What makes stainless steel grade 022Cr19Ni10 stand out? Known for its low carbon content and high resistance to corrosion, this versatile alloy is crucial in various industries. This article delves into its composition, compares it to other grades like 304L, and explains its applications. By reading further, you’ll gain a clear understanding of why 022Cr19Ni10 is a top choice for durability and performance in demanding environments.
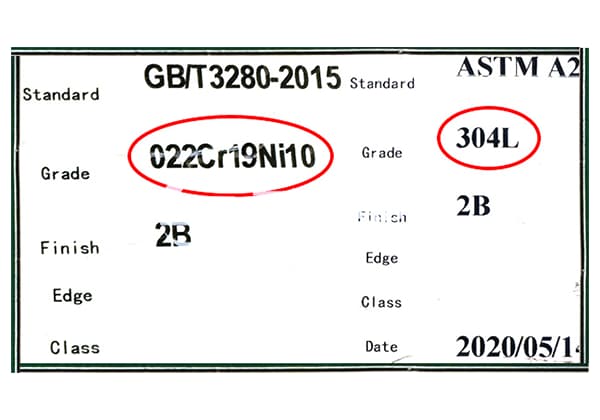
The stainless steel grade 022Cr19Ni10 represents a specific alloy composition, with each component of the designation providing crucial information about its elemental makeup:
This grade, similar to the widely known 304L stainless steel, offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, making it suitable for applications in chemical processing, food and beverage industries, cryogenic equipment, and marine environments. The ultra-low carbon content specifically addresses concerns related to sensitization during welding or high-temperature exposure, ensuring maintained corrosion resistance in the heat-affected zones.
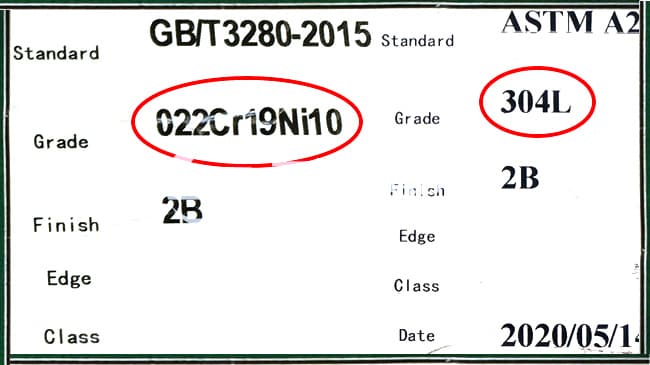
The “022” in the steel grade designation 2.022Cr19Ni10 specifically refers to the carbon content of the alloy. According to the latest national standards for stainless steel nomenclature, “022” indicates an ultra-low carbon content of 0.022% by weight. This precise designation is crucial for applications requiring minimal carbon to enhance specific material properties.
In the broader context of stainless steel classification:
This ultra-low carbon content in 2.022Cr19Ni10 offers several advantages, including improved weldability, reduced susceptibility to intergranular corrosion, and enhanced formability, making it suitable for critical applications in chemical processing, nuclear power generation, and high-purity environments.
Yes, 022Cr19Ni10 and 304L are essentially equivalent stainless steel grades, both represented by the UNS designation S30403. While there may be slight variations in their precise chemical compositions, these differences are minimal and generally fall within the same specification ranges.
It’s important to clarify that the numerical designation “022Cr19Ni10” provides an approximate indication of the steel’s composition, rather than exact required percentages. Specifically:
The actual elemental proportions in both 022Cr19Ni10 and 304L must fall within specified ranges as per international standards (e.g., ASTM A240). These ranges allow for slight variations in composition while maintaining the desired properties of low-carbon austenitic stainless steel, such as excellent corrosion resistance and good weldability.
When selecting between these grades for a specific application, it’s advisable to consult the exact material certificates or specifications to ensure compliance with project requirements, as minor compositional differences may affect performance in certain extreme environments or specialized manufacturing processes.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel, also known as ASTM 304 or SUS304, is an austenitic stainless steel alloy designed for a balance of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and formability. The alloy’s chemical composition significantly influences these properties.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel exhibits robust mechanical properties, making it suitable for various demanding applications. These properties ensure the material can withstand significant stress and deformation before failure.
