Ever wondered how to accurately calculate the weight of T-beam steel for your project? Understanding this can save you time and resources. In this article, we’ll explore the T Beam Steel Weight Calculator, a handy tool that simplifies these calculations. Discover how this can streamline your planning and ensure precise measurements!
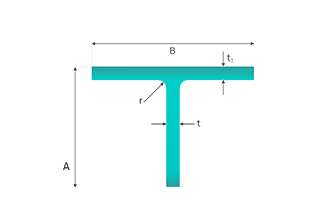
Calculating the weight of a T-beam is a fundamental aspect of structural engineering, ensuring that the beams used in construction can support the intended loads while maintaining structural integrity. This process involves understanding key parameters, utilizing specific formulas, and considering material properties.
Several dimensions and properties are critical for accurately calculating the weight of a T-beam:
Material Density: The density of the material used to manufacture the T-beam, typically measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). For steel, this density is generally around 7850 kg/m³, though it is always best to verify the current standard.
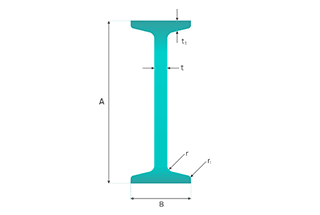
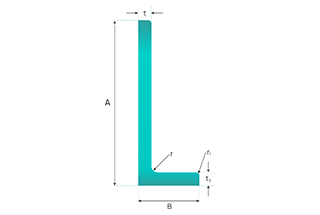
Height (h): The overall vertical measurement of the T-beam. This dimension is crucial as it impacts the beam’s bending strength and load-carrying capacity.
Flange Width (b): The horizontal width of the top portion of the T-beam. The flange width affects the distribution of loads across the beam.
Flange Thickness (s): The thickness of the top portion of the T-beam. This thickness influences the beam’s ability to resist bending and shear forces.
Web Thickness (t): The thickness of the vertical stem of the T-beam. The web thickness is important for shear strength and overall stability.
Accurately determine the mass of your T-beam steel sections with our precision calculator. This tool is essential for structural engineers, fabricators, and project managers working with T-beam profiles in construction and manufacturing.
You can use the following T-beam weight calculator to calculate the weight of T-beam.
Related Tool: Steel Weight Calculator
This chart provides the weights per meter for various T beam sizes, considering standard dimensions and steel density. It’s important to note that the actual weight may vary slightly depending on manufacturing tolerances and specific steel grades used.
| Category | Model | Section size | Weight | |||
| (Kg/m) | ||||||
| h | b | t1 | t2 | |||
| TW | 50*100 | 50 | 100 | 6 | 8 | 8.56 |
| TW | 62.5*125 | 62.5 | 125 | 6.5 | 9 | 11.9 |
| TW | 75*150 | 75 | 150 | 7 | 10 | 15.9 |
| TW | 87.5*175 | 87.5 | 175 | 7.5 | 11 | 20.2 |
| TW | 100*200 | 100 | 200 | 8 | 12 | 25.2 |
| TW | 100*200 | 100 | 204 | 12 | 12 | 28.3 |
| TW | 125*250 | 125 | 250 | 9 | 14 | 36.2 |
| TW | 125*250 | 125 | 255 | 14 | 14 | 41.1 |
| TW | 150*300 | 147 | 302 | 12 | 12 | 42.5 |
| TW | 150*300 | 150 | 300 | 10 | 15 | 47.3 |
| TW | 150*300 | 150 | 305 | 15 | 15 | 53.1 |
| TW | 175*350 | 172 | 348 | 10 | 16 | 57.3 |
| TW | 175*350 | 175 | 350 | 12 | 19 | 68.2 |
| TW | 200*400 | 194 | 402 | 15 | 15 | 70.3 |
| TW | 200*400 | 197 | 398 | 11 | 18 | 73.6 |
| TW | 200*400 | 200 | 400 | 13 | 21 | 86.1 |
| TW | 200*400 | 200 | 408 | 21 | 21 | 98.7 |
| TW | 200*400 | 207 | 405 | 18 | 28 | 116 |
| TW | 200*400 | 214 | 407 | 20 | 35 | 142 |
| TW | 74*100 | 74 | 100 | 6 | 9 | 10.7 |
| TM | 97*150 | 97 | 150 | 6 | 9 | 15.6 |
| TM | 122*175 | 122 | 175 | 7 | 11 | 22.1 |
