Have you ever wondered what those cryptic numbers on nuts and bolts mean? In this blog post, an experienced mechanical engineer demystifies thread pitch and explains how to decipher the code. With clear examples and helpful charts, you’ll learn the difference between metric and imperial thread standards and gain practical tips for avoiding costly mistakes. Whether you’re a professional or DIY enthusiast, this guide will give you the knowledge to confidently select the right fasteners for your project.
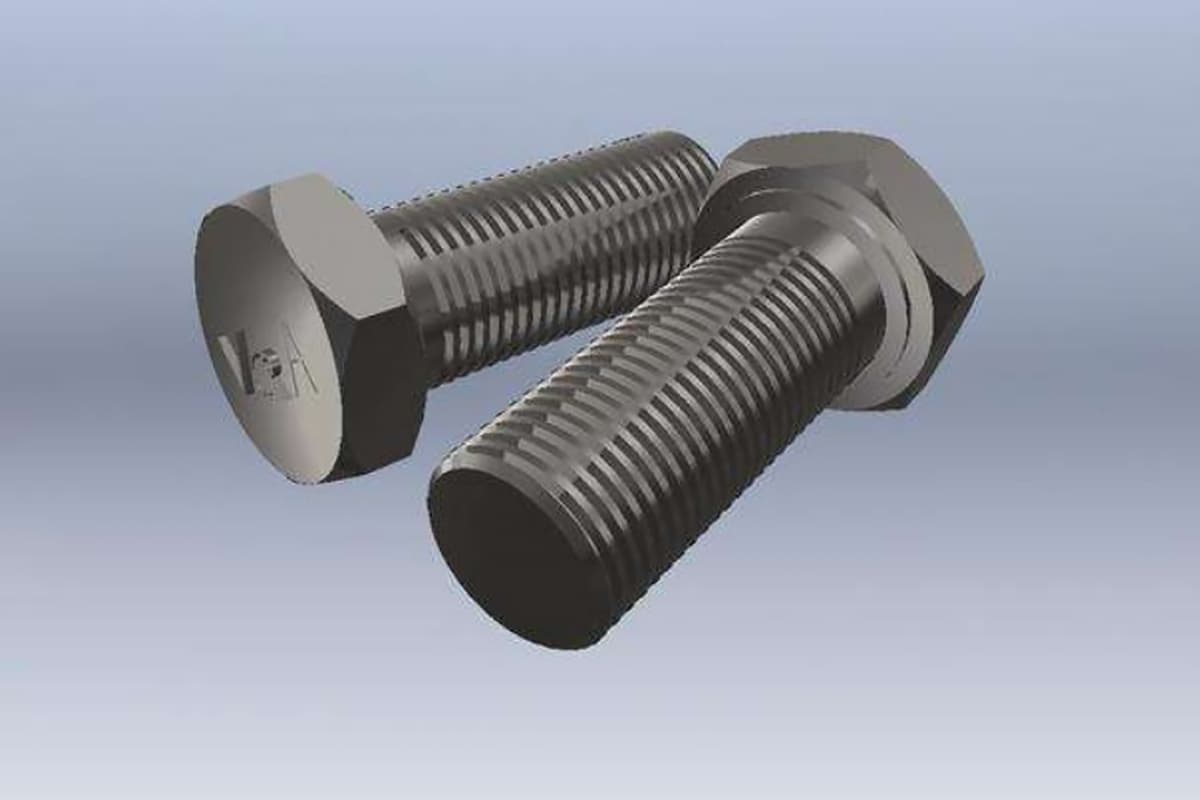

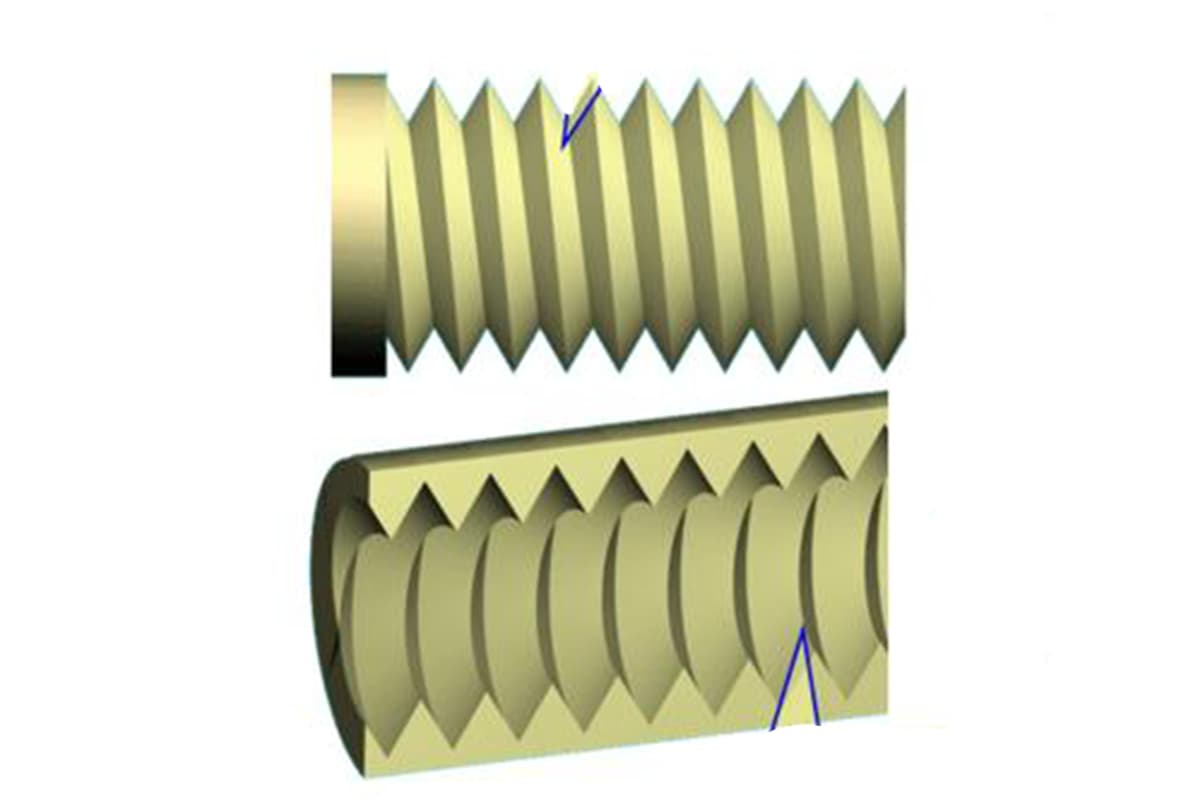
Thread Pitch: Also known as screw pitch, it refers to the axial distance between two corresponding points on the median line of adjacent threads, or the distance between adjacent crests or troughs.