The physical properties of 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel are essential for its performance in various environments.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is generally non-magnetic in its annealed condition. This characteristic is beneficial in applications where magnetic interference needs to be minimized, such as in electronic or medical equipment.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is commonly used in applications requiring high corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, such as kitchen equipment, chemical processing equipment, and architectural structures. It is also widely used in the food industry due to its resistance to food acids and ease of cleaning. When working with this material, it is important to use proper welding techniques to avoid carbide precipitation, which can reduce corrosion resistance. Fabrication techniques like machining, forming, and welding should be optimized to maintain the material’s integrity and performance. Industry standards such as ASTM A240 and EN 10088-2 provide guidelines for the material’s composition and properties, ensuring consistent quality and performance across different applications.
022Cr19Ni10, commonly known as 304L, is characterized by its low carbon content, which differentiates it from other grades like 304 and 316. The low carbon content (0.03% max) reduces the risk of carbide precipitation during welding, enhancing its corrosion resistance. In contrast, 304 stainless steel has a slightly higher carbon content, which can lead to higher tensile and yield strengths but increases the risk of sensitization.
316 stainless steel contains molybdenum (2-3%) in addition to chromium and nickel, significantly improving its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride environments. This makes 316 more suitable for harsh chemical environments compared to 022Cr19Ni10, which is more suited for general corrosion resistance applications.
Having understood the chemical compositions, let us now delve into the mechanical properties of these stainless steels. 022Cr19Ni10 exhibits a yield strength of 170 MPa and a tensile strength of 485 MPa. These values are slightly lower than those of 304 stainless steel, which typically has a yield strength of 205 MPa and a tensile strength of 515 MPa due to its higher carbon content. However, the lower carbon content in 022Cr19Ni10 makes it more ductile, with an elongation of 40%, compared to 304.
316 stainless steel, while having similar tensile properties to 304, benefits from the addition of molybdenum, providing enhanced mechanical properties in more aggressive environments. The mechanical properties of 301 and 302 stainless steels differ as well; 301 offers higher strength and ductility due to its higher manganese content, while 302 is more balanced for general-purpose applications.
022Cr19Ni10 is known for its excellent general corrosion resistance, thanks to its chromium content (18-20%) which forms a passive oxide layer. This resistance is comparable to other austenitic stainless steels like 304 and 316. However, 316 stainless steel, with its added molybdenum, offers superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it more suitable for marine and chloride-rich environments.
304 stainless steel, while similar in many respects to 022Cr19Ni10, can be more susceptible to intergranular corrosion if not properly heat-treated, due to its higher carbon content. The lower carbon content in 022Cr19Ni10 makes it preferable for welding applications where post-weld heat treatment is not feasible.
022Cr19Ni10 is widely used in industries requiring high corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, such as chemical processing, food and beverage production, and nuclear power. Its properties make it suitable for environments where welding is involved, as its low carbon content minimizes the risk of sensitization.
304 stainless steel is commonly used in similar applications but is favored in environments where slightly higher mechanical strength is required. 316 stainless steel, on the other hand, is preferred in more corrosive environments, such as marine applications and chemical processing involving chlorides.
Grades 301 and 302 stainless steels have their own niche applications. 301 is often used in applications requiring high strength and ductility, such as in springs and fasteners. 302, with its balanced composition, is used in general-purpose applications where corrosion resistance and formability are necessary.
022Cr19Ni10 typically undergoes solution treatment, where it is heated to dissolve carbides and then rapidly cooled to achieve a single-phase austenite structure. This treatment ensures stability and enhances corrosion resistance. Stabilization treatment can follow to ensure long-term stability.
In comparison, 304 stainless steel may require additional heat treatment to avoid sensitization during welding. 316 stainless steel, with its molybdenum content, requires similar heat treatment practices but benefits from its enhanced corrosion resistance in the final application.
