Have you ever wondered how high-tech industries achieve flawless heat treatments? Vacuum furnaces, capable of processes like brazing, annealing, and quenching, are key players in precision metalwork. This article explores various types of vacuum furnaces, their unique applications, and the benefits they bring to advanced manufacturing. Discover how these sophisticated tools enhance productivity and ensure superior quality in critical components.
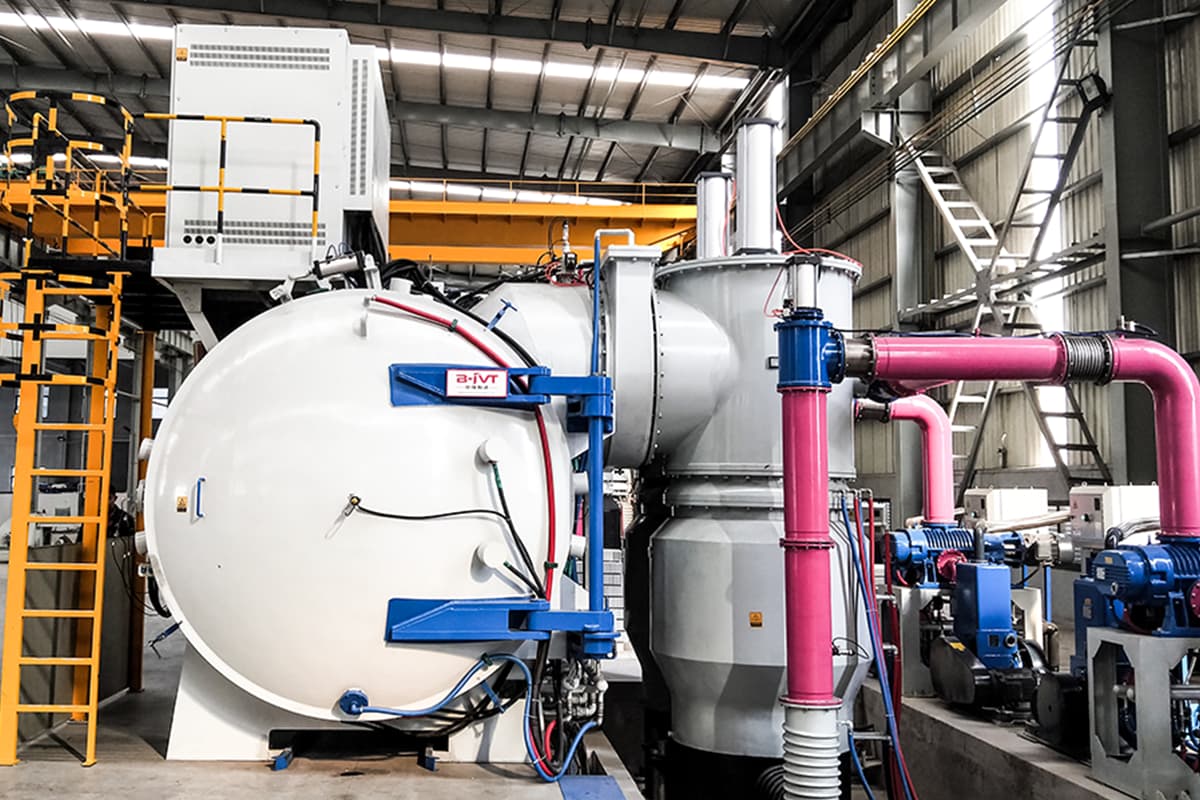

Vacuum furnaces can implement vacuum hardening and tempering, vacuum annealing, vacuum solid solution and aging treatment, vacuum sintering, vacuum chemical heat treatment, and vacuum coating, etc.
Therefore, vacuum furnaces can realize complex processes that other heat treatment equipment cannot handle.
The classifications of vacuum furnaces include vacuum brazing furnaces, vacuum gas quenching furnaces, vacuum sintering furnaces, vacuum annealing furnaces, vacuum tempering furnaces, vacuum oil quenching furnaces, and vacuum carburizing furnaces.
Let’s look at the uses of different types of vacuum furnaces and the benefits of using a vacuum furnace for workpiece processing!
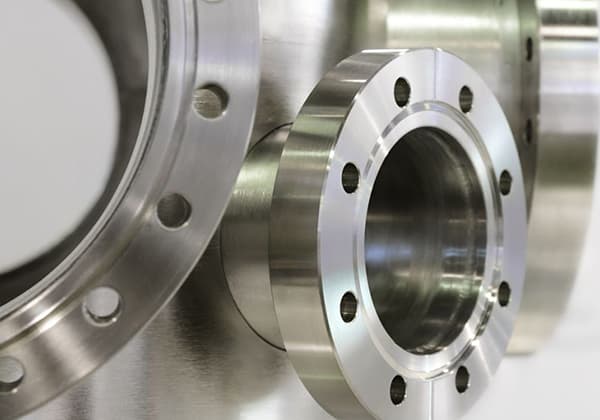
Vacuum brazing furnaces are mainly used for vacuum brazing of aluminum alloy heat exchangers and other aluminum products, brazing of stainless steel, titanium alloys, hard alloys, high-temperature alloys, non-ferrous metals, and vacuum tempering of high-speed steel, mold steel, bearing steel, stainless steel, etc., as well as aging and annealing treatments of non-ferrous metals, and vacuum brazing of stainless steel heat exchangers, engine oil coolers, and stainless steel thermos cups.

