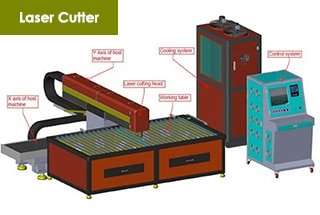
Ever wondered why a simple lens could make or break a laser cutting operation? This article reveals the critical role of high-quality protective lenses in laser cutting heads. You’ll learn how poor-quality lenses can cause significant damage, leading to costly repairs and downtime. Discover the importance of choosing the right materials to ensure optimal performance and protect your investment. Dive in to understand how a small component can have a massive impact on your laser cutting efficiency.

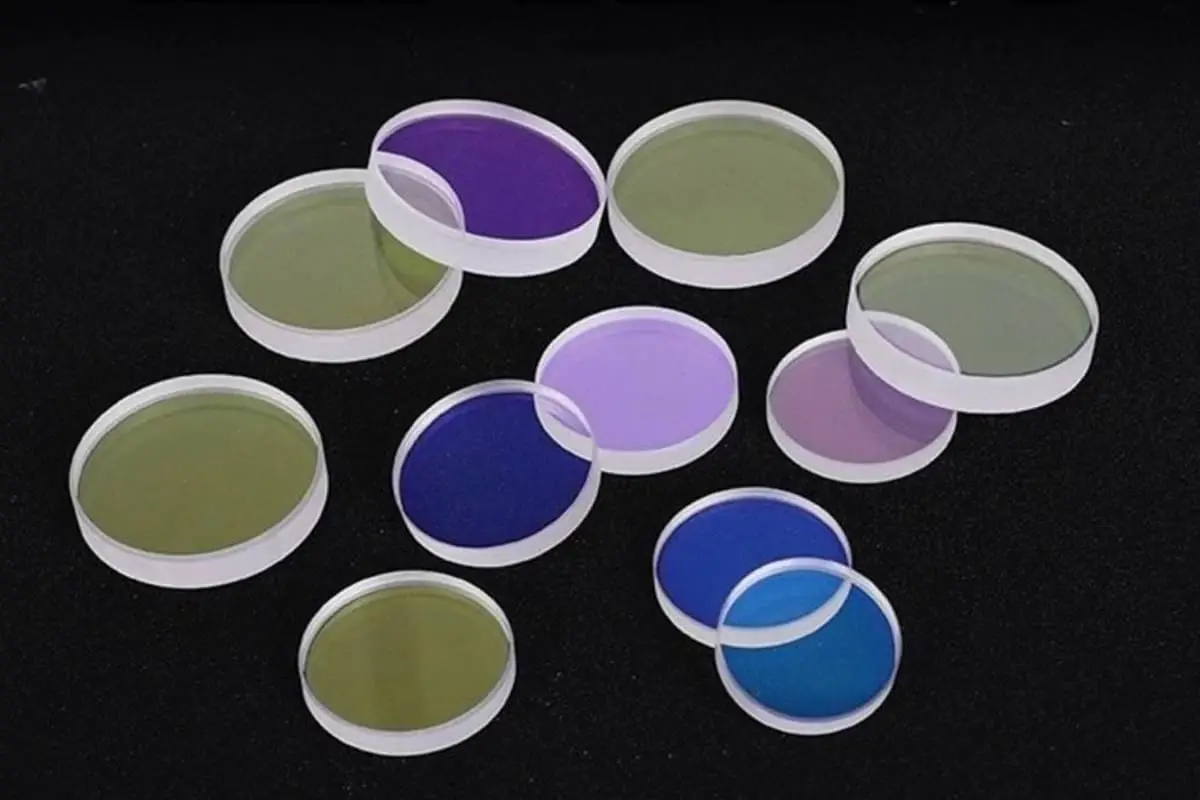
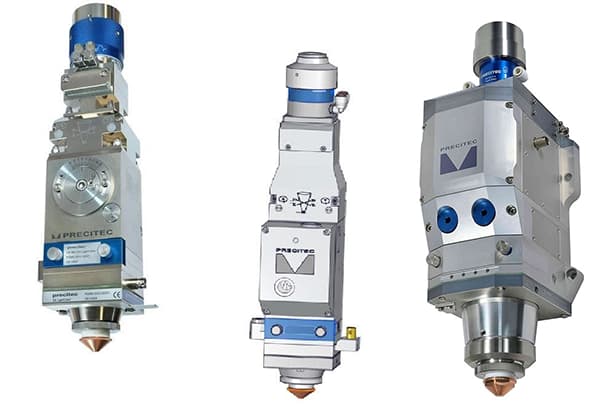
The cutting head of a laser cutting machine operates in a harsh environment, necessitating robust protection for its internal components, particularly high-value elements such as the collimator and focusing lens. To achieve this, upper and lower protective lenses are strategically installed within the cutting head assembly.