| TM | 147*200 | 147 | 200 | 8 | 12 | 28.7 |
| TM | 170*250 | 170 | 250 | 9 | 14 | 39.9 |
| TM | 200*300 | 195 | 300 | 10 | 16 | 53.7 |
| TM | 220*300 | 220 | 300 | 11 | 18 | 61.8 |
| TM | 250*300 | 241 | 300 | 11 | 15 | 57.5 |
| TM | 250*300 | 244 | 300 | 11 | 18 | 64.5 |
| TM | 300*300 | 291 | 300 | 12 | 17 | 68.5 |
| TM | 300*300 | 294 | 300 | 12 | 20 | 75.5 |
| TM | 300*300 | 297 | 300 | 14 | 23 | 87.3 |
| TN | 50*50 | 50 | 50 | 5 | 7 | 4.79 |
| TN | 62.5*60 | 62.5 | 60 | 6 | 8 | 6.67 |
| TN | 75*75 | 75 | 75 | 5 | 7 | 7.11 |
| TN | 87.5*90 | 87.5 | 90 | 5 | 8 | 9.11 |
| TN | 100*100 | 99 | 99 | 4.5 | 7 | 9.26 |
| TN | 100*100 | 100 | 100 | 5.5 | 8 | 10.8 |
| TN | 125*125 | 124 | 124 | 5 | 8 | 12.9 |
| TN | 125*125 | 125 | 125 | 6 | 9 | 14.8 |
| TN | 150*150 | 149 | 149 | 5.5 | 8 | 16.3 |
| TN | 150*150 | 150 | 150 | 6.5 | 9 | 18.7 |
| TN | 175*175 | 173 | 174 | 6 | 9 | 20.9 |
| TN | 175*175 | 175 | 175 | 7 | 11 | 25 |
| TN | 200*200 | 198 | 199 | 7 | 11 | 28.3 |
| TN | 200*200 | 200 | 200 | 8 | 13 | 33 |
| TN | 225*200 | 223 | 199 | 8 | 12 | 33.4 |
| TN | 225*200 | 225 | 200 | 9 | 14 | 38.2 |
| TN | 250*200 | 248 | 199 | 9 | 14 | 39.7 |
| TN | 250*200 | 250 | 200 | 10 | 16 | 44.8 |
| TN | 250*200 | 253 | 201 | 11 | 19 | 51.5 |
| TN | 300*200 | 298 | 199 | 10 | 15 | 47.6 |
| TN | 300*200 | 300 | 200 | 11 | 17 | 53.1 |
| TN | 300*200 | 303 | 201 | 12 | 20 | 60.1 |
| TN | 350*300 | 346 | 300 | 13 | 20 | 83 |
| TN | 350*300 | 350 | 300 | 13 | 24 | 92.5 |
| TN | 400*300 | 396 | 300 | 14 | 22 | 95.2 |
| TN | 400*300 | 400 | 300 | 14 | 26 | 105 |
| TN | 450*300 | 450 | 300 | 16 | 28 | 121.5 |
| TN | 125*255 | 125 | 255 | 14 | 14 | 41.1 |
When using this chart, consider the following factors:
T beam steel, also known as T-section steel or T-bar, is a structural steel profile cast or rolled into a distinctive T-shaped cross-section. This profile resembles the capital letter ‘T’, hence its name. T beam steel consists of a vertical web and a horizontal flange, forming a right angle. This configuration provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio and versatility in various applications.
Key characteristics of T beam steel include:
T beam steel finds extensive use in construction, mechanical engineering, and manufacturing industries due to its efficient load-bearing capabilities and ease of fabrication. Common applications include structural supports, machine components, and architectural elements.

There are two primary types of T-shaped steel:
1. Split T-shaped Steel:
This type is directly derived from H-shaped steel through a splitting process. It adheres to the same standard as H-shaped steel (GB/T 11263-2017). Split T-shaped steel serves as an excellent alternative to welded double angle steel, offering several advantages:
2. Hot-rolled Once-formed T-shaped Steel:
This type is predominantly utilized in machinery and hardware industries. It is manufactured through a single hot-rolling process, ensuring uniform material properties and precise dimensional control. The classification of T-shaped steel corresponds to H-shaped steel nomenclature:
The choice between these types depends on factors such as load requirements, fabrication methods, and specific industry applications. Both types offer unique benefits in terms of structural integrity, ease of fabrication, and cost-efficiency, making T-shaped steel a versatile option in modern construction and manufacturing processes.