The physical properties of 022Cr19Ni10, such as density, melting point, and specific heat capacity, are similar to those of other austenitic stainless steels. It has a density of approximately 7.9 g/cm³, a melting point of 1400-1450°C, and a specific heat capacity of 500 J/(kg·K). These properties are in line with those of 304 and 316 stainless steels, making them interchangeable in many applications based on physical performance.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is known for its excellent weldability, primarily due to its low carbon content. This minimizes the risk of intergranular corrosion and carbide precipitation in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) during welding. The material can be welded using various techniques without the need for pre- or post-weld heat treatments, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage industries.
Several welding processes are compatible with 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel, including:
Commonly used for thicker sections, SMAW provides good penetration and strong welds. For example, in the construction of large-diameter pipelines for water treatment plants, SMAW is preferred due to its robustness and ability to handle thicker materials efficiently.
Also known as MIG welding, GMAW is suitable for welding thin to medium-thickness sections and offers high welding speeds. This process is often used in the automotive industry for welding exhaust systems, where speed and precision are critical.
Also known as TIG welding, GTAW is ideal for precise welding applications and thin sections, producing high-quality welds with excellent appearance. This method is frequently employed in the aerospace industry for components that require high precision and minimal distortion.
It is recommended to use filler materials that match the base metal’s chemical composition, such as ER308L, to ensure the weldment retains similar corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
To ensure the integrity and quality of welds, various non-destructive testing methods may be employed, including ultrasonic testing (UT) and radiographic testing (RT). These methods help detect internal defects and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
For certain critical applications, original mill test certificates (MTC) in accordance with EN 10204 FORMAT 3.1/3.2 may be required, along with Positive Material Identification (PMI) tests. These certifications verify the material’s composition and properties, ensuring it meets the specified requirements.
Understanding the physical properties of 022Cr19Ni10 is crucial for its successful application in manufacturing and welding processes:
These properties indicate that 022Cr19Ni10 has a lower thermal conductivity and a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to carbon steel. These factors should be considered to manage thermal stresses and ensure the integrity of welded joints.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel, commonly known as 304L, is a widely used austenitic stainless steel known for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Its versatility makes it suitable for various applications, including chemical processing, food and beverage industry, and construction.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel adheres to several international standards that ensure its quality and performance.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is valued for its corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and versatility. These properties are crucial in various industries:
Mill test certificates (MTC) in accordance with EN 10204 FORMAT 3.1/3.2 provide detailed information about the chemical composition and mechanical properties, ensuring that the material meets specified standards.
Ultrasonic examination standards such as A578/A578M, A577/A577M, and A435/A435M are applied to detect internal defects, ensuring material integrity.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is certified for use in various critical applications, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards. Certifications include:
These standards and certifications guarantee the reliability and performance of 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel in diverse applications, from chemical processing to construction.
Below are answers to some frequently asked questions:
The chemical composition of 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel, which is a variant of the 304L stainless steel, includes the following elements: Carbon (C) at a maximum of 0.030%, Manganese (Mn) at a maximum of 2.00%, Phosphorus (P) at a maximum of 0.045%, Sulfur (S) at a maximum of 0.030%, Silicon (Si) at a maximum of 0.75%, Chromium (Cr) ranging from 18.0-20.0%, Nickel (Ni) ranging from 8.0-12.0%, and Nitrogen (N) at a maximum of 0.10%. This specific composition is characteristic of austenitic stainless steels, known for their excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and suitability for welding applications, particularly due to the lower carbon content compared to standard 304 stainless steel.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is commonly used in a variety of industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and welding properties. In the chemical and petroleum industry, it is ideal for equipment and parts that need to withstand severe corrosive conditions. The food and beverage industry utilizes this stainless steel in food processing equipment due to its resistance to corrosion, particularly against nitric acid and saline solutions. It is also employed in architectural and decorative applications for outdoor use, thanks to its durability and aesthetic appeal. High-temperature applications benefit from its high-temperature oxidation resistance and low thermal expansion coefficient, making it suitable for parts like gas turbine components. Additionally, the lower carbon content of 022Cr19Ni10 makes it a preferred choice in welding and fabrication, especially for manufacturing stainless steel seamless pipes and tubes. Lastly, its ultra-high strength and corrosion-resistant properties make it valuable in the oil, petrochemical, and refinery industries, where it performs well in severely corrosive environments.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is essentially the same material as 304L stainless steel, with both designations indicating a low-carbon version of the popular 304 stainless steel. The key comparison points between 022Cr19Ni10 and 304L stainless steel are as follows:
The chemical composition of 022Cr19Ni10 includes less than 0.03% carbon, 18-20% chromium, and 8-12% nickel, which aligns precisely with the composition of 304L. This ultra-low carbon content in 022Cr19Ni10 minimizes carbide precipitation during welding, thereby enhancing its corrosion resistance, particularly in environments prone to intergranular corrosion.
