Attention all mechanical engineers and manufacturing professionals! Are you struggling with pesky anodizing defects in your aluminum products? Look no further! In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of anodizing defects, exploring their causes, characteristics, and practical solutions. With insights from industry experts, you’ll gain valuable knowledge to tackle these challenges head-on and elevate the quality of your anodized aluminum components. Get ready to master the art of anodizing and take your manufacturing game to the next level!
Various defects produced in the oxidation production of aluminum and aluminum alloys can be divided into three categories:
Surface defects are the most common at the production site and result in the highest scrap rate. These defects include:
These defects account for a smaller scrap rate in production and include:
These defects affect the final appearance and performance of the products and include:
The following sections will provide a detailed list of the names (in English according to the American AA standard and data technology discourse), causes, definitions, characteristics, and countermeasures of various defects. This information can be used as a reference for technicians, production personnel, and quality inspection personnel.
The surface defects of oxidized surface treatment products are produced most at the production site, and the scrap rate is also the highest.
The most important are fingerprint corrosion, scratch, adhesion, coarse sand, light sand, poor degreasing, oxidation bubbles, unclean film removal, snowflake corrosion, oxidation white spots, electric injury, slag inclusion, oxide film peeling, pitting, film explosion, hole sealing and coloring, pinhole corrosion, color difference, acid-base water corrosion, hole sealing and dusting, no paint film, pitting, electrophoretic bubbles, oxide film pulverization, etc.
| Name | Fingerprint corrosion | Cause | Operation |
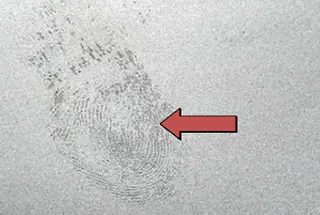
| Definition: fingerprint or glove like corrosion spot | |||
| Features: the surface of aluminum without surface treatment reacts by contacting sodium chloride, lactic acid and other substances in human sweat. The corrosion trace produced is called fingerprint corrosion, and the most common is finger pattern point corrosion. | |||
Appearance: 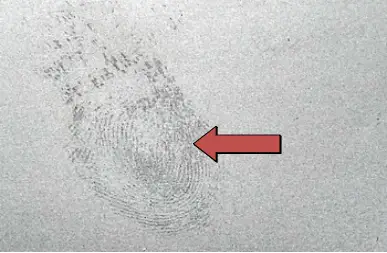 Fingerprint-like corrosion Fingerprint-like corrosion | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. During sawing and basket loading in the extrusion process, the gloves used by the workers are dirty, leaving stains after contacting with the surface of the profile.After aging, the surface stains of the profile cannot be removed by oxidation;2. In the process of oxidation and upper discharge, the worker’s gloves are used for too long, especially after oil stain is adhered, the handprint is left at the end of the profile, and the handprint is in the form of spot corrosion after oxidation;3. After the upper row, the parking time is too long without oxidation treatment;4. Incomplete degreasing before oxidation. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Pay attention to the cleanliness of gloves during the extrusion process and upper row, and replace dirty and wet gloves in time;2. After oxidation, the profile shall not be placed for more than 6 hours;3. Extend the degreasing time. | |||
| Name | Scratch | Cause | Operation |
| Definition: profile surface damage and scratch. | |||
| Features: it has thin and long line or point scars, with flickering luster and various shapes. It is usually called continuous scars as handling scars. Sometimes improper packing will also produce scars during transportation. | |||
Appearance:  Scratch | |||
| Cause of occurrence: Collision between materials, improper operation or collision and scratch between materials and frames, etc | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. The upper row shall be handled with care, and the material shall be lifted without collision between materials;2. The edge of the material frame must be covered with a protective rubber sleeve;3. Each lifting shall not exceed 6 rows, and profiles with different lengths shall be placed separately;4. Damaged cushion strips shall not be used in the lower row process, and savage collision is not allowed. | |||
| Name | Crossing overlapping | Cause | Operation |
| Definition: Materials overlap during oxidation or electrophoresis, resulting in abnormal formation of skin film due to abnormal proximity. | |||
| Features: the imprint of the laminated profile can be seen in the part where the film has never been formed and the part where the end becomes thinner, and sometimes part of the rainbow (interference color) can be seen. | |||