Vacuum gas quenching furnaces are primarily used for the high-pressure gas quenching of materials such as high-speed steel, tool steel, mold steel, and alloy structural steel.
They can also be used for high-temperature brazing and solid solution of stainless steel materials; sintering and aging treatments of powder materials etc. It also has a quick cooling function during annealing and solid solution.
Vacuum sintering furnaces are used under a hydrogen gas protection status after vacuum pumping, using the principle of medium frequency induction heating, causing the tungsten crucible in the coil to generate high temperatures, which is transmitted to the work by thermal radiation conduction, suitable for research and military units for sintering powder forming of refractory alloys such as tungsten, molybdenum, and their alloys. It is divided into horizontal vacuum sintering furnaces and vertical vacuum sintering furnaces.
The place where the electric furnace is installed should meet the requirements of vacuum hygiene, the surrounding air should be clean and dry, and there should be good ventilation conditions, and the work site should not easily raise dust, etc.
Vacuum sintering furnaces are mainly used for the sintering process of semiconductor components and power rectifier components. They can perform vacuum sintering, gas protection sintering, and conventional sintering.
It is a novel process equipment in the semiconductor equipment series. It has a novel design concept, convenient operation, and compact structure. It can complete multiple process flows on the bench equipment. It can also be used for other vacuum heat treatments and vacuum brazing processes.
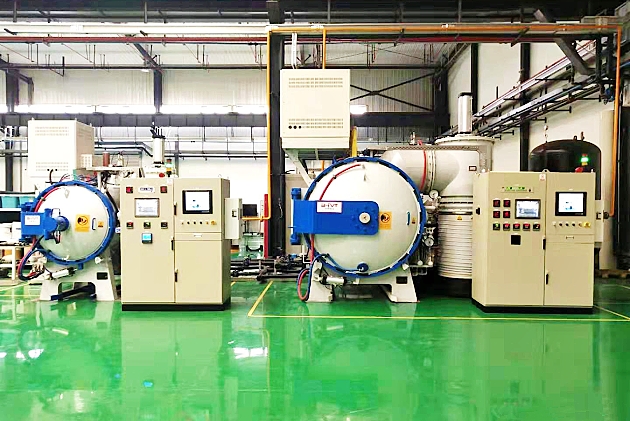

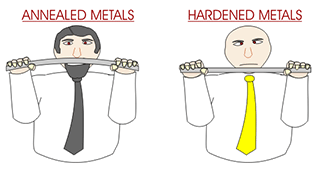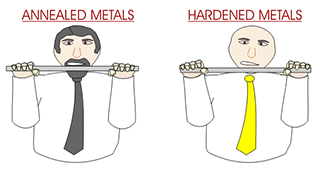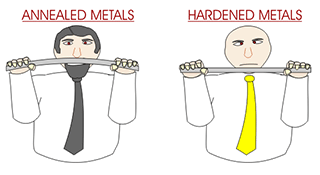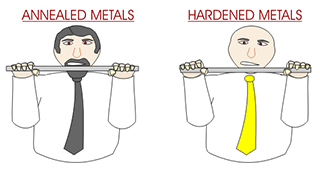
The vacuum annealing furnace is primarily utilized for deep drawing of stainless steel components such as plumbing fixtures, ensuring no oxidation.
Notably, the vacuum annealing furnace provides high productivity and a bright, non-oxidized surface of the treated products. It is widely applied in fields including stainless steel bearings, cutting tools, self-tapping and self-drilling screws, and stainless steel wire coils.
The furnace can also operate under a protective atmosphere, causing minimal pollution. The primary function of the vacuum is to serve as a barrier preventing high-precision metal components from coming into contact with complex gas compositions under high-temperature conditions, which can also be used for atmosphere annealing.
The vacuum tempering furnace is generally suitable for parts that require a bright and non-oxidized surface after tempering. It can be applied for high-temperature tempering of mold steel, high-temperature alloys, elastic alloys, copper alloys, titanium alloys, stress relieving and softening annealing of copper and copper alloys, while also offering quick cooling functionality.

The vacuum oil quenching furnace is suitable for the vacuum heat treatment of mold steel, spring steel, stainless steel, bearing steel, high-temperature alloy steel, and can also perform annealing.
Its main advantages include a wide range of applicable materials, strong hardenability, low cost, and reusable quenching oil.
However, it has the drawback of relatively larger deformation, requiring subsequent cleaning of the workpiece.
Structurally, vacuum oil quenching furnaces can be divided into two-chamber furnaces and three-chamber furnaces.
The vacuum carburizing furnace can flexibly implement various heat treatment processes such as vacuum carburizing, vacuum carbonitriding, vacuum carburizing plus oil quenching, vacuum carburizing plus gas quenching, and other functions of the vacuum furnace. It can be used to perform relevant heat treatments on various materials and parts in the industrial field.
For instance, carburizing and post-carburizing quenching of high alloy carburizing steels like 12Cr2NI4A, 12CrNi3A, carburizing and post-carburizing quenching of structural steels like 20CrMnTi, carburizing and post-carburizing quenching of stainless steels like 1Cr13, and quenching and annealing of mold steels like H13, W6Mo5Cr4V2, gear components, bushings, precision bearings, oil pump nozzles, and precision mechanical parts.
With the increasing demand for heat treatment quality control in high-end equipment manufacturing and significant improvements in equipment levels, vacuum heat treatment is increasingly favored, and the industry’s demand for vacuum heat treatment equipment technology is growing year by year.