During the cutting process, debris and molten metal spatter generated at the workpiece surface pose a significant risk to the focus lens if they infiltrate the cutting head. The lower protective lens serves as a critical barrier, effectively blocking these potentially damaging particles.
The cleanliness of the protective lenses is paramount to maintaining optimal performance and cut quality in laser cutting operations. Contamination of these lenses not only degrades cutting efficacy and efficiency but also risks damaging sensitive internal components of both the cutting head and laser output assembly.
To ensure peak performance, it is essential to utilize protective lenses fabricated from materials exhibiting high light transmittance, low coefficients of thermal expansion, and superior durability. Regular inspection and maintenance protocols should be implemented, with lenses cleaned or replaced promptly upon contamination.
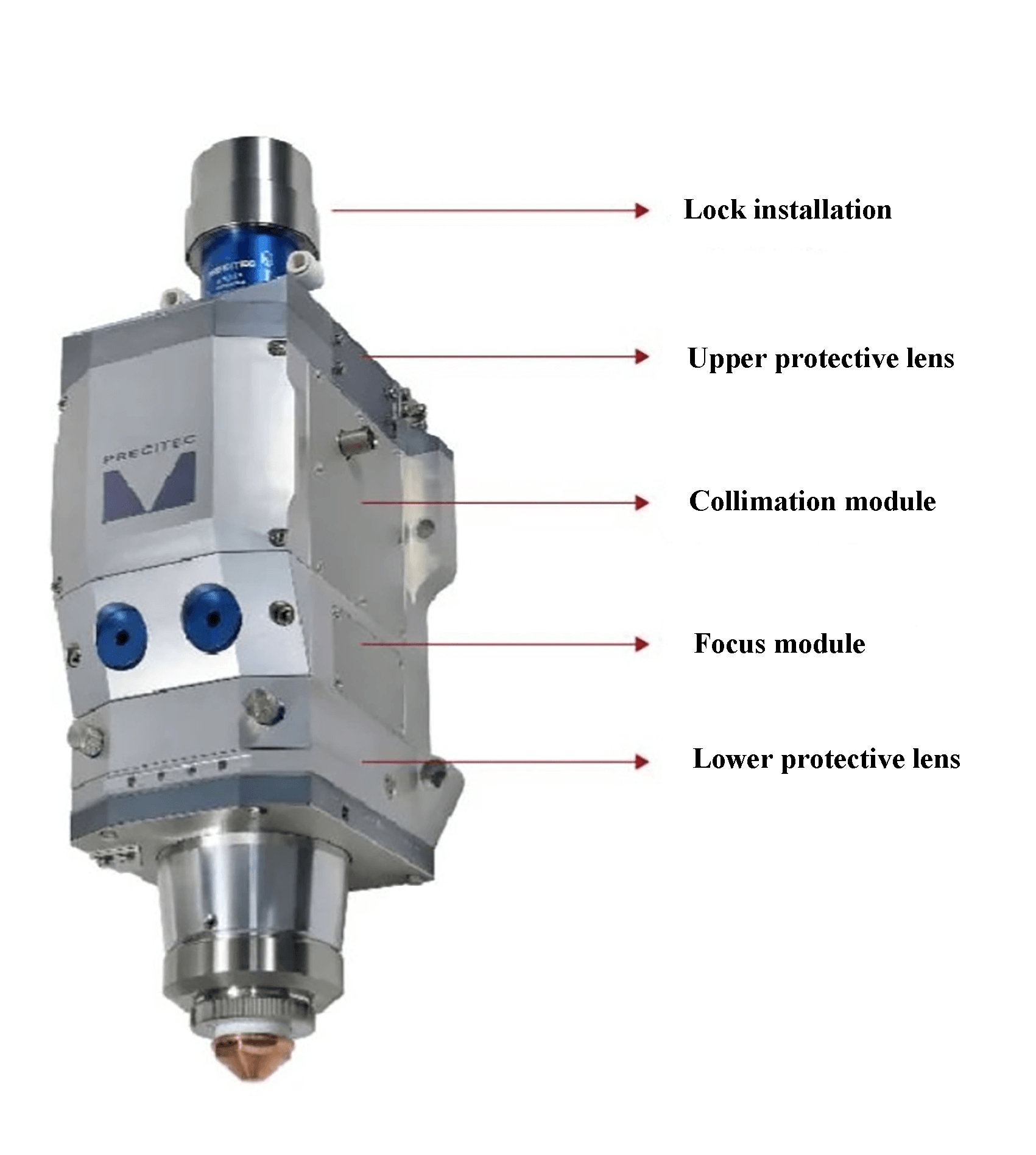