Appearance: 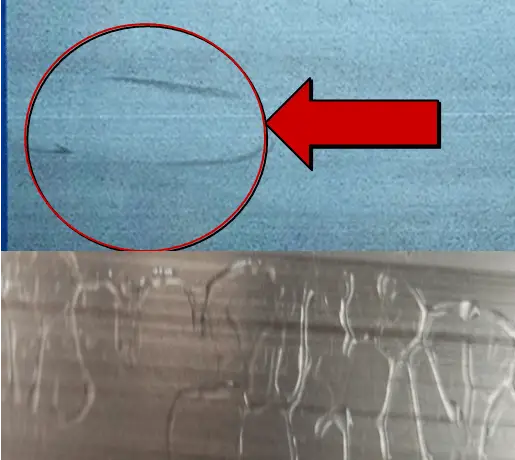 Crossing overlapping | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The binding clearance is too dense, resulting in abnormal contact;2. The binding and drainage strength is not enough. During the washing process, the aluminum wire or fixture is loose, resulting in the sliding of the profile on the row rod, resulting in the connection between materials, which is caused by alkali corrosion, acid corrosion, oxidation and electrophoresis treatment. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Adopt the correct binding and arrangement method, bind three aluminum wires with electrophoretic materials (two small materials), and maintain a distance of 2-3 fingers between the upper and lower profiles;2. The profile with large falling range in the middle must be tied with the center line according to the order requirements;3. The slope of the lower groove increases, and the exhaust process of the electrophoresis groove should be slow to avoid adhesion between profiles caused by violent shaking. | |||
| Name | Rough etching | Cause | Alkali etching process |
| Definition: surface roughness of aluminum due to excessive alkali corrosion. | |||
| Features: due to excessive etching, the surface is rough and dull. In serious cases, the dimensional accuracy is affected due to the dissolution of profiles. | |||
Appearance:  Rough etching | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The temperature of alkali tank is too high;2. The alkali concentration is too high;3. The aluminum ion concentration in the alkali tank is too low;4. The alkali corrosion time is too long;5. The alkali tank liquid is polluted;6. There are many times of rework. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Adjust the tank liquid conditions (sodium hydroxide concentration, dissolved aluminum ion content and temperature);2. Adjust the processing time;3. Regularly clean the tank slag and adjust the tank liquid;4. Reduce the number of repeated processing. | |||
| Name | Insufficient etching | Cause | Alkali etching process |
| Definition: the phenomenon that the effect of eliminating surface defects fails to achieve the expected goal due to insufficient etching in the alkali etching process of aluminum. | |||
| Features: the surface has no sand surface effect or can not meet the customer’s requirements. | |||
Appearance:  Insufficient etching | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The temperature of the alkali tank is too low;2. The alkali corrosion time is too short;3. The alkali concentration is too low;4. The aluminum ion concentration in the alkali tank is too high. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Pay attention to controlling the temperature and concentration of the alkali tank;2. The alkali corrosion time shall be extended appropriately;3. Reasonably adjust the aluminum ion concentration. | |||
| Name | Uneven degreasing | Cause | Oil removal process |
| Definition: uneven alkali corrosion caused by incomplete degreasing | |||
| Features: uneven etching on the surface of aluminum due to incomplete degreasing. The surface of aluminum presents different luster after anodizing, and the color of the surface after coloring is uneven or there are color spots. | |||
Appearance: 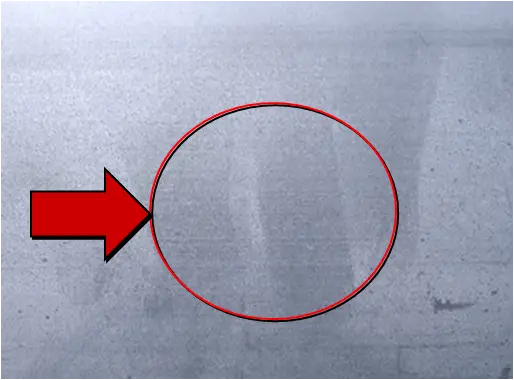 Uneven degreasing | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Insufficient degreasing time;2. The effective components of degreasing tank liquid are insufficient;3. The oil stain on the workpiece surface is serious. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Add degreasing agent;2. Extended soaking time ≥ 3 minutes;3. The workpieces with serious oil stain on the surface shall be manually wiped and pretreated. | |||
| Name | Bubble(anodic oxide) | Cause | Anodizing and operation |
| Definition: The gas produced in electrolysis or the air used for stirring stays in the gap or corner of the material, so it can not form oxide film and usually can not be colored. | |||
| Features: the gap or corner of the material, the local film is very thin or not, and there are residual bubbles on the surface of the anodic oxide film. If electrolytic coloring is carried out, uniform color cannot be obtained. | |||
Appearance: .png) Bubble(anodic oxide) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Improper hoisting angle;2. Too fast grooving speed;3. The shape of aluminum is not conducive to the elimination of gas;4. The defoaming bag is damaged. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. By controlling the slope of the lower groove;2. Extend the prepreg time;3. Damaged defoaming bags shall be replaced in time. | |||
| Name | Peel off the net | Cause | Alkali etching process |
