet metals. This method is advantageous for joining dissimilar materials and relatively thin sheets. Adhesive bonds also offer a smooth, aesthetic appearance and can redistribute stress across the joint.
Soldering is a process that uses a filler material, or solder, which is melted and applied to the joint surfaces to create a bond. Capillary action helps the solder flow and form a connection between the sheets. Soldering is often used for applications that cannot withstand high temperatures and require a low-stress bond.
Selecting the appropriate joining technique requires considering various factors such as material compatibility, joint strength requirements, and cost. Moreover, proper surface preparation, joint design, and process control are crucial to ensure a successful sheet metal joining process.
In conclusion, sheet metal joining plays a vital role in today’s industrial world. The industry continually develops new techniques and technologies to address the specific needs and challenges associated with joining sheet metals, ultimately enhancing the quality, durability, and performance of the final products.
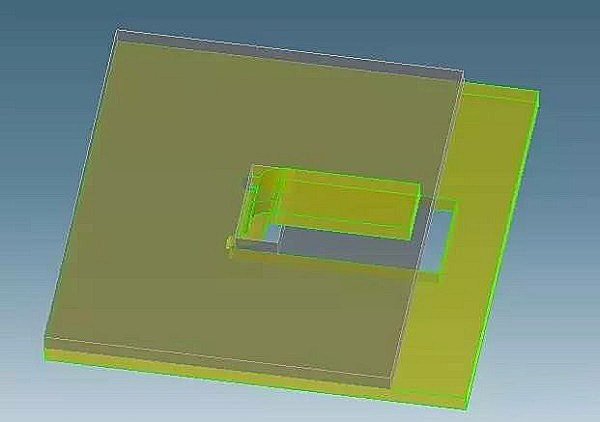
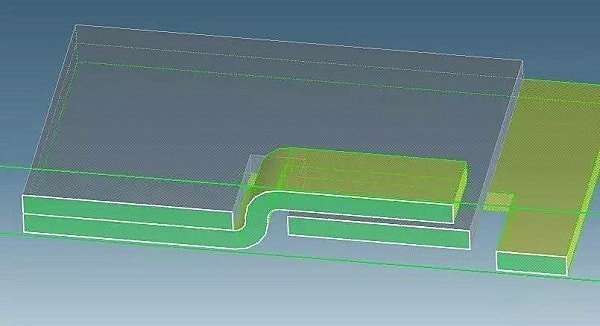
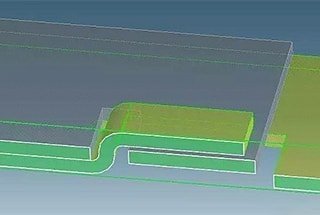
Sheet metal parts can be connected to each other by folding or bending tabs in the form of a buckle and a clamping slot. This method of assembly is simple and convenient, resulting in quick assembly.
However, it may not guarantee full positioning, and additional auxiliary positioning may be required.

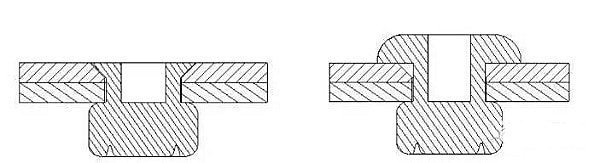
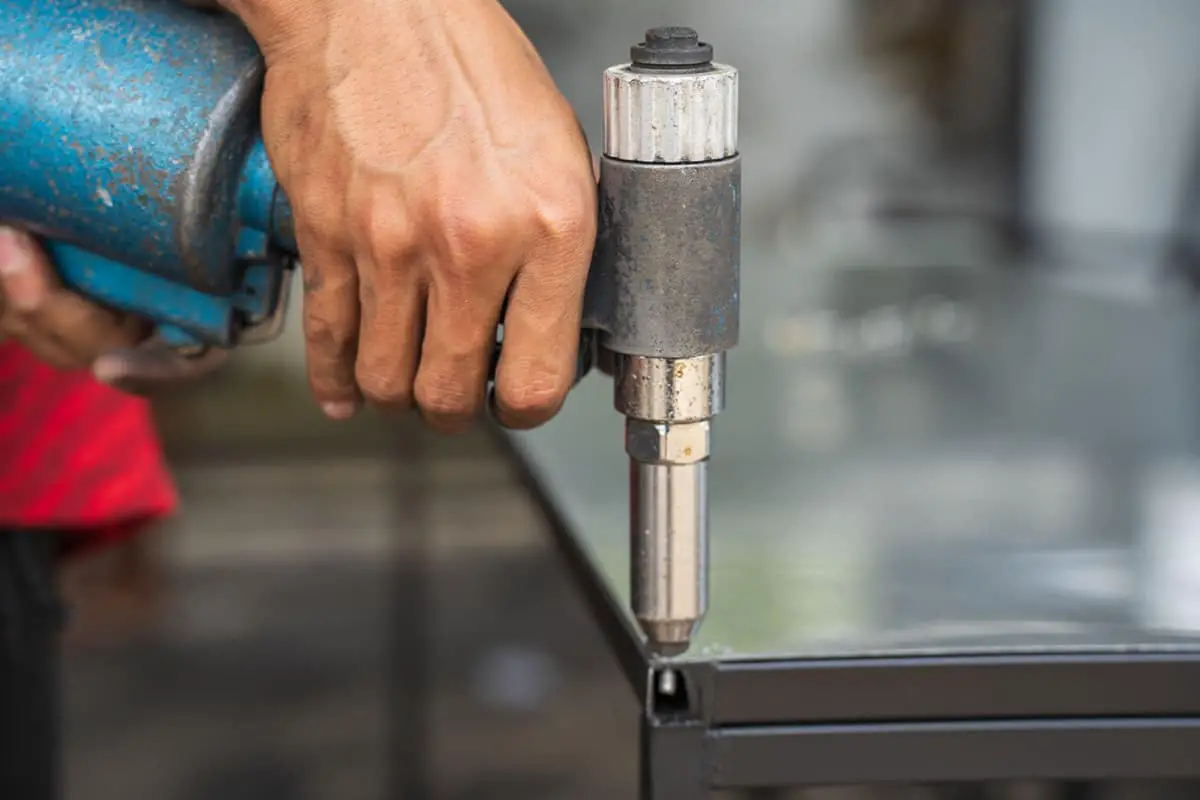
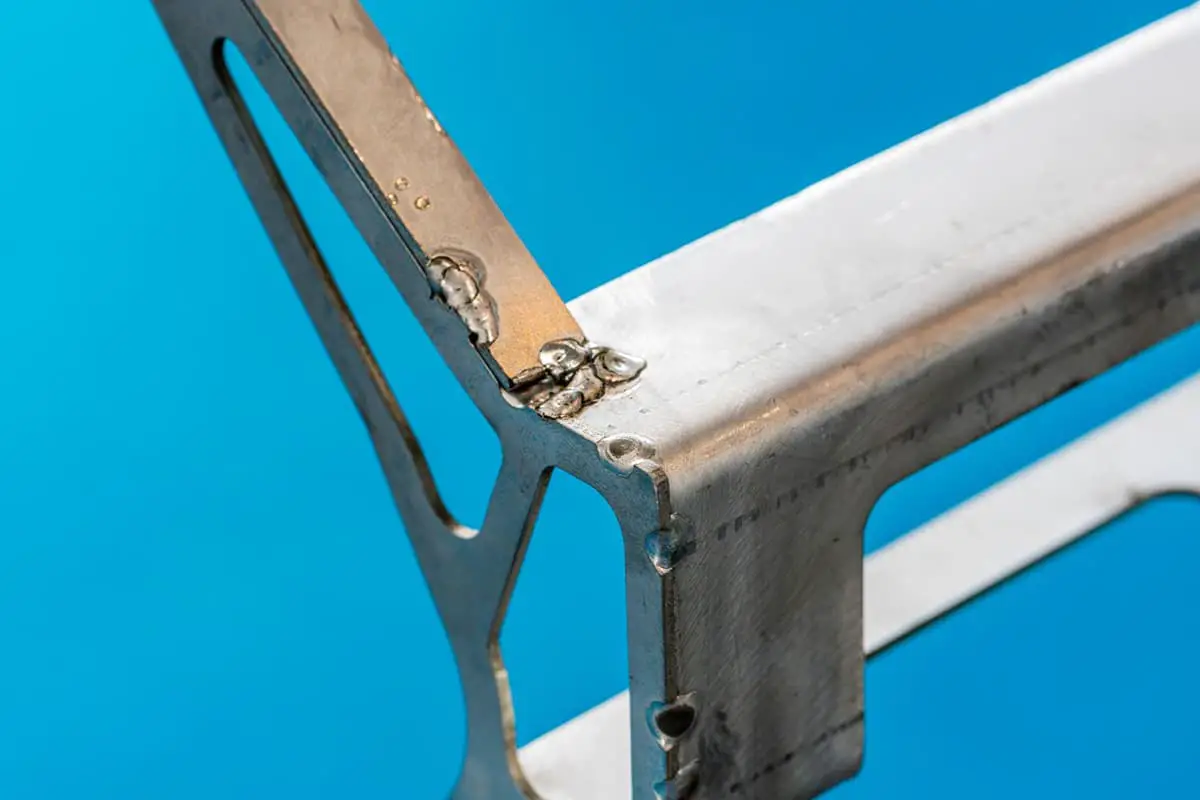
Riveting is carried out in the hole corresponding to the two parts, and a rivet gun is used to pull the rivet, expanding and deforming the outer rivet sleeve to fix the two parts together.
This connection is simple, convenient, and fast.
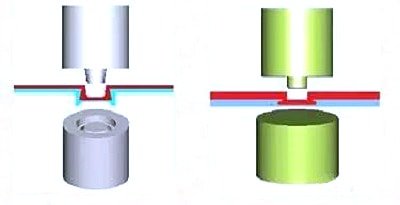
Self-riveting is a method of using mutual deformation between sheet metal parts to achieve mutual fixation.
Although this method is simple, it is often used in applications where disassembly is not required.


