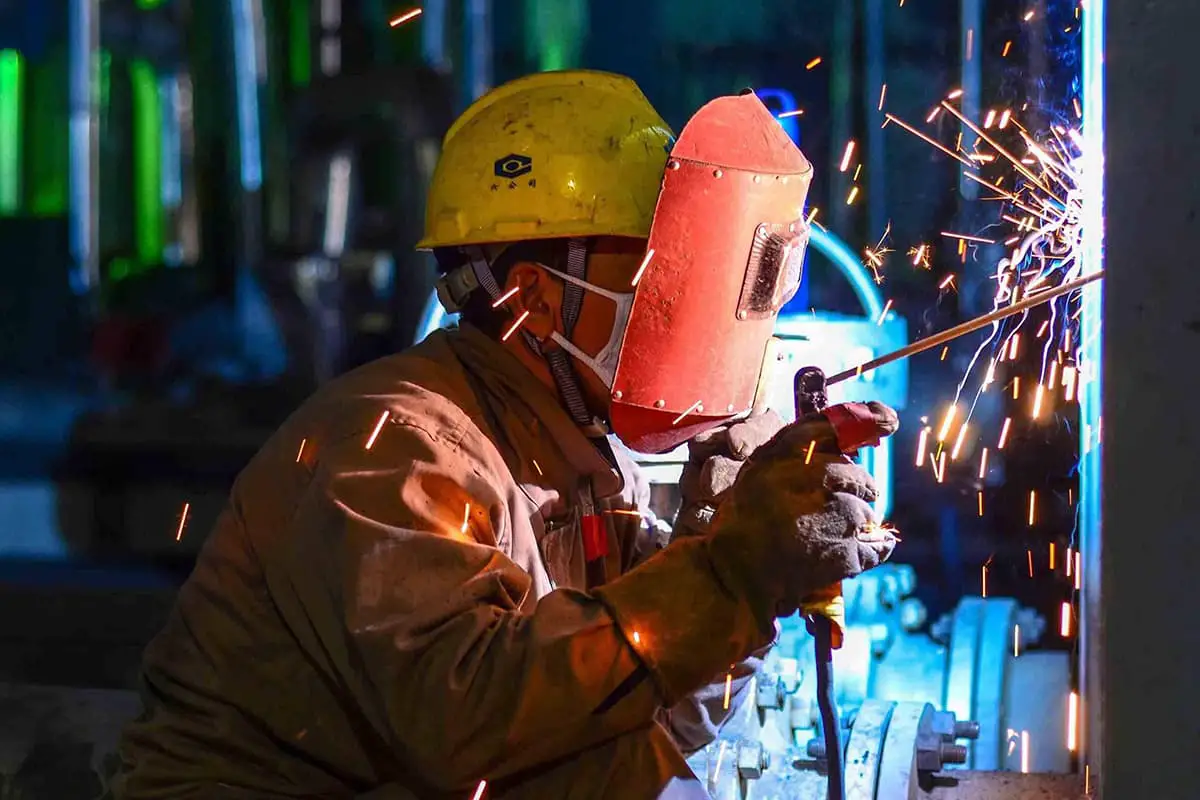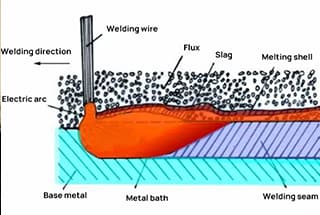
Have you ever wondered what makes welding so effective? The secret lies in flux, an essential material that cleans and prepares metal surfaces for strong bonds. In this article, you’ll discover how flux removes oxides, reduces surface tension, and enhances the overall welding process. By the end, you’ll understand why choosing the right flux is crucial for achieving durable and high-quality welds.

Flux is an indispensable auxiliary material in SMT welding process.
In wave soldering, flux and solder are used separately, while in reflow soldering, flux is an important part of solder paste.
The welding effect is not only related to the welding process, components and PCB quality but also the selection of flux is very important.