| Definition: the anodic oxide film is not completely removed | |||
| Features: this phenomenon occurs in the reworked profile. Because the old oxide film is not removed during rework, a new oxide film cannot be formed in this area during reoxidation, and a concave convex stripping layer will appear at this time. | |||
Appearance: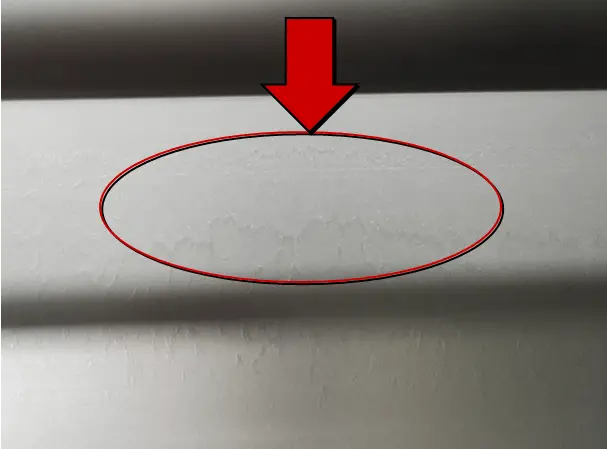  Peel off the net | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Insufficient soaking time of reworked stripping profile in sulfuric acid soaking tank;2. Insufficient alkali etching demoulding time. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Prolong the soaking time of sulfuric acid solution;2. Extend the alkali etching time. | |||
| Name | Rinse water corrosion | Cause | |
| Definition: pitting corrosion produced in water washing caused by impurities contained in materials. | |||
| Features: it looks like a snowflake. There is a black spot in the center of the spot as the core, which spreads around and extends many claws, just like an octopus in the sea. | |||
Appearance: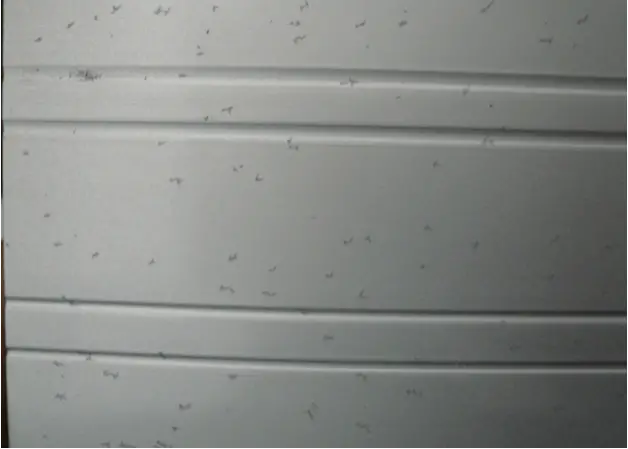  Rinse water corrosion | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The extruded profile contains a small amount of zinc or gallium, which reacts with Cl – or f-ions in the water washing tank after neutralization treatment process;2. After the embryo material is neutralized, it stays in the water tank for too long;3. The sink is polluted. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Monitor the production process of aluminum rod and control the content of zinc or gallium;2. Control the material making speed to ensure that the embryo material is not soaked for no more than 10 minutes;3. Nitric acid concentration in neutralization tank ≥ 5% (5% – 8%);4. Increase the drainage volume to ensure the cleanliness of the sink. | |||
| Name | White color | Cause | Casting, extrusion and oxidation process |
| Definition: white punctate or punctate uncolored traces on the surface of aluminum without oxide film peeling. | |||
| Features: Different from “peeling”, it is a white spot like defect with peeling. The white spot is that the crack is generated on the film and has not been formed. For normal skin film, its peripheral part is not colored, which occurs more along the extrusion direction, and there is a hand feeling when touching with hands. | |||
Appearance:  White color | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. There are inclusions in the alloy, making the oxide film discontinuous;2. Alkali mist is attached on the oxide film. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Strictly control the rod casting process;2. Arrange oxidation for the workpiece after the upper row as soon as possible;3. Improve the ventilation facilities of the workshop. | |||
| Name | Electrical burning | Cause | Anodizing and operation |
| Definition: during anodic oxidation treatment, the current density is too high locally, forming the appearance of burning or electric shock. | |||
| Features: burning marks appear on the oxide film, generally in black or yellow. In serious cases, the profile breaks down. | |||
Appearance: 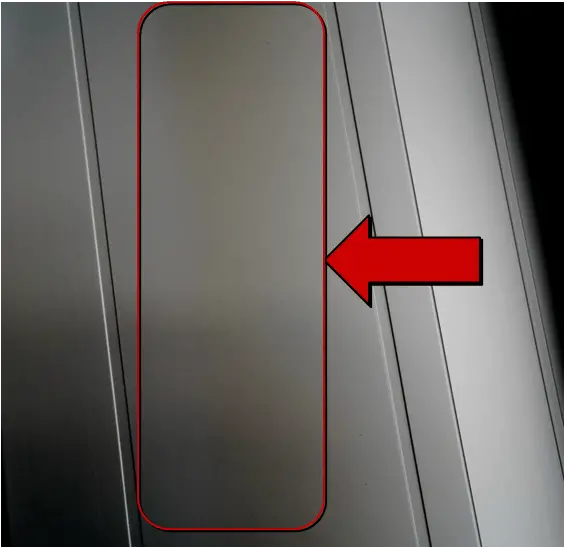 Electrical burning | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Excessive oxidation current density;2. Short circuit occurs when aluminum is in contact with cathode plate;3. Poor contact between aluminum and fixture;4. The current rises too fast during anodic oxidation;5. The cathode is damaged and the area is too small; Preventive measures. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. The oxidation current density should not be too high, and the current density should be controlled between 1.2-1.5mA/dm²;2. The distance between poles shall be well controlled when lowering the groove, and it is strictly prohibited for profiles to touch the cathode plate;3. The upper row of bars shall be polished, the screws on the bent shall be tightened, and the material head shall be tightened when clamping;4. The setting of current soft rise time shall meet the requirements;5. Replace the damaged cathode plate in time. | |||
| Name | Slag | Cause | Extrusion, casting, mould |
| Definition: there are non-metallic inclusions in the structure of metal, which can be seen by the naked eye in the low magnification sample. After oxidation treatment, the surface of metal products will be exposed, which can be seen by the naked eye or felt by touching the products with hands. | |||
| Features: it is generally in broken line shape and consistent with the extrusion direction. It is invisible after extrusion and visible after oxidation treatment. | |||