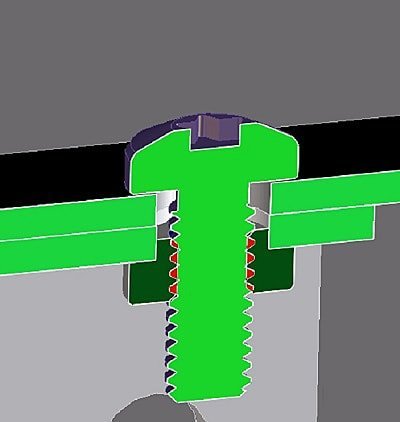
Self-tapping refers to the process of using self-tapping screws to create threads directly on a sheet metal piece, resulting in a tight fit and the ability to be disassembled.

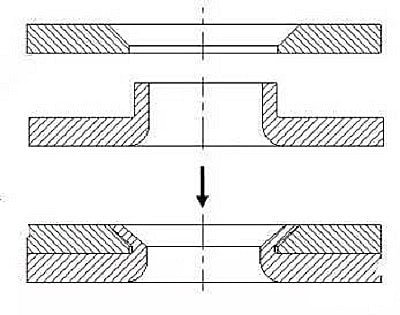
The press rivet process involves pressing a crimp nut or screw against the sheet metal, which can then be mated with a corresponding outer nut or screw.
The main purpose of spot welding is to create a row of solder joints on two sheet metal parts.
This is achieved by melting the local sheet metal material at the welding head to complete the connection between the sheet metal parts.
In the above content, we introduced various sheet metal joining methods.
Finally, a table is used to summarize the advantages and disadvantages of each joining method.
| Joining methods | Tools used | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folding / Tab Joints | none | 1. Low cost 2. Quick assembly | Can not completely limit all degrees of freedom, other fixing devices are needed |
| Pulling Rivet | rivet gun | 1. Easy to operate, good fluidity 2. Self-positioning | 1. Need to pre-punch 2. The pull stud will have a bump 3. There is a limit to the use space of the rivet gun |
| Self-clinching | dedicated mold | Self-guided, no positioning required | 1. Need to do the countersinking process 2. Do not disassemble 3. The yield rate is difficult to guarantee |
| Screw Joint / Fasteners | screwdriver | Low cost, detachable | Limited number of disassembly |
| Pressing Rivet | dedicated equipment | 1. Safe and reliable 2. Removable | Higher cost |
| Welding Joints | spot welding machine | 1. Simple process 2. No pre-processing required | 1. Equipment complexity 2. Weak welding force, easy to remove welding 3. Unable to remove 4. Welding materials should match |
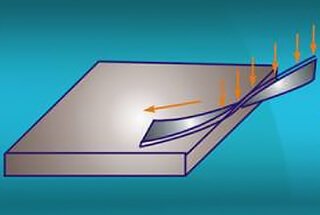
New sheet metal connection technologies, like pressure connection, primarily achieve the joining of sheet metal parts by applying pressure. The working principle of this technology can be referred to the friction welding principle, that is, the frictional heat generated by the pressure and relative motion between the contact surfaces of the weldments causes the contact surfaces to melt and combine.
Although friction welding is mentioned here, the basic principle of pressure connection is similar, that is, promoting the binding of materials by applying pressure.
The advantages of pressure connection mainly include:
Selecting the most appropriate sheet metal joining method requires initial consideration of material characteristics, which include comprehensive performance, cost, performance, and processability of the material. Commonly used connection methods in sheet metal processing include welding and riveting, each having their distinct features and application scenarios.
When choosing a connection method, consider the following factors:
Choosing the most suitable sheet metal joining method requires a comprehensive consideration of material characteristics, design requirements, cost-effectiveness, and processability. By comparing the characteristics and application scenarios of welding and riveting, and considering the specific project requirements and material properties, the most suitable choice can be made.
The latest research advancements in sheet metal connection technology for enhancing mechanical performance mainly include the following aspects:
Lightweight structure manufacturing technology:
With the increasing requirements for material properties in fields such as aerospace, lightweighting has become an important research direction. Sheet metal parts, as key components of light alloy sheet connections, have become one of the hotspots of research at home and abroad. This includes the application progress and development trend of superplastic forming/diffusion bonding technology, which can effectively realize the manufacturing of lightweight structures.
Precision sheet metal forming technology:
In the manufacturing of advanced aircraft sheet metal wall panels, the application of precision sheet metal forming technology is an important means to improve mechanical performance. This involves multiple stages including sheet metal, heat treatment, machining, connection, and surface treatment, and is one of the key technologies in large aircraft body structure and manufacturing process.
Non-flaring internal rolling connection technology:
This is a new type of connection technology that has been applied in the development status of aerospace metal part forming technology. This technology can improve the mechanical performance of the connection area, especially in applications that require high-strength connections.
High-pressure gas bulging forming technology for titanium alloy sheet metal components:
This technology is mainly used in the research progress of aerospace titanium alloys and their precision forming technologies. Through high-pressure gas bulging forming technology, the precision forming of titanium alloy sheet metal components can be realized, thereby improving their mechanical performance.