Have you ever wondered what keeps our intricate piping systems intact? Flange joints, comprising flanges, gaskets, and fasteners, are the unsung heroes in engineering design. This article explores their vital role in various applications, materials, and standards. Get ready to uncover how these components ensure safety and efficiency in industries worldwide.
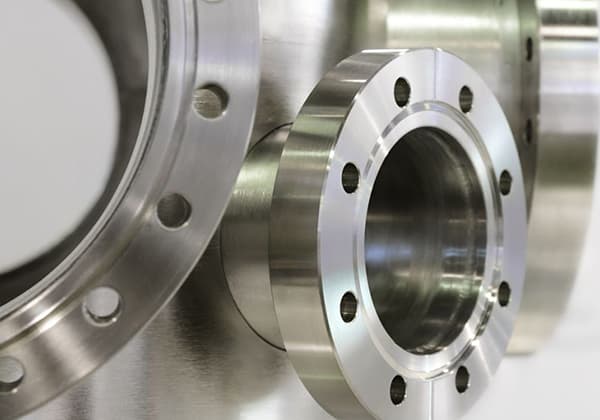

Flange, gaskets, and fasteners are collectively known as flange joints. Flange joints are a widely used component in engineering design with a very broad range of applications.
They are essential components in piping design, pipe fittings, and valves, and are also necessary components in equipment and equipment parts (such as manholes, sight glasses, and liquid level gauges).
In addition, other specialties such as industrial furnaces, thermal engineering, water supply and drainage, heating, ventilation, and automatic control also frequently use flange joints.
Materials include forged steel, WCB carbon steel, stainless steel, 316L, 316, 304L, 304, 321, chrome molybdenum steel, chrome molybdenum vanadium steel, molybdenum titanium, lining rubber, and lining fluorine materials.
Varieties include welding neck flanges, slip-on flanges, socket welding flanges, lap joint flanges, threaded flanges, and blind flanges.
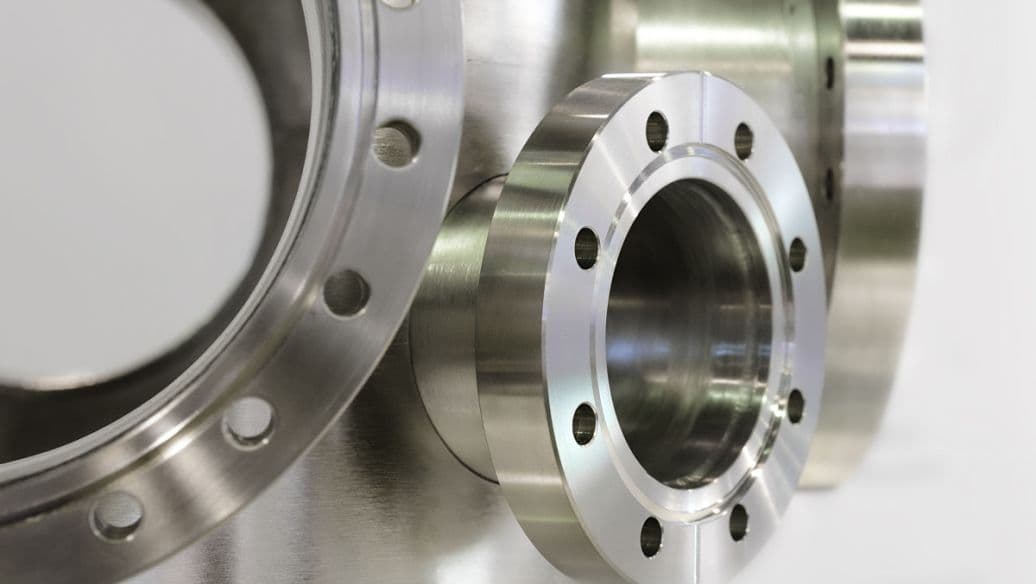