Appearance: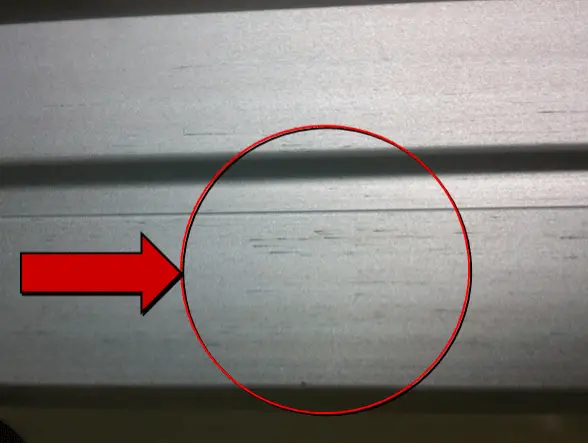  Slag | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The extrusion cylinder is not centered with the extrusion rod, so that the foreign matters on the surface layer of the ingot or the inner wall of the extrusion cylinder are involved and appear on the surface of the extruded profile;2. Because the position of the die hole is too close to the outer circle during die design. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. In the mold design, the mold hole shall be located in the center of the mold as far as possible; For hollow profiles, the circumscribed circle of the shunt hole shall be reduced;2. Regularly check the alignment of the extrusion cylinder and extrusion rod and adjust them in time to leave more residual pressure;3. Remove the foreign matters on the inner wall of the extrusion cylinder and the fixed extrusion pad;4. Reduce the temperature of the extrusion pad and avoid excessive lubrication;5. Increase the temperature of the extrusion barrel and ingot. | |||
| Name | Spalling | Cause | Anodizing and coloring |
| Definition: when coloring, the oxide film peels off in a half dot shape, producing non colored spots. | |||
| Features: white dots or blocks are irregularly distributed on the surface of profiles, and there is no hand feeling when touching with hands. | |||
Appearance:  Anodizing and coloring | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Coloring voltage is too high or coloring time is too long;2. The coloring solution is polluted;3. The barrier film formed during oxidation is too thin or uneven. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Correct the coloring conditions;2. Remove impurities;3. Increase the oxidation voltage. | |||
| Name | Black point | Cause | anodic oxidation |
| Definition: black star shaped corrosion pit on the aluminum surface. | |||
| Features: it is black dot-shaped and irregularly distributed, and there is no oxide film at the location of corrosion points. | |||
Appearance:  Black point | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The concentration of chloride ion in oxidizing electrolyte is too high. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Replace the tank liquid to ensure the stability of the oxidation tank liquid. | |||
| Name | Pinhole pinholing | Cause | Anodizing and operation |
| Definition: due to the large difference between the thermal expansion coefficient of the oxide film and aluminum matrix, the oxide film is cracked and damaged under external force or high temperature. | |||
| Features: when viewed in the direction inclined to the surface under strong light, flake scales can be seen. | |||
Appearance: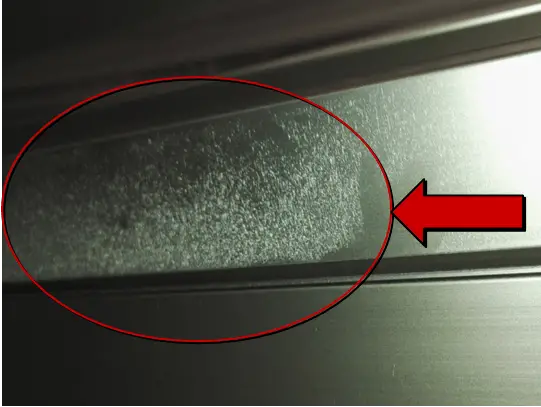  Pinhole pinholing | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The hole sealing time is too long;2. High film material is stirred without air; The heat is not exchanged in time;3. The lower row is operated savagely, the stress on the profile is too large, and the oxide film is cracked. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Adjust the hole sealing time;2. Aerate and stir when high film material is oxidized;3. Standardize the lower row operation. | |||
| Name | Iridescence | Cause | Hole sealing |
| Definition: also known as rainbow film or interference film, it is a phenomenon of light interference, indicating the existence of a surface film. | |||
| Features: rainbow color can be seen when viewed in the direction inclined to the surface. | |||
Appearance: 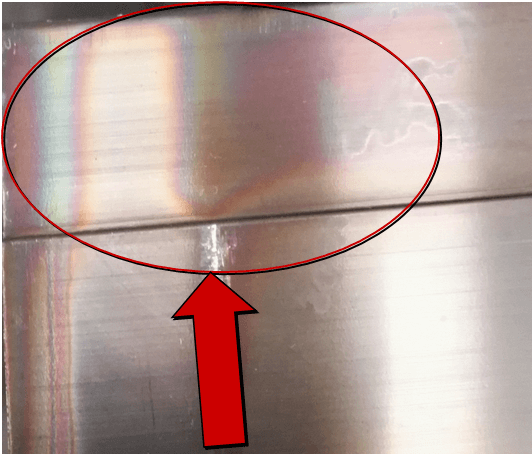 Iridescence | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. In the heat sealing hole, poor sealing is caused by the presence of silica and phosphate;2. In cold sealing holes, over sealing is caused by a too high concentration of sealing tank liquid, too high tank temperature, too long sealing time, etc;3. Poor anodic oxidation and electrolysis;4. The sealing film is corroded | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Adjust the composition of tank liquid;2. Properly reduce the tank liquid temperature and reduce the hole sealing time;3. Reduce the nickel ion content in the sealing groove;4. Regularly clean the tank liquid slag and filter the tank liquid frequently to keep the tank liquid clear. | |||
| Name | Pinhole(film) | Cause | Oil removal by electrophoresis |
| Definition: pinhole pitting corrosion. | |||
| Features: the paint film surface is irregularly arranged with small hole like depressions or perforations. When viewed along the direction inclined to the surface, the paint film pinholes are more clear. | |||
