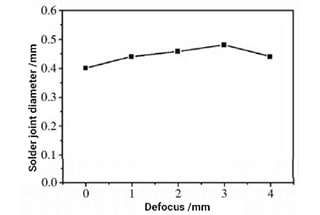
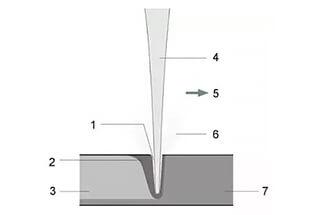
In the rapidly evolving world of laser welding, innovation is key. As manufacturers push the boundaries of what’s possible, a handful of companies stand out as leaders in the field. But what sets these top players apart? Join us as we delve into the cutting-edge technologies and visionary strategies that have propelled these manufacturers to the forefront of the laser welding revolution.

The laser welding industry has seen significant growth in recent years, with numerous companies emerging as leaders in the field. Below is an overview of some of the top manufacturers, both in China and internationally.

IPG Photonics is a world-leading producer and developer of high-performance fiber lasers and amplifiers, serving a wide range of industries and applications. The company’s innovative products are renowned for their exceptional performance, reliability, and value, making them a preferred choice across various sectors.
IPG Photonics offers a comprehensive range of fiber lasers and amplifiers, categorized into low-power, medium-power, and high-power segments. These products are utilized in numerous applications, including:
IPG Photonics has established itself as a pioneer and leader in the fiber lasers and amplifiers market. The company’s commitment to innovation and quality has enabled it to increase its market share significantly. Several factors contribute to IPG’s market leadership:
IPG Photonics’ fiber lasers are continuously replacing traditional laser equipment in many existing applications. This shift is driven by the superior performance, efficiency, and versatility of fiber lasers compared to conventional laser technologies. As a result, IPG is not only enhancing current applications but also paving the way for new and advanced laser technology applications.
Established in 1923, the Trumpf Group has cemented its position as a global leader in the industrial lasers and laser systems industry. Over the past century, Trumpf has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, setting new standards and driving innovation in manufacturing processes.
As one of the foremost companies in global manufacturing technology, Trumpf offers an extensive array of products and services. Their offerings span multiple domains, including:
Trumpf’s dedication to continuous innovation is evident in its ongoing efforts to develop and refine products that meet the evolving needs of its customers. By investing in research and development, Trumpf ensures that it remains at the forefront of technological advancements.
Trumpf’s diverse product portfolio is designed to cater to a wide range of industrial applications. Key areas of focus include:

Amada Weld Tech is indeed a prominent manufacturer known for its extensive range of welding equipment and systems. Here is a refined and optimized version of your text, ensuring accuracy and enhanced readability:
Amada Weld Tech stands at the forefront of the welding industry, renowned for its comprehensive portfolio of advanced welding equipment and systems. Their offerings encompass a variety of welding technologies, including:
Amada Weld Tech is dedicated to serving a broad spectrum of industries with its innovative welding solutions. Their products are integral to sectors such as:
Amada Weld Tech’s commitment to quality and innovation makes them a trusted partner in these industries, driving advancements and ensuring superior performance across their product range.

Founded in 1867, Emag is a well-established medium-sized enterprise based in Germany. The company has built a reputation for its successful strategy of anticipating customer needs and responding flexibly to them. This customer-centric approach has allowed Emag to thrive in various industrial sectors.
The Emag Group primarily serves a diverse range of industries, including:
Emag offers a comprehensive range of products designed to meet the needs of various industries. These include:
Emag Lasertec is a division of the Emag Group renowned for its high-performance laser welding systems. These systems are known for their precision, efficiency, and reliability, making them a preferred choice in industries requiring advanced welding solutions.

Panasonic began its welding business in 1957. Prior to this, manufacturers primarily relied on resistance welding, which uses resistance heat, and arc welding, which depends on the discharge phenomenon in air, for manufacturing automobile bodies.
In 2015, Panasonic introduced its first complete laser welding robot solution, known as Lapress. This advanced welding method offers greater complexity and precision compared to traditional welding techniques.

