Have you ever wondered why airplanes and rockets can withstand extreme conditions? This article explores the fascinating world of titanium and aluminum alloys, revealing their unique properties and crucial roles in aerospace engineering. Discover how these remarkable materials shape the future of high-speed travel and advanced machinery.
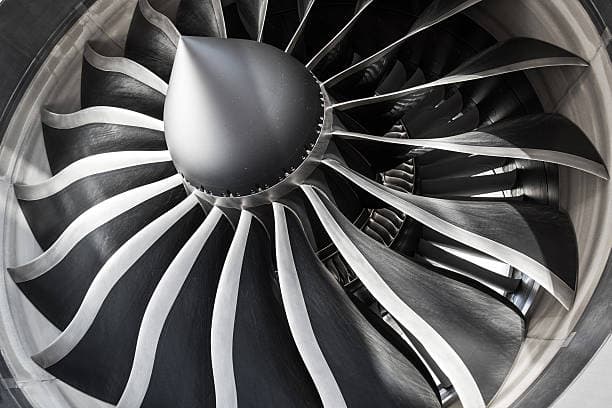


Titanium alloys are a group of metals that consist of titanium and other elements. Titanium, which is an essential structural metal, was first developed in the 1950s.
Titanium alloys are highly valued for their exceptional strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and impressive heat resistance. During the 1950s and 1960s, the focus was mainly on the development of high-temperature titanium alloys for aero-engines, as well as structural titanium alloys for airframes.
In the 1970s, several corrosion-resistant titanium alloys were introduced, and since the 1980s, the development of both high-strength and corrosion-resistant titanium alloys has continued.
Titanium alloys are primarily used for producing compressor parts of aircraft engines, followed by structural components of rockets, missiles, and high-speed aircraft.

Aluminum-based alloys, consisting of varying amounts of alloying elements, are known for their lightweight and high strength properties. Apart from the general characteristics of aluminum, these alloys exhibit specific characteristics due to the type and amount of alloying elements added.
The density of aluminum alloys ranges from 2.63 to 2.85 g/cm3, with high strength (σb ranges from 110 to 650 MPa), specific strength similar to high-alloy steel, and higher specific rigidity than steel. They possess excellent casting and plastic processing properties, as well as good electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and weldability.
These alloys can be used as structural materials and are widely applied in various industries, including aerospace, aviation, transportation, construction, electromechanical, light industry, and daily necessities.
The main differences are different in nature, characteristics and application, as follows:
Aluminum alloy
It is an alloy based on aluminum and added with a certain amount of other alloying elements. It is one of the light metal materials.
Titanium alloy is an alloy composed of titanium and other elements.
Aluminum alloy
Besides the general characteristics of aluminum, aluminum alloys exhibit specific traits that vary depending on the type and amount of alloying elements added.
The density of aluminum alloy ranges from 2.63 to 2.85 g/cm³, and it possesses high strength (with σb ranging from 110 to 650 MPa). Its specific strength is comparable to that of high alloy steel, and its specific rigidity surpasses that of steel.
Aluminum alloys display excellent casting and plastic processing properties, good electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as exceptional corrosion resistance and weldability. As a result, they can serve as suitable structural materials.
Titanium alloy
Titanium alloy exhibits high strength, low density, good mechanical properties, excellent toughness, and corrosion resistance. However, it also has poor processability and can be difficult to cut.
During hot processing, it tends to absorb impurities like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, resulting in reduced wear resistance and a more complex production process.
Aluminum alloy
It is widely used in the marine industry, chemical industry, aerospace, metal packaging, transportation, and other fields.
Titanium alloy
Titanium alloy is primarily utilized for producing compressor components of aircraft engines, followed by structural parts of rockets, missiles, and high-speed aircraft.