Appearance: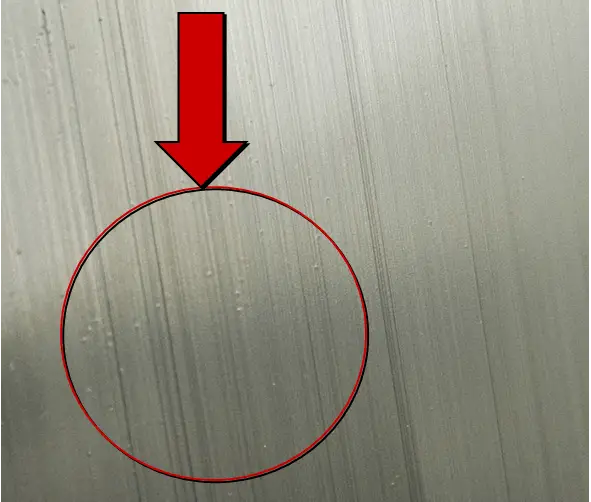  Pinhole(film) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. When the aluminum material enters the electrophoresis tank, bubbles or air on the surface of the paint solution are drawn in;2. There is air entrainment in the circulating system;3. The cathode shielding is poor or the defoaming bag is damaged, and there are fine bubbles in the paint solution;4. The electrophoresis voltage is too high and the electrolytic reaction is violent, resulting in bubbles;5. Impurities mixed into electrophoretic paint adhere to the paint film;6. The temperature of the electrophoresis bath is too high;7. The low pH value of the electrophoresis tank solution and excess solvent make the polarization ability of the paint film lower, resulting in the weak ability to resist impurities;8. Poor degreasing of pretreatment;9. The surface of the blank is corroded due to its long storage time. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. The lower groove should be inclined and shake up and down for several times;2. Regularly check the operation of the equipment;3. Replace the defoaming bag;4. Reduce electrophoresis voltage;5. Replace the filter bag regularly;6. The temperature of the electrophoresis tank shall be controlled within the process range;7. Adjust the process parameters of tank liquid to the normal range;8. Increase the degreasing intensity of pretreatment, add nitric acid regularly and improve the passivation strength9. The extruded embryo shall be oxidized and electrophoresed in time. | |||
| Name | Chromatic aberration | Cause | Coloring and operation |
| Definition: visual color difference | |||
| Features: color difference between oxidized aluminum and standard aluminum | |||
Appearance: 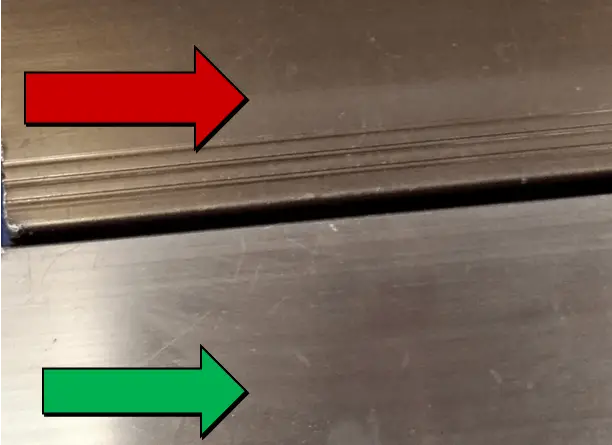 Chromatic aberration | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Poor conductivity;2. The clamp is not tight;3. The coloring is inaccurate. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Polish the water chestnut of the conductive rod until the color of the substrate is exposed;2. Clamp the material tightly to prevent loosening;3. The colorist shall check the color strictly according to the standard color board, and correct any deviation in time. | |||
| Name | Acid slobbery stain | Cause | operation |
| Definition: the surface of the profile is corroded by acid and alkaline water | |||
| Features: there are white flow marks or round spots on the surface of the profile | |||
Appearance: 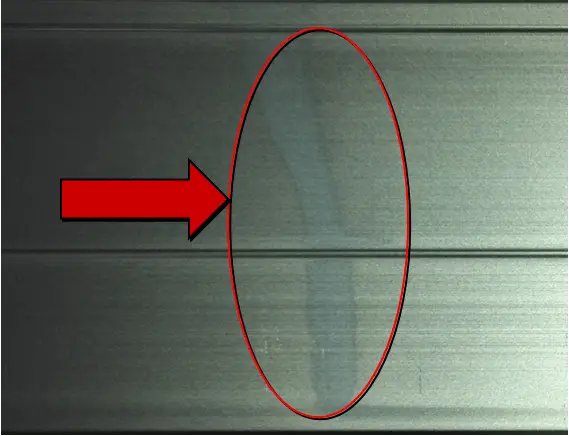 Acid slobbery stain | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The acid and alkali solution attached to the fixture or material rack is not completely cleaned in the subsequent water washing process and flows to the surface of the aluminum;2. There is acid-base solution on the aluminum surface that has not been cleaned;3. When the sealing is finished, the other materials are crossed from the draining area. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Thoroughly clean the fixture and material rack;2. The profile of the small inner cavity shall be cleaned for many times;3. Do not cross from other material racks;4. Ensure that the process parameters of each washing tank meet the production requirements;5. When lowering the oxidation tank, flush the conductive girder with water pipe. | |||
| Name | Sealing smut | Cause | Hole sealing |
| Definition: after sealing the hole, a layer of calcified material is attached to the surface of the profile | |||
| Features: the surface of the oxidized profile is attached with erasable white ash, and the surface of the colored profile is attached with indelible yellow ash. | |||
Appearance: 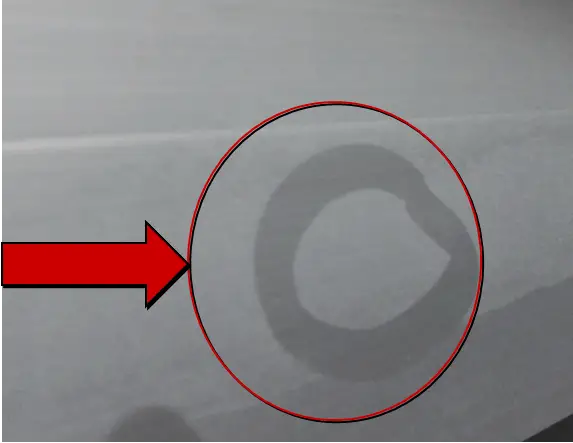 Sealing smut | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The calcium ion or magnesium ion in the sealing tank is too high;2. Turbidity in the sealing groove is absorbed to the aluminum surface, which is not cleaned in the subsequent water washing process;3. The hole sealing time is too long;4. The sealing fluid is aged. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Ensure the dryness of the groove after washing;2. Increase the filtration of sealing tank liquid to reduce sedimentation;3. Grasp the hole sealing time;4. Configure new tank liquid. | |||
| Name | Local film-free | Cause | Electrophoresis and operation |
| Definition: when electrophoretic coating is applied, the aluminum profile is not coated with organic paint film | |||
| Features: compared with the profile with paint film on the surface, the brightness is lower, and the hand feel is rough and touching | |||