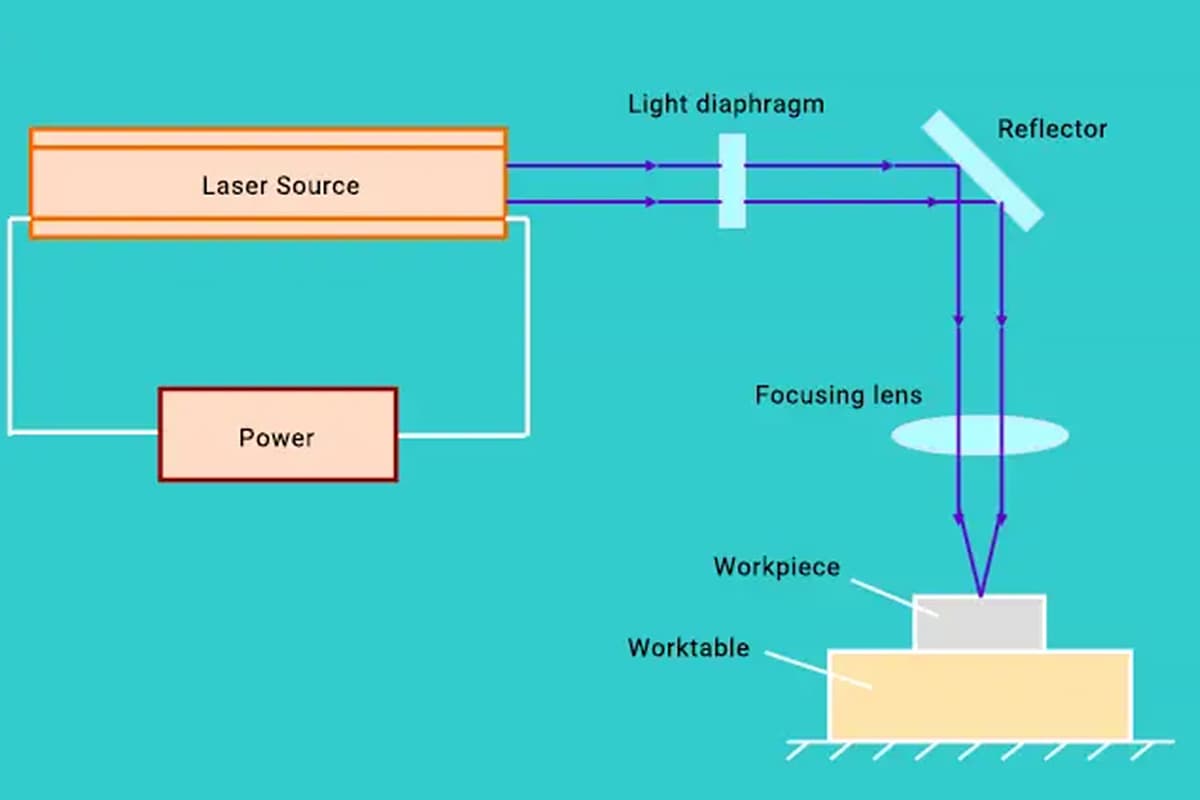
Fig. 1 Laser cutting head
The manufacturing process for high-quality protective lenses demands meticulous attention to several key factors:
These exacting requirements are reflected throughout the manufacturing process, from material preparation and forming to precision grinding, core drilling, and application of specialized coatings.
Rigorous quality control measures and comprehensive testing are essential before protective lenses can be deemed market-ready. Attempting to reduce costs by utilizing inferior substrate materials or omitting critical coating processes inevitably results in substandard lenses characterized by poor light transmittance, inadequate heat resistance, and increased susceptibility to fracture. Such compromised lenses risk catastrophic failure during operation, potentially releasing particulate matter that can contaminate the entire cutting head assembly and damage high-value components like focusing lenses and sensors.