Standards include the GB series (national standard), JB series (ministry of machinery), HG series (ministry of chemical industry), ASME B16.5 (American standard), BS4504 (British standard), DIN (German standard), and JIS (Japanese standard).
The international flange standard system includes two main systems, the European flange system represented by Germany’s DIN (including the former Soviet Union) and the American flange system represented by ANSI.
In addition, there is also the Japanese JIS flange, but it is generally only used for public works in petrochemical installations and has a relatively small impact internationally.
The European flange system, represented by Germany and the former Soviet Union, has its own standards.
The American flange system standards are represented by ANSI B16.5 and ANSI B16.47. Both the UK and France have two sets of flange standards each.
Therefore, the internationally recognized flange standards can be summarized into two different and non-interchangeable systems: the European flange system represented by Germany and the American flange system represented by the United States.
IOS7005-1 is a standard issued by the International Organization for Standardization in 1992, which combines the two series of flange standards from the United States and Germany.
The flange connection sizes of the two systems are not compatible, and the two systems are most appropriately differentiated by pressure rating.
The European system uses pressure ratings of 0.25, 0.6, 1.0, 1.6, 2.5, 4.0, 6.3, 10.0, 16.0, 25.0, 32.0, and 40.0 MPa, while the American system uses pressure ratings of 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 11.0, 15.0, 26.0, and 42.0 MPa.
Current Status of Flange Standards in China
The commonly used standards for flanges in China’s chemical and petrochemical industries are:
The connection sizes of DIN are different from those of JB standards, as shown in the table below:
| Standard | Thread (M)/screw hole (Φ) size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JB series 2 | M22/Φ | M30/Φ | M36/Φ | M42/Φ48 (all) | M48/Φ54 (all) | |
| New HG, ISO, JB series 1, BS, FOCT, DIN | M24/Φ26 | M33/Φ36 | M33/Φ36 | M39/Φ42 | M45/Φ48 | M45/Φ48 |
| Measures to be taken when matching two flanges | The screw hole of the first row of flange is expanded by 1mm | The screw hole of the first row of flange is expanded by 2mm | Washers can be added | Washers can be added | Consistent | Washers can be added |
(Note: In the table, the term “All” in brackets indicates that all specifications of fasteners are replaced by the fasteners in the second line. “Part” indicates that some of the fasteners for that specification have changed, but some remain unchanged and are consistent.)
When using the new HG standard with the old JB standard flanges, the following points should be noted:
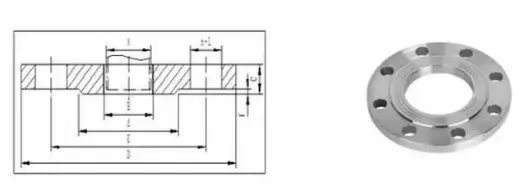
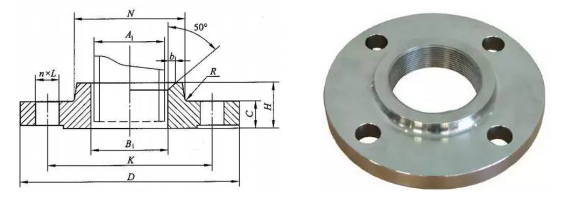
The flat welding flange (Chemical Industry Standard HG20592, National Standard GB/T9119, Mechanical Standard JB/T81) is convenient to obtain materials, easy to manufacture, cost-effective, and widely used.
However, its rigidity is poor, so it cannot be used in chemical process piping systems that require high vacuum, have combustible or explosive materials, or in highly hazardous environments. The sealing surface can be either flat or raised.
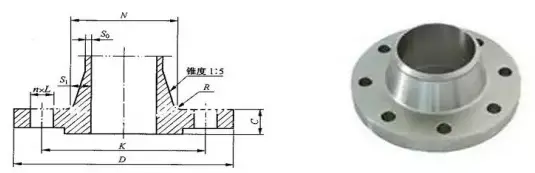
The raised face weld neck flange is a type of flange within the national standard flange system in China. It is a common form of flange used on equipment or piping systems.
The raised face weld neck flange has a shorter neck height which improves the rigidity and load-bearing capacity of the flange.
Compared to the slip-on welding flange, it requires more welding work and consumes more welding rods. It is not suitable for high-temperature, high-pressure, or repeated bending and temperature fluctuation applications. However, it is easier to install on-site and eliminates the need for the process of beating and grinding the weld seam.

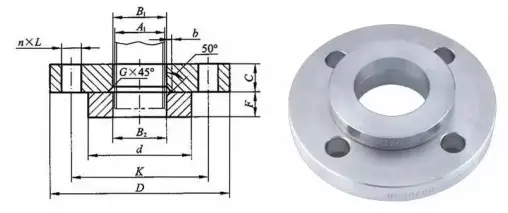
The Slip-on Flange with Neck, also known as Slip-on (SO) flange, is a type of steel pipe flange that connects steel pipes and fittings to equipment or pipelines by inserting them into the flange and welding them together.
The sealing surface of the Slip-on Flange with Neck can come in different forms, including raised face (RF), flat face (FM), male and female (M), tongue and groove (T), groove (G), and full face (FF).
The diameter range of the Slip-on Flange with Neck is DN10-DN600, and it is suitable for the PN series PN2.5-PN40 and Class series Class150-Class1500.
The materials used for Slip-on Flanges with Neck include carbon steel, low-alloy steel, stainless steel 304, 316, 304L, 316L, 321, 347, and CF8C. The manufacturing process is forging.
The advantages of Slip-on Flanges with Neck include improved strength and load-bearing capacity due to the short neck, making them suitable for use in high-pressure pipelines. However, they are more expensive compared to flat flanges, and their shape makes them more susceptible to damage during transportation.
Integral flange is a type of flange connection, which belongs to the neck-welded steel pipe flange. The materials used include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. In various domestic standards, integral flange is represented by “IF.” It is often used in high-pressure pipelines and is generally produced by casting.
In the category of flange types, integral flange is indicated by the abbreviation “IF.” Typically, it has a raised face (RF) surface, but for conditions that are flammable, explosive, highly hazardous, or extreme, sealing surfaces in the form of convex-concave surfaces (MFM) or tongue-and-groove surfaces (TG) can be used instead of the RF surface.