The company specializes in laser automation equipment, as well as PCB and automation equipment.
The company is a leading provider of laser processing equipment in China, with a strong focus on laser cutting and marking technologies. Its laser welding equipment is predominantly utilized in the automotive and battery industries.
According to data from 2020, the company generated a total revenue of 12 billion yuan. Within this, the high-power laser intelligent equipment segment contributed an operating revenue of 2.018 billion yuan. This substantial revenue positions the company as a leader in both scale and technology within the industry. Notably, the company holds significantly more patents than its competitors, underscoring its technological edge.
All these winning bids are associated with the new energy battery sector, which has significantly expanded the company’s presence and influence in this rapidly growing field.

Huagong Technology specializes in several key areas within the laser processing and photonics industry:
Huagong Technology has established itself as a significant player in the laser processing equipment market. The company’s product range is extensive and includes:
In 2020, Huagong Technology achieved an impressive operating revenue of 6.138 billion yuan. Notably, the company’s high-power laser welding market, specifically the 4 kW and 6 kW segments, contributed 300 million yuan to this revenue.
Huagong Technology holds a leading position in the Body-in-White (BIW) welding market for the automotive industry. The company’s laser equipment is highly regarded for its performance and reliability.
The company is also a key player in the lithium battery industry, providing essential laser processing solutions that meet the industry’s stringent requirements.
Huagong Laser, a subsidiary of Huagong Technology, has made significant strides in the new energy vehicle sector. The company has developed an all-aluminum body welding production line, a groundbreaking achievement that has disrupted the previous dominance of Japan, South Korea, Europe, and the United States in this field. This production line, independently created by Huagong Laser, has successfully passed arrival acceptance tests and is now in mass production, with deliveries already made to customers.

Founded: 2005
Public Listing: June 2020
Main Business: Laser welding equipment and lasers
United Winners Laser is a leading enterprise in the power battery laser welding sector. The company specializes in the development and manufacturing of advanced laser welding equipment and lasers, catering to the needs of the power battery industry.
United Winners Laser serves several prominent companies in the power battery industry, including:
United Winners Laser was awarded a significant project for the power battery laser welding production line by German Times New Energy Technology (Thuringia) Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Ningde Times (CATL). The project involves the delivery, installation, and commissioning of laser welding equipment in Germany. The technical team is currently on-site, and the progress is reported to be smooth.

Hymson is a leading provider of general laser and automation equipment, with a specialized focus on power battery laser and automation equipment. The company’s product portfolio includes:
Founded with a strong emphasis on innovation and technology, Hymson has established itself as a key player in the lithium battery industry. The company has demonstrated significant growth and industry impact, as evidenced by its financial performance and strategic milestones.
Hymson boasts extensive professional capabilities and robust process control within the lithium battery industry. By integrating laser and automation technologies, the company has developed comprehensive solutions that cater to the evolving needs of the market. These solutions not only enhance production efficiency but also ensure high-quality output, positioning Hymson as a leader in the field.
Hymson’s products have carved out a significant competitive advantage in the industry. The company’s financial reports highlight its strong market presence and customer trust:

HSG Laser specializes in the manufacturing and provision of laser cutting machines and laser welding machines. The company is renowned for its advanced laser industrial application solutions.
Founded in 2006, HSG Laser has grown into a leading large-scale manufacturing enterprise in the laser equipment industry. The company is dedicated to the research and development (R&D), production, and sales of a wide range of laser equipment. Their product portfolio includes fully automatic metal laser welding machines, optical fiber laser cutting machines, and pipe cutting machines, among others.
HSG Laser offers a diverse range of laser welding machines, including:
In February 2021, HSG Laser reported for IPO guidance registration, marking a significant step towards further growth and expansion. The company is recognized as a key player in the laser equipment industry in South China, with a strong market presence and a commitment to innovation and quality.