Metric thread pitch is directly marked with distance (in millimeters, mm). For example, in M8*1.25, the 1.25 indicates that the thread pitch for M8 is 1.25MM.
Sometimes, out of habit, people tend to omit the thread pitch for commonly used metric threads, such as M8, which implies that the thread pitch is 1.25MM by default.
However, it’s best to avoid abbreviation to prevent unnecessary misunderstanding.

The thread pitch of a British or Imperial nut is marked by the number of threads contained within each inch.
For example, in 1/4-20, the 20 indicates that there are 20 threads per inch, which is approximately equivalent to 1.27mm in metric units.
However, it is not indicated as 1.27. For standard threads with a diameter less than 1/4 inch, the diameter is no longer indicated as a fraction like “1/4,” but is indicated by the number, as seen in 10#-24, 8#-32, etc.
(Including Coarse and Fine Threads)
Units are in millimetres (mm)
| Nominal Diameter | Thread Pitch (i.e., Threads per Inch) | |
| Coarse Threads (UNC) | Fine Threads (UNF) | |
| M1 | 0.25 | 0.2 |
| M1.2 | 0.25 | 0.2 |
| M1.6 | 0.35 | 0.2 |
| M2 | 0.4 | 0.25 |
| M2.5 | 0.45 | 0.35 |
| M3 | 0.5 | 0.35 |
| M3.5 | 0.6 | 0.35 |
| M4 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| M5 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| M6 | 1 | 0.75 |
| M8 | 1.25 | 1 |
| M10 | 1.5 | 1.25 |
| M12 | 1.75 | 1.25 |
| M14 | 2 | 1.5 |
| M16 | 2 | 1.5 |
| M18 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| M20 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| M22 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| M24 | 3 | 2 |
| M27 | 3 | 2 |
| M30 | 3.5 | 2 |
| (M33) | 3.5 | 2 |
| M36 | 4 | 3 |
| (M39) | 4 | 3 |
| M42 | 4.5 | 3 |
| (M45) | 4.5 | 3 |
| M48 | 5 | 3 |
(Including Coarse and Fine Threads)
| Nominal Diameter | Diameter Size | Thread Pitch (i.e., Threads per Inch) | ||
| inch | mm | Coarse Threads (UNC) | Fine Threads (UNF) | |
| 0# | 0.06 | 1.524 | – | 80 |
| 1# | 0.073 | 1.854 | 64 | 72 |
| 2# | 0.086 | 2.184 | 56 | 64 |
| 3# | 0.099 | 2.515 | 48 | 56 |
| 4# | 0.112 | 2.845 | 40 | 48 |
| 5# | 0.125 | 3.175 | 40 | 44 |
| 6# | 0.138 | 3.505 | 32 | 40 |
| 8# | 0.164 | 4.166 | 32 | 36 |
| 10# | 0.19 | 4.826 | 24 | 32 |
| 12# | 0.216 | 5.486 | 24 | 28 |
| 1/4″ | 0.25 | 6.35 | 20 | 28 |
| 5/16″ | 0.3125 | 7.938 | 18 | 24 |
| 3/8″ | 0.375 | 9.525 | 16 | 24 |
| 7/16″ | 0.4375 | 11.113 | 14 | 20 |
| 1/2″ | 0.5 | 12.7 | 13 | 20 |
| 9/16″ | 0.5625 | 14.288 | 12 | 18 |
| 5/8″ | 0.625 | 15.875 | 11 | 18 |
| 3/4″ | 0.75 | 19.05 | 10 | 16 |
| 7/8″ | 0.875 | 22.225 | 9 | 14 |
| 1″ | 1 | 25.4 | 8 | 12 |
| 1-1/8″ | 1.125 | 28.575 | 7 | 12 |
| 1-1/4″ | 1.25 | 31.75 | 7 | 12 |
| 1-3/8″ | 1.375 | 34.925 | 6 | 12 |
| 1-1/2″ | 1.5 | 38.1 | 6 | 12 |
| 1-3/4″ | 1.75 | 44.45 | 5 | – |
| 2″ | 2 | 50.8 | 4.5 | – |