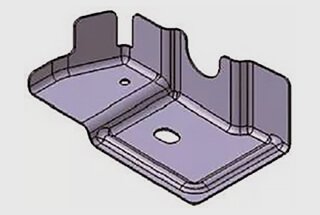
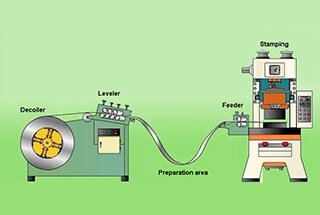
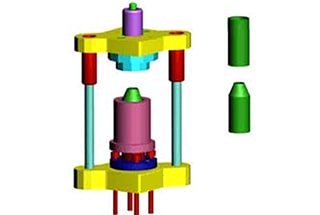
Imagine being able to shape metal into any form you desire with precision and efficiency. This article delves into the various types of dies used in metalworking, classified by hardness, quality, complexity, and size. Discover how different dies are designed to meet specific manufacturing needs, ensuring high-quality results and long-lasting performance. From soft dies used for smaller projects to hard dies for large-scale production, this guide provides a comprehensive overview. Get ready to learn how to select the right die for your next project and improve your metalworking skills.
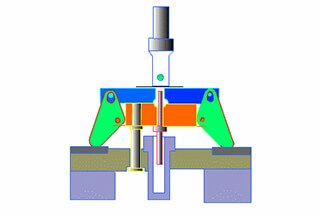
Die steel that has been pre-hardened, with a lower hardness of HB 400 or less and a production life of 500,000 times or less without quenching, is widely used.
The steel die undergoes annealing and the processing is divided into two stages: rough machining and finish machining.
After rough machining, the die is quenched to achieve a hardness of HRC48° or higher.
It is important to retain an allowance of approximately 0.2 after rough machining. Failure to do so may cause deformation of the workpiece during quenching treatment if the finishing process does not meet the requirements of the workpiece.
This type of die is commonly used for small-scale production, with a lifespan ranging from 50 to 1 million uses.
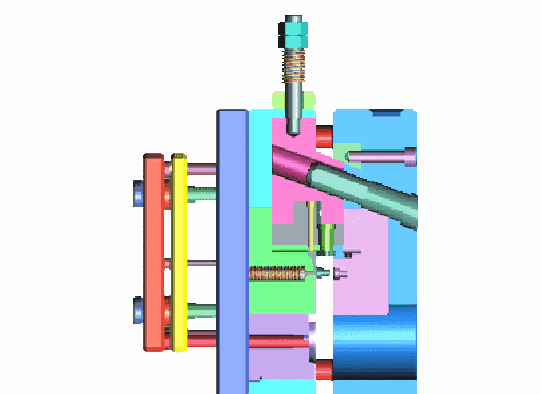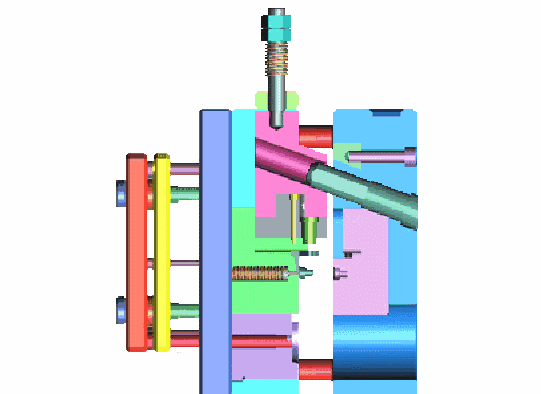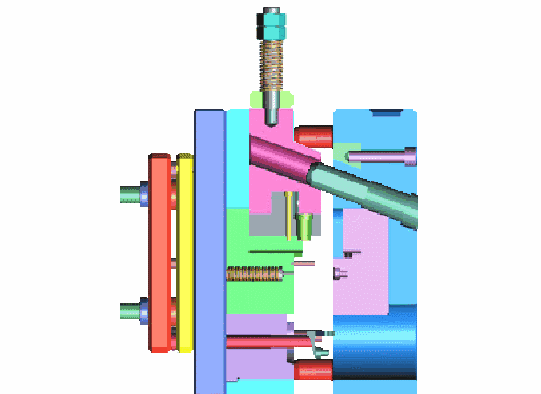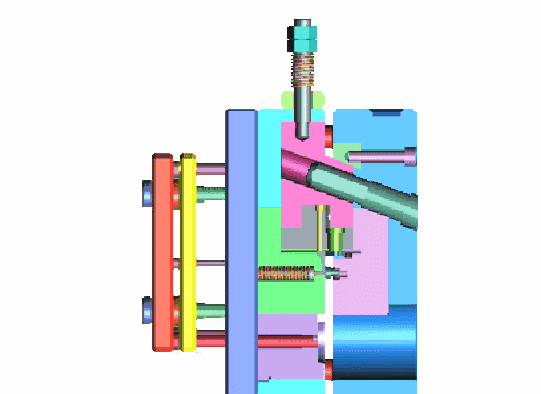
The dies must be able to endure one million or more die sinking processes.