Yifi Laser specializes in providing advanced laser processing solutions, including:
Founded in 2005, Yifi Laser has been at the forefront of developing intelligent laser welding systems. By 2007, the company had expanded its expertise to encompass laser welding and related applications, specifically targeting the new energy vehicle power battery sector.
Yifi Laser continues to lead the industry with its commitment to innovation and excellence in laser processing technologies, providing cutting-edge solutions that meet the evolving needs of modern manufacturing.

The company specializes in the development and production of advanced laser systems, including:
Founded in 2001, the company has established itself as a key player in the laser technology industry. It achieved a significant milestone by going public on the New Third Board in 2014, reflecting its growth and commitment to innovation.

Quick Laser is a leading company in the laser intelligent equipment industry, offering a diverse range of products and services. Their main business areas include:
Founded in 2009, Quick Laser has established itself as a key player in the laser intelligent equipment market. The company is dedicated to the research and development (R&D), production, sales, and service of high-end laser equipment. Their commitment to innovation and quality has positioned them as a preferred choice for customers seeking advanced laser solutions.
Quick Laser’s extensive product line includes:
Quick Laser targets the high-end market, providing cutting-edge solutions that meet the stringent demands of modern manufacturing. Their products are known for their reliability, precision, and innovation, making them a trusted partner for businesses in various sectors.
With a strong emphasis on R&D, Quick Laser continuously strives to push the boundaries of laser technology. Their dedicated team of experts works tirelessly to develop new and improved solutions that address the evolving needs of their customers. The company’s comprehensive service offerings ensure that clients receive the support they need throughout the lifecycle of their products.

ChuTian Laser specializes in various laser technologies, including:
ChuTian Laser, established in 1988, has a rich history of innovation in the laser technology industry. Notably, the company was a pioneer in developing laser welding machines. These machines have found applications across several high-tech and industrial sectors, including:
In 2006, ChuTian Laser expanded its capabilities by forming a joint venture with the Italian Elen Group. This collaboration focused on the production of high-power laser cutting machines, further solidifying ChuTian Laser’s position as a leader in the laser technology market.

Penta Laser specializes in the production and development of laser cutting machines and laser welding machines.
Penta Laser is a joint venture between ChuTian Laser and the Italian Allen Group. The company primarily focuses on laser cutting technology, offering a range of products that include ultra-large format laser welding equipment and precision parts welding systems. This collaboration combines the strengths of ChuTian Laser’s expertise in laser technology with the Italian Allen Group’s advanced engineering capabilities, resulting in high-quality and innovative laser processing solutions.
Penta Laser’s products are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where precision and reliability are paramount. The joint venture leverages cutting-edge technology and international expertise to deliver superior laser processing solutions, contributing significantly to advancements in manufacturing and production processes.
Laser welding is a sophisticated and highly precise welding technique that utilizes a high-energy laser beam to locally heat and melt materials, creating a strong and durable joint. This method is particularly advantageous for applications involving thin-walled materials and precision components.
The process begins with the laser welding machine emitting a concentrated laser beam that targets a specific area on the material. The high-energy laser beam generates intense heat, which is then diffused into the material through heat conduction. This localized heating causes the material to melt, forming a molten pool. As the laser moves along the joint, the molten pool solidifies, creating a strong weld.
Laser welding is renowned for its versatility and precision, making it suitable for a variety of welding tasks, including:
The technique offers numerous advantages:

Laser welding has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s. Initially, it was primarily used for welding thin-walled materials and low-speed welding applications. The process was characterized by heat conduction, where a high-energy laser heats the surface of the workpiece, and the heat is then diffused into the interior through conduction. This method allowed for precise control over the molten pool by adjusting parameters such as width, energy, peak power, and repetition frequency of laser pulses, making it suitable for the precision welding of micro and small parts.
The advent of high-power CO2 and YAG lasers marked a significant advancement in the field, enabling deep penetration welding based on the small hole effect theory. This technique has found widespread industrial applications, particularly in sectors like machinery, automobiles, and steel manufacturing, due to its numerous advantages.
Laser welding offers several distinct advantages over traditional welding technologies:
Despite its many advantages, laser welding has certain limitations:
China has established itself as a global leader in laser welding technology, with its production capabilities for laser welding equipment continuing to expand. This growth is driven by advancements in technology, increased demand from various industries, and supportive government policies.
According to the China Laser Industry Development Report 2021, laser welding is the second largest segment in the revenue share of the industrial laser market, following laser cutting. In 2020, laser welding accounted for 13% of the market revenue. This significant share underscores the importance and widespread adoption of laser welding technology in industrial applications.
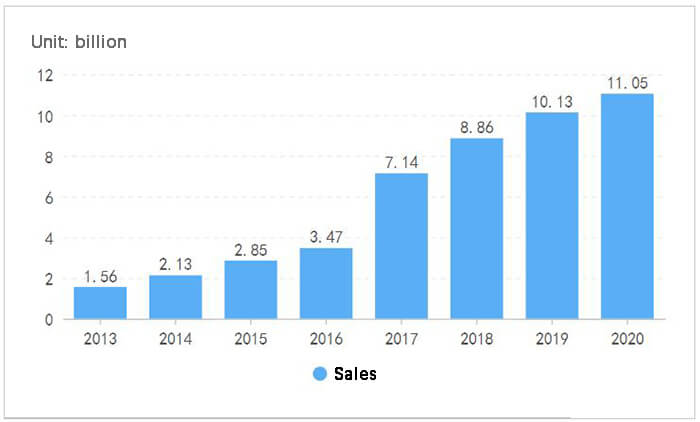
The volume of laser welding in China has seen remarkable growth over the past decade. In 2013, the market volume was 1.56 billion yuan. By 2020, this figure had surged to 11.05 billion yuan, representing an impressive growth rate of 608%. This exponential increase reflects the rapid development and scaling of laser welding technologies and their applications across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing.
Several factors contribute to the robust growth of the laser welding market in China:
Welding is a crucial process in manufacturing and construction, used to join materials, typically metals or thermoplastics. With advancements in technology, various welding methods have been developed, each with its unique advantages and applications. This comparison focuses on laser welding and traditional welding methods, highlighting their differences, advantages, and potential applications.
Laser welding is a modern technique that uses a high-powered laser beam to melt and join materials. It is known for its precision and efficiency.
Traditional welding encompasses several techniques, including arc welding, gas welding, and resistance welding. Each method has its specific characteristics and applications.
Comparison between laser welding equipment and traditional welding methods
| Item | Laser welding | Arc welding | Brazing | Resistance welding |
| Average welding speed (m/min) | 4 | 0.7 | 3-4 | 5 |
| Welding shape variable | Small | More | Less | Normal |
| Welding accuracy | High | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Welding slag adhesion | Very few | Very few | Very few | Very few |
| Consumables consumption | Less | More | Less | More |
| Price | High | Normal | Low | Low |
Their extensive product lineup includes over 60 models tailored for various laser applications.
Dapeng Laser is recognized for its high-performance laser welding solutions, particularly:
Their advanced technology supports a wide range of industrial applications.
Haiwei Laser offers:
With 17 years of R&D experience, Haiwei Laser delivers innovative welding solutions.
GWEIKE Laser excels in laser processing applications, offering:
Their independent R&D focuses on laser power control technology, beam quality optimization, and dynamic focusing systems.
Senfeng Laser provides a comprehensive business chain covering:
Their diverse product portfolio drives advancements in manufacturing efficiency.
A subsidiary of Amada Co. Ltd., Amada Weld Tech offers high-end welding solutions using various laser technologies:
Their products cater to industries such as medical, automotive, aerospace, and electronics, providing laser welding workstations, custom systems, laser heads, and accessories.
With over a century of experience, Panasonic ventured into the laser technology market in 1993. They produce:
Panasonic collaborates with companies like IPG Photonics to enhance their laser offerings.
IPG Photonics, a global leader in laser technology with three decades of experience, offers a broad range of laser solutions, including:
IPG Photonics continues to innovate and lead in the laser technology market.
Laser welding machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency for a wide range of applications. This chapter explores various types of laser welding machines, their unique features, and the industries they serve.