The financial implications of a damaged cutting head can be severe, with repair costs potentially reaching 2-50% of the price of a new unit. Furthermore, the associated production downtime can lead to significant economic losses. To mitigate these risks, it is strongly recommended to source laser cutting accessories, including protective lenses, from reputable manufacturers through established supply channels.
A poor quality protective lens can increase the laser’s absorptivity. After sustained exposure to laser light, the temperature will rise, causing thermal deformation and the thermal lens effect. This, in turn, leads to the focus drift of the cutting head. The higher the power and the processing of high reflection materials, the faster the thermal expansion of the optical element, and the more pronounced the thermal lens effect will be.

Fig. 2 Thermal lens effect
A lower protective lens with poor quality has limited ability to block dust and spatter during processing and is prone to causing a fire point. When processing with a 10000 watt ultra-high power head, it is crucial to carefully select the protective lens. A lens of poor quality can result in burn-through of the lens when exposed to the 10000 watt laser in severe situations.

Fig. 3 Protective lens burning point / burn-through
If the burn-through of the protective lens is not detected in a timely manner, the continuous laser processing will generate particulate dust, which can contaminate the installation components, sealing ring, and lower surface of the focusing lens.
This can result in the formation of a burn point on the surface of the focusing lens. In this case, it is necessary to thoroughly clean and replace the entire set of installation components and the focusing lens module.
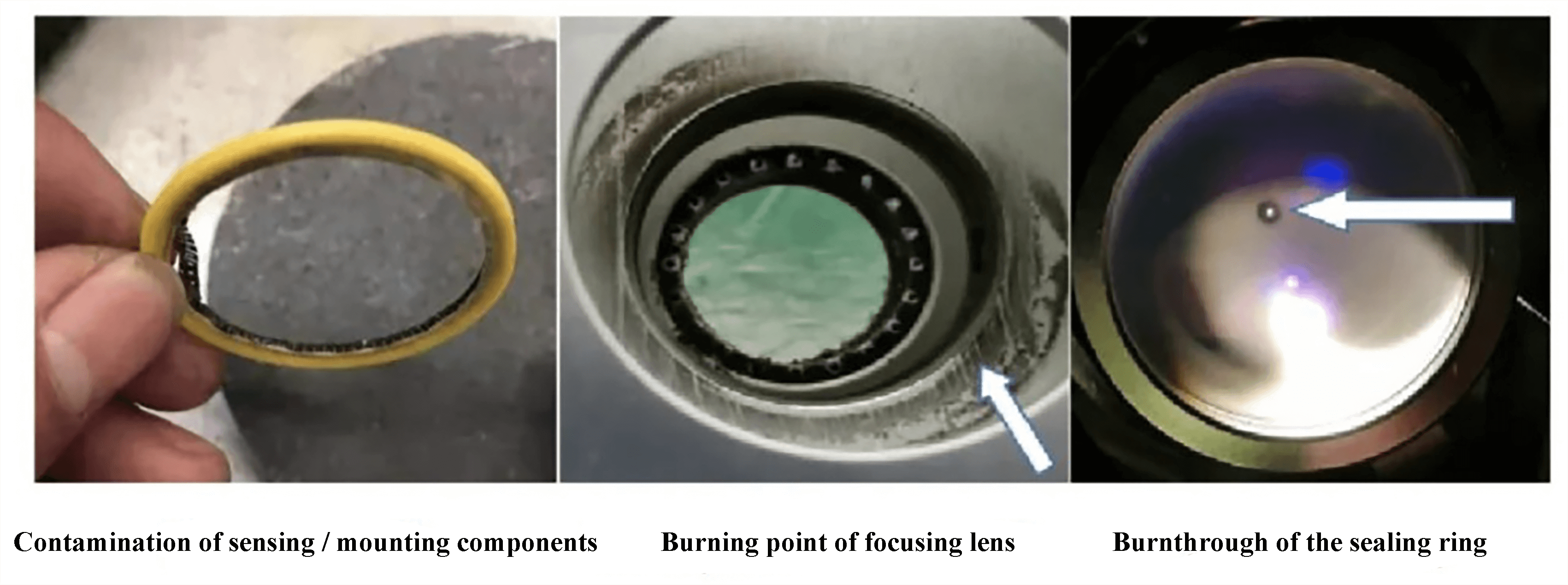
Fig. 4 Burning point of focusing lens
If the protective lens burns out, the collimator and focusing lens module in the cutting head are vulnerable to damage under the high power laser.