For Level 1 dies, customers demand the use of top-quality materials and accessories to produce the best possible dies.
The requirements for Level 1 dies are as follows:
(1) Detailed die design, with computer drawings and material specifications.
(2) The die base must have a minimum hardness of HB280.
(3) The die core must be hardened to at least HRC50, and all rows and fittings must also be hardened.
(4) The thimble must be centered on the side of the tube.
(5) The die position must have a wear plate.
(6) The mold must have a temperature control monitor installed in the die or row position, according to feasibility.
(7) All cooling water channels are recommended to be nickel-plated (ELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATING) to prevent rust and facilitate cleaning.
(8) A positioning lock must be added to the parting line.
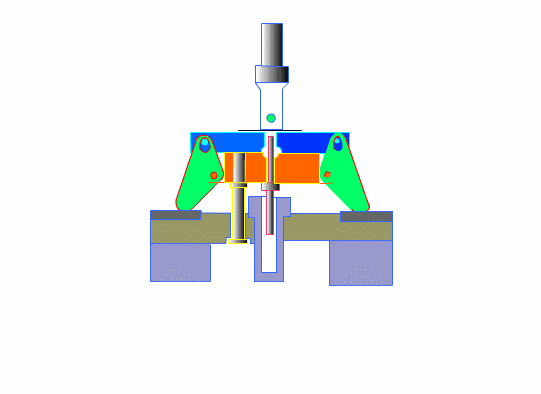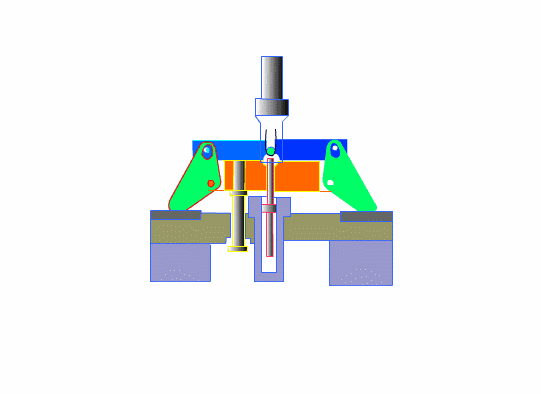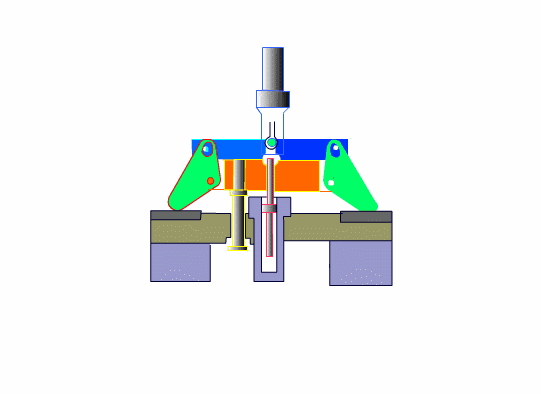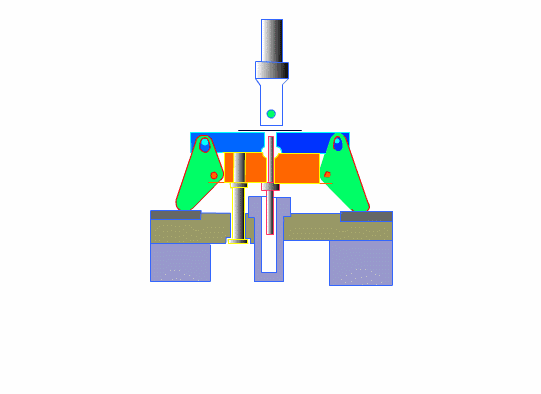
The dies must be able to endure half a million or more die sinking processes.