Fiber laser welding machines use fiber optic cables to deliver the laser beam to the welding point. These machines are known for their high efficiency, excellent beam quality, and flexibility in beam delivery. They are highly reliable and efficient, making them suitable for welding both thin and thick materials, including metals like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and their alloys.
Applications:
CO2 laser welding machines use carbon dioxide gas as the laser medium. They are particularly suitable for welding thicker materials, including plastics, ceramics, and certain metals. These machines provide a continuous welding beam, which results in efficient and durable welds that can easily penetrate both metals and non-metallic bodies.
Applications:
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser welding machines utilize a crystal to generate the laser beam. These machines are known for their high peak power and pulse energy, making them suitable for spot welding and drilling applications.
Applications:
Disk laser welding machines use a thin disk of laser-active material to generate the laser beam. These machines offer high power and beam quality with efficient cooling systems, providing excellent stability and reliability.
Applications:
Hybrid laser welding machines combine laser welding with another welding process, such as arc welding or electron beam welding. These machines offer enhanced process flexibility, deeper penetration, and higher welding speeds.
Applications:
Pulsed laser welding is ideal for metals that are light in nature and have low thickness. This method involves intermittent exposure to the metallic body, preventing burning or melting.
Applications:
Continuous laser welding is used for parts that have high thickness and are strong. Although this type of welding is costlier, it saves money and labor in the long run.
Applications:
These compact and flexible machines are suitable for welding various workpieces such as kitchen utensils, doors, windows, and sheet metal.
Applications:
These machines use a high-speed scanning galvanometer to control the laser direction, making them suitable for precision parts like microelectronic components and integrated circuit leads.
Applications:
Automated laser welding systems enhance production efficiency and reduce operational complexity.
Applications:
Understanding the different types of laser welding machines and their specific applications is crucial for selecting the best machine for your industrial needs. Each type offers unique advantages and is suited to particular materials and welding requirements.
The power output of a laser welding machine is a fundamental specification as it determines the machine’s ability to weld various materials and thicknesses. For example, a 1000W laser welding machine can effectively weld up to 3mm thick stainless steel, making it suitable for welding thin plates typically less than 6mm thick.
Several welding parameters are crucial for achieving optimal weld quality:
The laser power setting must be adjusted based on the material thickness to prevent burn-through in thin materials and ensure full penetration in thicker materials. For instance, welding 1mm stainless steel might require a power setting of 300W, while 5mm steel might need 1500W.
Welding speed should be moderate to avoid inadequate fusion or distortion. The speed should decrease as the material thickness increases. For example, welding 2mm aluminum might be done at 2 meters per minute, whereas 6mm steel might require a speed of 0.5 meters per minute.
Proper focal point positioning is essential for equalizing energy distribution, controlling the heat-affected zone, and achieving the desired weld depth-to-width ratio. Adjusting the focus can be crucial for materials like titanium, where precise energy control is needed to prevent oxidation.
Laser welding machines offer high precision due to the focused laser beam, which is vital for applications requiring tight tolerances. Advanced control systems monitor and adjust welding parameters in real-time, ensuring optimal performance. Handheld laser welding machines provide precise control over the welding process, enabling pinpoint accuracy and minimal heat-affected zones.
Laser welding machines are capable of handling a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, carbon steel, and non-ferrous metals. The specific materials a machine can handle depend on its type and power output. For example, a fiber laser is excellent for welding stainless steel and aluminum, while a CO2 laser can weld both metals and plastics.
Modern laser welding machines are equipped with advanced safety mechanisms such as enclosed workspaces, interlock systems, and real-time monitoring of laser parameters to mitigate risks. Efficient multi-load loading, intelligent bus operating systems, and minimal deformation due to the rapid cooling process contribute to higher efficiency and reduced production costs.
Laser welding machines are available in various configurations, including manual, semi-automatic, and automatic. The choice depends on the production scale and workstation arrangement. Automatic machines are ideal for large-scale manufacturing, while manual and semi-automatic machines are better suited for small to medium-scale production. Laser welding robots offer automation and high throughput, making them suitable for repetitive tasks in large-scale manufacturing.