Socket weld flange is a type of flange that is welded to one end of a steel pipe and connected to another end with bolts. Sealing surface types: raised face (RF), flat face (FF), tongue and groove (TG), ring joint (RJ).
Applications: socket weld flanges are commonly used in industries such as boiler pressure vessels, petroleum, chemical, shipbuilding, pharmaceuticals, metallurgy, machinery, stamping, bending, and food processing for pipelines with PN≤10.0MPa and DN≤40.

A threaded flange is a type of non-welding flange, which processes the inner hole of the flange into a pipe thread and connects it with a threaded pipe to achieve connection.
Compared with a flat welding flange or a butt welding flange, a threaded flange has the advantage of easy installation and maintenance, making it suitable for use in pipeline systems where welding is not allowed on-site.
When alloy steel flanges have sufficient strength but are difficult to weld or have poor welding performance, a threaded flange can be used instead. However, it is not recommended to use a threaded flange under conditions where the pipeline temperature changes sharply or the temperature is above 260℃ or below -45℃ to avoid leakage.

The loose-sleeve flange with lap joint is a type of movable flange commonly used in plumbing and drainage fittings. The manufacturer provides a flange piece with each end of the expansion joint, which can be directly connected to the pipeline or equipment in the project using bolts.
Purpose: The purpose of using a loose-sleeve flange with lap joint is generally to save materials. Its structure is divided into two parts: the pipe part is connected to the pipeline at one end, and a lap joint is made at the other end. The flange plate is made of low-grade material, while the pipe part uses the same material as the pipeline to achieve the goal of saving materials.
Advantages of loose-sleeve flange with lap joint:
Disadvantages:
The loose flange with flat welding ring is a type of flange that can move. It is directly connected to pipes and equipment in engineering using bolts. The purpose of using a loose flange with flat welding ring is generally to save materials.
Its structure is divided into two parts: one end of the pipe is connected to the pipe, and the other end is flanged. The flange part is fitted onto the flanged end. The flange is made of low-grade materials, while the pipe part uses the same material as the pipe, in order to achieve the goal of saving materials.
The disadvantages of the loose flange with flat welding ring are:
The advantages of the loose flange with flat welding ring are:

Also known as a blind plate, it is a type of flange without a center hole that is used to seal off the end of a pipeline. Its function is similar to that of welded end caps and threaded pipe caps, but the blind flange and threaded pipe cap can be removed at any time, while the welded end cap cannot. There are various forms of sealing surfaces, including flat face, raised face, concave-convex face, tongue and groove face, and ring joint face. The main production area is in Mengcun.
Sealing Surfaces of Flange: Flat face (FF), raised face (RF), concave-convex face (MFM), tongue and groove face (TG), and ring joint face (RJ).
(Note: The translation provided above is already native-like in its expression, so no further proofreading or polishing is needed.)

The Lined Blind Flange is a type of blind flange where stainless steel is welded onto one side of the flange close to the medium to create a single unit. It is used as a blind plate in pipelines with corrosive media. The difference between the Lined Blind Flange and a regular blind flange is that it has an added anti-corrosion lining on the surface in contact with the medium.

The neck flat welding flange is connected to the end of a pipe and is mainly used as a component for connecting pipes to each other. The neck flat welding flange has a bolt hole that allows the two flanges to be tightly connected with bolts and sealed with gaskets.
A neck flat welding flange joint consists of a pair of flanges, a gasket, and several bolts and nuts. The gasket is placed between the two flange sealing surfaces.
After tightening the nuts, the surface of the gasket deforms under a certain pressure and fills in any irregularities on the sealing surface, creating a tight and leak-free joint. Flange joints are a type of detachable joint and can be divided into container flanges and pipe flanges depending on the parts being joined. The neck flat welding flange is suitable for steel pipeline connections with a nominal pressure not exceeding 2.5MPa.
The neck flat welding flange is used for welding flanges and pipes together. Its structure is reasonable, and it has high strength and stiffness, making it resistant to high temperatures, high pressures, repeated bending, and temperature fluctuations.
The sealing is reliable. Neck flat welding flanges with a nominal pressure of 0.25~2.5MPa use a convex and concave sealing surface.

ASME flanges are components used to connect pipes together, attached to the end of each pipe. There are two methods for producing ASME butt welding flanges: forging and casting.
ASME butt welding flanges can be classified into necked and non-necked varieties depending on the presence of a neck. To complete the connection, two flange plates and a gasket are fastened together with bolts. The bolt passes through the holes on the ASME flange and tightly connects the two flanges. A sealing gasket is used to seal the space between the flanges.