Level 2 dies are considered high-quality and must use good materials and accessories, along with meeting certain standards for dimensional accuracy in mold tolerances.
The requirements for Level 2 dies are as follows:
(1) It is recommended to have a detailed die design.
(2) The die base should have a hardness of at least HB280.
(3) The core of the die must have a minimum hardness of HRC48 and all rows and fittings must undergo heat treatment.
(4) A temperature control monitor should be installed in the die, or in the line position if feasible.
(5) A positioning lock must be present on the parting line.
(6) The following requirements can be specified on an individual basis and at the time of quotation.
The die must withstand at least 25,000 sinking processes, and this requirement applies to both general and production dies.
For level 3 dies, the following requirements must be met:
(1) It is recommended to have a die design.
(2) The die base must have a minimum hardness of HB165.
(3) The core of the die must have a hardness of at least HB280.
(4) All other requirements, in addition to the above three basic requirements, are considered optional and can be specified as additional requirements.
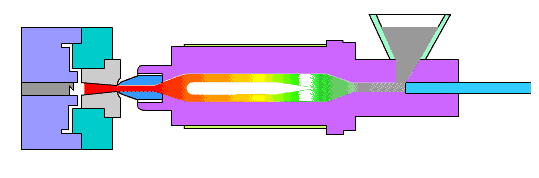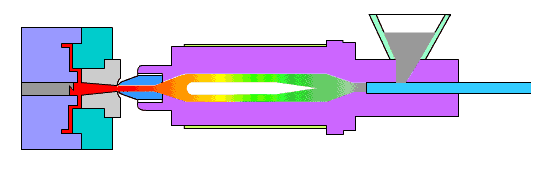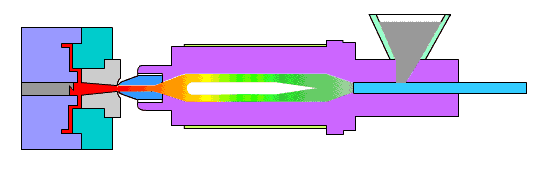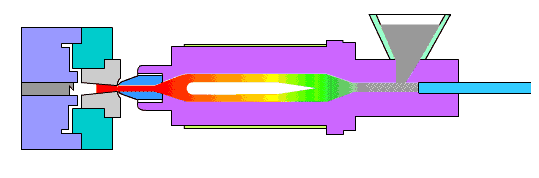
The die is expected to withstand approximately 10,000 sinking processes and is considered a low production die. While there are no specific requirements, the quality of the die should be high and acceptable to the customer.
For level 4 dies, the following requirements must be met:
(1) It is recommended to have a die design.
(2) The die base can be made of regular copper or aluminum.
(3) The die material can be made of aluminum or steel, subject to the customer’s approval.
(4) All other requirements, in addition to the above three basic requirements, are considered optional and can be specified as additional requirements.
Extra-large: dies with a width of 800mm or more.
Large: dies with a width between 600 and 800mm (excluding 800).
Medium: dies with a width between 350 and 600 mm (excluding 600).
Small: dies with a width of 350mm or less.