Appearance:  Local film-free | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Poor conductivity;2. Soaking time in RO1 and ro2 water washing tanks is too long;3. The solvent content in the water washing tank is too high;4. The pH value of the electrophoresis tank is too high;5. The temperature of the hot water tank is too high and the soaking time is long, and the oxide film hole is closed. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Check whether the line and tie bar are firm;2. Strictly control the soaking time of the water washing tank (2-3 minutes);3. Control the content of solvent according to the process requirements;4. The pH value of the tank liquid shall be detected frequently and refined in time when it is high;5. Strictly control the hot water tank process. | |||
| Name | Dust stain | Cause | electrophoresis |
| Definition: fine granular foreign matters formed by dust and other foreign matters adhering to the surface or under the paint film. | |||
| Features: dots are irregularly distributed on the surface of profiles, and there is a bulge feeling when touching with hands. | |||
Appearance: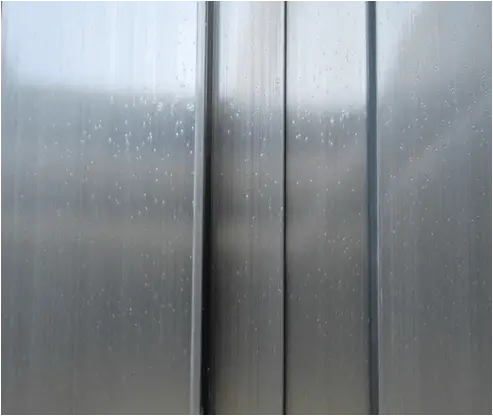  Dust stain | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The water washing tank before the electrophoretic painting process is not clean or the conductivity is too high;2. There are coarse mechanical impurities in the electrophoresis tank solution;3. Floating objects such as dust in the air of the workshop fall on the aluminum materials placed in the drainage area;4. There are dust and other impurities in the curing furnace. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Replace the water in the water washing tank and check the water quality regularly;2. Strengthen the filtration frequency of electrophoresis tank solution and replace the filter bag;3. The electrophoresis workshop shall have an independent air circulation system and be cleaned every day;4. Regularly clean the curing furnace and clean or replace the hot air circulating filter screen. | |||
| Name | Bubble(film) | Cause | Electrophoresis and operation |
| Definition: bubble mark on profile surface due to bubble attachment | |||
| Features: generally irregular circular bubble traces with different sizes. | |||
Appearance: .png) Bubble(film) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. When the aluminum material is immersed in the electrophoresis tank, it will be involved in bubbles or air on the surface of the paint solution;2. The paint solution contains tiny bubbles;3. There are too many bubbles on the aluminum surface and the paint liquid has poor fluidity and cannot be brought out;4. The inclination angle is not enough in the process of aluminum entering the groove;5. The paint inlet valve is not closed tightly and air is inhaled;6. The content of solvent A in the tank liquid is low. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Increase the slope of the lower groove of the profile, lower the groove slowly, stand for 30 seconds after lowering the groove, and conduct electrophoresis after energization;2. Check whether the defoaming bag is damaged;3. Add a certain amount of solvent B or increase the circulation;4. Check the closing condition of the valve after the paint liquid is pumped every time;5. Add an appropriate amount of solvent A | |||
| Name | Powdering(JIS) | Cause | Electrophoresis and anodizing |
| Definition: after anodizing, white powder is formed on the surface of the film. | |||
| Features: after anodizing, the film is white powder and opaque; It’s easy to wipe the powder off by hand. | |||
Appearance: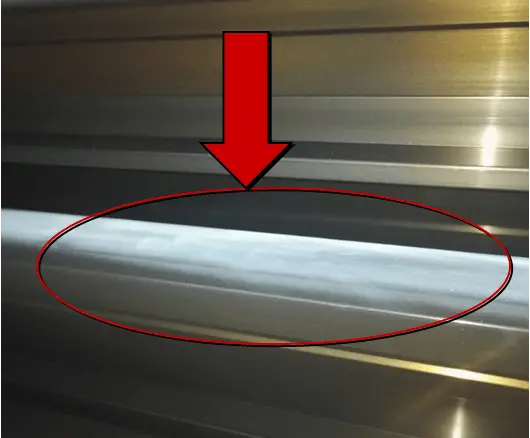  Pwodreing(JIS) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The electrolyte temperature is too high;2. Aluminum ion concentration is too high;3. Excessive current density;4. Too long oxidation time;5. Too long immersion time after oxidation;6. Insufficient mixing of oxidation tank liquid;7. Local hanging materials are too dense. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Adjust the tank liquid temperature;2. Often separate excess aluminum ions;3. Use appropriate current density;4. Grasp the oxidation time;5. Control the immersion time;6. Fully ventilate and stir during anodizing;7. Control the distance between the upper rows. | |||
| Name | yellowing(combined anodic oxide film) | Cause | Anodizing, electrophoresis |
| Definition: the phenomenon of yellow paint film or oxide film. | |||
| Features: the profile composite film looks yellow as a whole. | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The coating is too thick;2. The curing temperature is too high or the curing time is too long;3. The electrophoresis tank is polluted;4. Abnormal quality of electrophoretic paint;5. After oxidation, soak in the water tank for too long, resulting in yellowing of the oxide film, and yellowing of the product due to the transparency of the paint film; | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Improve painting conditions and reduce coating thickness;2. Adjust the furnace temperature to the range required by the process;3. Refining electrophoresis tank liquid; 4. Purchase electrophoretic paint with stable quality and conduct regular sampling inspection for quality stability;5. Control the water quality and washing time of washing water after oxidation. | |||