Flux with good performance shall have the following functions:
(1) Remove the oxide on the welding surface, prevent the reoxidation of solder and welding surface during welding, and reduce the surface tension of solder.
(2) The melting point is lower than that of solder. Before the solder melts, the flux must melt first in order to give full play to the role of welding aid.
(3) The infiltration diffusion rate is faster than that of molten solder, and the expansion is usually required to be about 90% or more.
(4) The viscosity and specific gravity are smaller than those of solder. The viscosity will make it difficult to infiltrate and diffuse. If the specific gravity is large, the solder surface cannot be covered.
(5) No weld bead spatter, toxic gas and strong pungent odor will be generated during welding.
(6) The residue after welding is easy to remove and has the characteristics of non-corrosion, non hygroscopic and non-conductive.
(7) Non stick, do not touch hands after welding, and the solder joint is not easy to sharpen.
(8) Stable storage at room temperature.

Traditional flux is usually based on rosin. Rosin has weak acidity and hot melt fluidity, and has good insulation, moisture resistance, non-corrosive, non-toxic and long-term stability. It is a rare welding aid material.
At present, active flux based on rosin is mostly used in SMT.
Because the chemical composition and properties of rosin vary greatly with the variety, origin and production process, the optimization of rosin is the key to ensuring the quality of flux.
The general flux also includes the following components: active agent, film-forming material, additives and solvents.
Active flux is an active substance added to the flux in order to improve the welding ability.
The activity of active agent refers to its ability to chemically react with the surface oxides of solder and welded materials in order to clean the metal surface and promote wetting.
Active agents are divided into inorganic active agents, such as zinc chloride, ammonium chloride, etc;
Organic active agents, such as organic acids and organic halides.
Generally, the inorganic active agent has good welding aid, but it has a long action time and high corrosivity, so it is not suitable to be used in electronic assembly;
The organic active agent has the advantages of soft action, short time, low corrosivity and good electrical insulation. It is suitable for electronic assembly.
The content of the active agent is about 2% – 10%. In the case of the chlorinated compound, the chlorine content shall be controlled below 0.2%.
By adding film-forming material, a compact organic film can be formed after welding, which protects the solder joint and substrate, and has anti-corrosion and excellent electrical insulation. Commonly used film-forming materials include rosin, phenolic resin, acrylic resin, vinyl chloride resin, polyurethane, etc.
Generally, the addition amount is 10% – 20%. Excessive addition will affect the expansion rate and reduce the welding aid.
In the assembly of ordinary household appliances or electrical appliances with low requirements, film-forming substances are used, and the electrical components after assembly are not cleaned to reduce the cost.
However, in the precision electronic assembly, they still need to be cleaned after welding.
Additives are substances with special physical and chemical properties added to adapt to the process and environment. Common additives are:
(1) Regulator:
Materials added to adjust the acidity of the flux, such as triethanolamine, can adjust the acidity of the flux;
Adding hydrochloric acid to inorganic flux can inhibit the formation of zinc oxide.
(2) Matting agent:
It can make the solder joint dull and overcome eye fatigue and vision decline during operation and inspection.
Generally, inorganic halides, inorganic salts, organic acids and their metal salts are added, such as zinc chloride, tin chloride, talc, copper stearate, calcium, etc.
(3) Corrosion inhibitor:
The addition of corrosion inhibitor can protect the printed board and device-free lead, has moisture-proof, mildew-proof and corrosion resistance, and maintains excellent weldability.
Most of the materials used as corrosion inhibitors are organic compounds with nitrides as the main body.
(4) Brightener:
It can make the solder joint glow. Glycerol and triethanolamine can be added. Generally, the addition amount is about 1%.
(5) Flame retardant:
Materials added to ensure safe use and improve flame resistance.
Most practical fluxes are liquid. Therefore, the solid components of the flux must be dissolved in a certain solvent to make it a homogeneous solution.
Isopropanol and ethanol are mostly used as solvents. Various solid components used as flux have good solubility.
(1) It has good solubility for various solid components in flux.
(2) The volatilization degree is moderate at room temperature and volatilizes rapidly at welding temperature.
(3) Low odor and toxicity.
(1) According to the state, it can be divided into liquid, paste and solid.
(2) It can be divided into three categories: brushing, spraying and impregnation.
(3) According to the activity of flux, it can be divided into non activated and low activated.