Performance metrics include the machine’s power output, which determines its ability to weld different materials and thicknesses. Higher power output generally translates to faster welding speeds and the ability to handle thicker materials. Maintenance requirements vary by machine type, with fiber and diode lasers known for their low maintenance needs. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
By considering these technical specifications and features, you can select a laser welding machine that aligns with your specific application needs, ensuring high-quality welds, efficiency, and safety.
Laser welding machines offer significant customization and versatility, making them highly adaptable for various industrial applications. These options enable manufacturers to optimize their production processes, enhance weld quality, and achieve greater flexibility.
One of the key features of advanced laser welding machines is the ability to switch between different welding techniques and modes. For example, 4-in-1 laser welding heads allow operators to perform spot welding, seam welding, stitch welding, and more, all with a single machine. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in the automotive industry, where different welding techniques are required for assembling various parts of a vehicle. It also benefits the aerospace industry, where precision and versatility are crucial for fabricating complex components.
Laser welding machines are designed to handle a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, titanium, and plastics. They come with adjustable settings to accommodate different material properties. For instance, machines equipped with Adjustable Ring Mode (ARM) technology can modify the beam profile to suit specific materials and applications, ensuring optimal weld quality. Studies have shown that ARM technology can improve weld consistency and reduce defects, making it a valuable feature for industries like medical device manufacturing, where material precision is critical.
The integration of robotic automation with laser welding technology significantly enhances production efficiency and precision. Robotic laser welding machines can be programmed to perform various welding tasks with high accuracy, making them ideal for intricate assemblies. For example, in the electronics industry, robotic laser welding is used to assemble small and delicate components with precision. Machines like the KirinLaser KR-3000P can be customized with different welding fixtures, worktables, and automation components to meet specific project needs, providing tailored solutions for complex welding operations.
For applications requiring mobility, handheld laser welding machines offer excellent versatility. These machines are perfect for on-site repairs, small-scale projects, and scenarios where access is limited. They combine the power of laser welding with portability, allowing operators to control welding angles and positions freely. Additionally, the addition of a rotary axis to certain machines enables the welding of cylindrical components, ensuring uniform heat application and consistent weld quality around the entire circumference. This feature is particularly useful in the construction and pipeline industries.
Some laser welding machines integrate multiple functions into a single unit, enhancing their versatility. 4-in-1 portable laser welding machines can perform welding, cutting, cleaning, and even simple machining tasks. This multifunctionality makes them valuable assets in various industrial applications, such as manufacturing, repair, and maintenance, by providing a comprehensive solution in a compact form. For instance, in the shipbuilding industry, these machines can be used for both welding and cleaning metal surfaces, streamlining the production process.
The power output of laser welding machines can be customized to match specific welding requirements. Higher-wattage machines enable faster welding speeds and deeper penetration, suitable for thicker materials. Balancing power with energy efficiency is essential to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. For example, in the heavy machinery industry, high-power laser welders are used to join thick steel plates efficiently, while energy-efficient settings help minimize operational expenses.
Depending on the production workflow, manufacturers can choose between stationary and portable machines. Portable machines are compact and suitable for rapid welding tasks in various locations, while stationary machines are ideal for batch production or continuous welding of components with consistent geometries. This flexibility allows manufacturers to select the most appropriate machine configuration for their specific operational needs. For example, in the furniture manufacturing industry, portable machines can be used for on-site assembly, while stationary machines handle high-volume production in the factory.
By leveraging these customization and versatility options, manufacturers can optimize their laser welding processes, enhance production efficiency, and ensure high-quality welds across a wide range of applications.