In terms of mechanical properties, 022Cr19Ni10 (304L) has slightly lower tensile and yield strengths compared to standard 304 stainless steel. Specifically, 304L has a tensile strength of about 485 MPa and a yield strength of approximately 170 MPa. Despite the slightly lower mechanical properties, 304L is highly valued for its excellent weldability and does not require post-weld annealing when welding thin sections, making it ideal for applications involving extensive welding.
Both 022Cr19Ni10 and 304L exhibit outstanding corrosion resistance, suitable for use in environments containing organic and diluted mineral acids. They are commonly used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing due to their ability to resist corrosion and ease of fabrication.
In summary, 022Cr19Ni10 is an equivalent designation for 304L stainless steel, emphasizing its ultra-low carbon content, superior corrosion resistance, good weldability, and slightly reduced mechanical properties compared to standard 304 stainless steel. This makes it a preferred choice in applications where welding and resistance to intergranular corrosion are critical factors.
The welding properties of 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel are highly favorable due to its specific chemical composition and mechanical characteristics. This steel contains a low carbon content (≤0.03%), which is instrumental in minimizing carbide formation in the heat-affected zone during welding. This ensures that the material maintains its corrosion resistance and prevents intergranular corrosion, which can otherwise compromise the integrity of the welds.
022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel is highly weldable thanks to the presence of chromium and nickel. The low carbon content allows for welding without the need for post-weld heat treatment, simplifying the welding process and reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion. Additionally, the mechanical properties of this steel, including a yield strength of at least 180 MPa, tensile strength of at least 480 MPa, and elongation at break of at least 40%, provide good ductility and strength, which are advantageous during welding operations.
This stainless steel also retains excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion after welding, making it particularly suitable for applications where corrosion resistance is critical. The welded products made from 022Cr19Ni10 can undergo various quality assurance tests, such as ultrasonic examination and Positive Material Identification (PMI) tests, to ensure the quality and integrity of the welds.
Overall, 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel’s low carbon content, excellent corrosion resistance, and favorable mechanical properties make it a highly suitable and convenient choice for welding in various applications, including mechanical structures, railroad vehicles, and building roofing and wall coverings.
The 022Cr19Ni10 stainless steel complies with several international and national standards, reflecting its widespread acceptance and use across various industries. The key standards associated with 022Cr19Ni10 are as follows:
In Chinese standards, it is classified under GB/T 4237 as an austenitic stainless steel. For American standards, it is equivalent to ASME S30403, ASTM 304L, and UNS 304L. In Japanese standards, it corresponds to JIS SUS304L. European standards include DIN 1.4306, DIN 1.4307, EN X2CrNi18-9, and EN X2CrNi19-11. For British standards, it is equivalent to BS 304S31 and BS 304S12. Additionally, it is known as grade S30403 under the GB-T standard, with the old grade designation 00Cr19Ni10.
These standards ensure the material’s consistency and compatibility across different regions and industries, making 022Cr19Ni10 a versatile choice for various applications, including chemical, petrochemical, and other sectors where corrosion resistance and durability are critical.