| Name | Dull color | Cause | electrophoresis |
| Definition: after the electrophoretic profile is cured, the surface of the profile is attached with granular electrophoretic paint. | |||
| Features: it is generally irregularly distributed on the surface of the profile, and the attached particles are large and small. | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The electrophoresis main tank and RO water washing tank have not been cleaned for a long time, and the tank wall is attached with solidified old paint, which is scratched and attached to the profile during production;2. When acid is mixed into the main electrophoresis tank or RO water washing tank, part of the coating resin condenses and adheres to the profile;3. When adding paint solution to the main electrophoresis tank, the mixing is uneven and the emulsification is not complete. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Regularly clean the electrophoresis main tank and RO water washing tank to reduce the old paint attached to the tank;2. Prevent acid from mixing into the main electrophoresis tank and RO water washing tank;3. When adding paint solution to the electrophoresis main tank, stir for at least 30 minutes, and pump it into the main tank after complete emulsification. | |||
| Name | acid slobbery stain(film) | Cause | electrophoresis |
| Definition: after the electrophoretic profile is cured, there are paint spots or paint flow marks on the surface of the profile. | |||
| Features: there are irregular paint spots or paint flow marks on the surface of the paint film. | |||
Appearance: .png) acid slobbery stain(film) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The retention time after electrophoresis out of the tank is too long;2. Improper concentration of coating;3. Insufficient washing after electrophoresis;4. The solid content of RO2 washing tank is too high;5. There are acid-base water drops on the conductive beam. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. The residence time of electrophoresis after grooving shall be within 1 min;2. Control the coating concentration in strict accordance with the process requirements;3. Appropriately extend the washing time after electrophoresis;4. Reduce the solid content of RO2 water washing tank;5. The oxidation process shall fully spray water to wash the girder. | |||
| Name | Water spot | Cause | Electrophoresis and operation |
| Definition: also known as watermark, it refers to the spot-like or water drop-like pattern caused by water droplets attached to the paint film surface (especially the paint film surface in the horizontal or inclined position) before or during curing. | |||
| Features: it is easy to occur on the horizontal part or inclined part, with irregular distribution, and its shape is spotted or drop like pattern. | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Water droplets are attached to the surface of semi-dry paint film, resulting in changes in gloss during curing;2. There are impurities in the water droplets attached to the surface of the paint film, which changes the luster or color;3. The water quality of the previous hot pure water washing is unqualified or the soaking time is short. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Extend the drainage time;Ensure sufficient hot water and soaking time. | |||
| Name | Bubble(colored) | Cause | Extrusion, anodizing, operation |
| Definition: the gas produced in electrolytic coloring or the air used for stirring stays in the gap or corner of the material and covers the oxide film layer, so that the colored metal ions cannot enter the pore diameter of the oxide film and form bubble colored spots. | |||
| Features: the gap or corner of the material, the local film is very thin or not, and there are residual bubbles on the surface of the anodic oxide film. If electrolytic coloring is carried out, uniform color cannot be obtained. | |||
| Appearance:
Bubble(colored) | |||
| Cause of occurrence: Improper hoisting angle;Too fast grooving speed;The shape of aluminum is not conducive to the elimination of gas;The defoaming bag is damaged. | |||
| Countermeasures: By controlling the slope of the lower groove;Prolonging the prepreg time;Damaged defoaming bags shall be replaced in time. | |||
The appearance and performance defects of oxidized surface treatment products mainly include unqualified hole sealing, unqualified oxide film thickness, unqualified pencil hardness of paint film, unqualified corrosion resistance of paint film, etc.