In severe cases, if the internal optical elements of the cutting head are damaged, the optical path will become abnormal and the reflected light will cause excessive heating of the window piece in the laser fiber output head, leading to the burnout of the QBH or LOE crystal. In this scenario, the entire laser output head must be replaced.
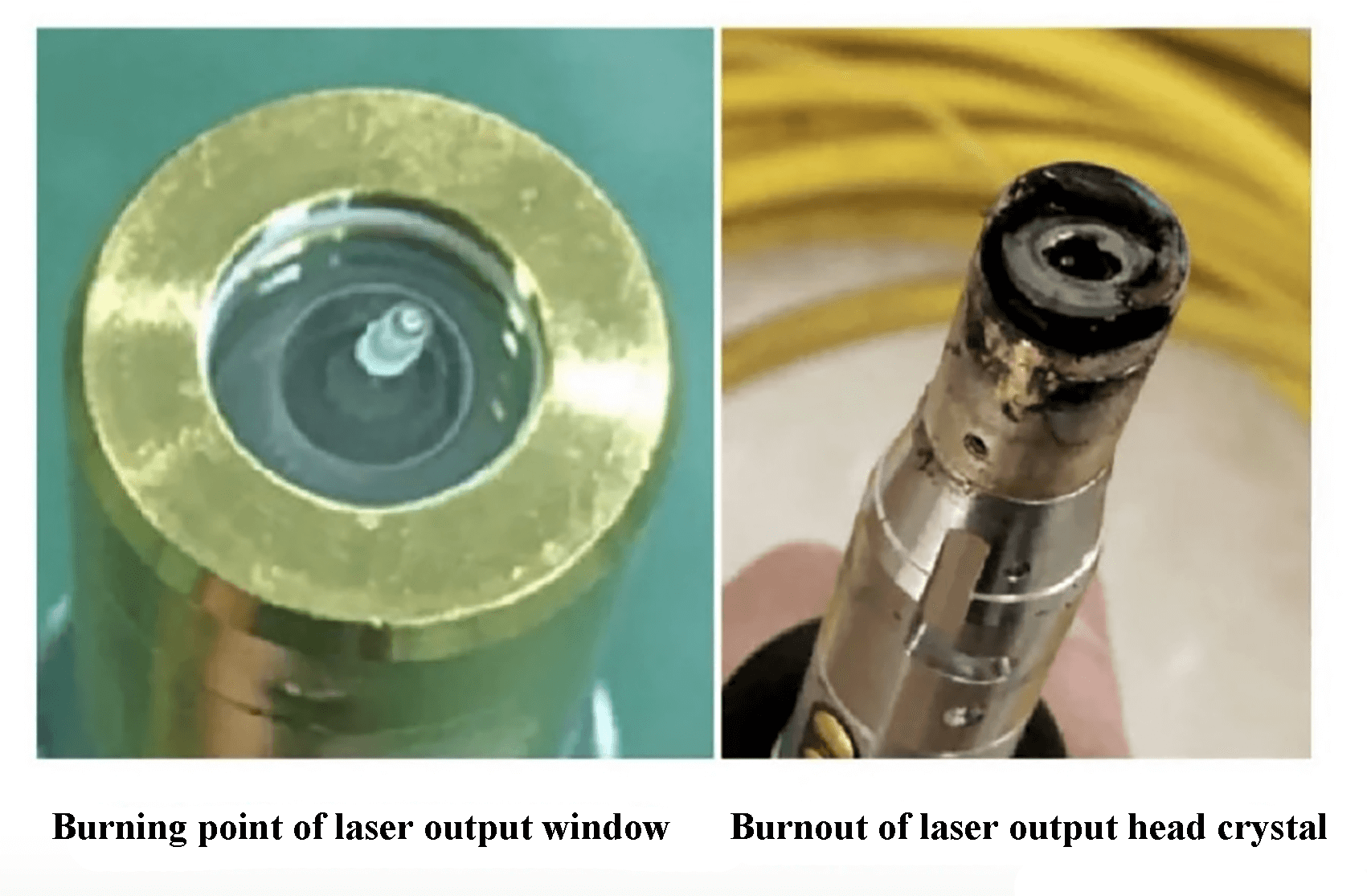
Fig. 5 Burnout of the laser output head
The use of low-quality protective lenses not only shortens the lifespan of the cutting head and leads to various accidents, but also negatively impacts the processing progress and quality of the factory, resulting in increased processing costs and reduced factory efficiency.
Therefore, it is advised that users only purchase protective lenses from reputable manufacturers and through reliable channels, in order to avoid significant losses and unsatisfactory gains.