Generally, once such defects are produced, they are often scrapped in batches, resulting in heavy losses, which must be prevented from time to time.
| Name | Sealing failure | Cause | Hole sealing |
| Definition: the weight loss of hole sealing does not comply with GB / t5237 | |||
| Features: the sealing quality does not achieve the expected effect. The water-based pen is used to dye the spot on site, which cannot be wiped off after drying | |||
Appearance: 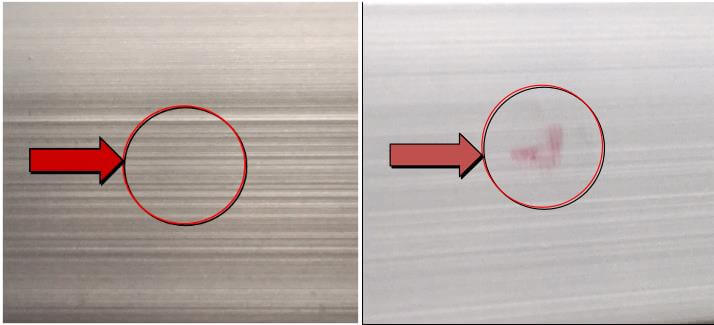 Sealing failure | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Insufficient hole sealing time;2. The sealing temperature is low;3. The pH value of the tank solution is not within the process range;4. The oxide film thickness seriously exceeds the specified film thickness. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Extend the hole sealing time;2. Adjust the sealing temperature;3. Adjust the tank liquid parameters to the process range;4. Measure the thickness of oxide film and determine the sealing time according to the actual film thickness. | |||
| Name | Oxide film thickness is not up to the standard | Cause | anodic oxidation |
| Definition: the thickness of oxide film does not meet the requirements. | |||
| Features: the thickness of oxide film obtained after anodizing cannot meet the customer’s requirements, as shown in Figure 1 below; Or seriously exceed the customer’s requirements, as shown in Fig below.At this time, although the customer can accept it, it is not advisable to increase the oxidation cost; Oxide film thickness standard. | |||
Appearance:  Oxide film thickness is not up to the standard | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. Inaccurate calculation of oxidation time;2. The output current of the silicon generator is inconsistent with the setting;3. The binding bar is loose. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Calculate the appropriate oxidation time in strict accordance with the standard;2. Check the actual output value of silicon oxide machine current frequently to facilitate production and adjust oxidation time in time;3. The binding and arrangement should be strengthened. | |||
| Name | Pencil hardness is not qualified | Cause | electrophoresis |
| Definition: profile electrophoretic paint film pencil hardness < 3H | |||
| Features: use a blade to draw a part of the paint film, grind it by hand in a sheet or roll shape, and the paint film is poorly powdered | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The water temperature of the hot water tank is low and does not meet the process requirements;2. The curing temperature and time do not meet the lower limit of process requirements;3. Soak in hot water for a long time, and the oxide film is closed;4. Aging of tank liquid;5. The combination ratio of hard monomer and soft monomer in the original paint does not meet the requirements. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Keep the temperature of the hot water tank within the process range;2. Adjust the curing furnace temperature and curing time to the process range;3. Control the soaking time of the hot water tank at about 6 minutes;4. Replace some tank liquid;5. Adjust the combination ratio of hard monomer and soft monomer in the original paint. | |||
| Name | Corrosion resistance is not qualified | Cause | electrophoresis |
| Definition: the corrosion resistance monitoring of paint film does not comply with GB / t5237 | |||
| Feature; | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The thickness of paint film does not meet the requirements of the national standard;2. Hot water tank and pure water tank are polluted;3. The acid value of tank liquid is high; | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Regularly check the thickness of paint film to ensure that the thickness of paint film meets the requirements of the national standard;2. Frequently replace the filter bags of hot water tank and pure water tank, regularly detect the pH value of tank liquid, and timely replace some tank liquid if it exceeds the process range;3. Separate tower C for several times and adjust the acid value within the normal process range. | |||
Oxidation surface treatment has a low impact on the size of products.
There are few such defects, which often flow into the previous process.
The impact of this process is mainly concentrated on two defects: excessive binding marks and thin reworked wall thickness.
| Name | Holding device impression | Cause | operation |
| English | Holding device impression | ||
| Definition: the binding mark exceeds the drawing requirements. | |||
| Features: during surface treatment, the contact between aluminum and hanger affects the impression produced by the surface treatment of this part.
This trace is inevitable, but it cannot exceed the length limited by the customer, otherwise, it will be unqualified. | |||
Appearance: 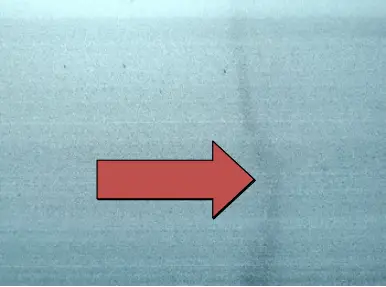 Tie line mark | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The positioning of the conductive rod in the upper row is not accurate;2. The upper binding row is loose, causing the profile to move up and down and dislocation during pretreatment;3. The binding angle and lower groove angle are insufficient.4. The specification of the conductive rod does not meet the process requirements. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. The distance between the conductive rods shall be determined during the upper row, and the upper and lower binding rows shall be consistent.For workpieces with special requirements, special conductive rods and fixtures shall be used;2. Aluminum wire binding shall be used for the upper row, and the profile shall not be loose.Fixture shall be used for the upper row to ensure that the profile cannot slide up and down;3. Tie and arrange from the bottom hole of the conductive rod to ensure that there is sufficient angle inclination at both ends. When lowering the groove, the angle is required to be greater than 30 °;4. The conductive rod shall meet the requirements of the operation specification for conductive rod in the oxidation workshop, and those that do not meet the requirements shall be replaced in time. | |||
| Name | Rework wall thickness | Cause | Operation |
| Definition: the wall thickness of reworked products is lower than the customer’s requirements. | |||
| Features: it is often produced in repeated reworked products, and the wall thickness measurement is lower than the lower limit required by customers. | |||
| Appearance: | |||
| Cause of occurrence: 1. The size of extruded incoming materials is unqualified;2. The oxidation process has been reworked for many times. | |||
| Countermeasures: 1. Strengthen incoming material inspection in the upper row;2. Try to make finished products successfully at one time. | |||